- Page 2:
Soil Biology Series Editor: Ajit Va
- Page 6:
Professor Dr. Ajit Varma Jawaharlal
- Page 10:
VI Preface Intheframeworkofagricult
- Page 14:
Contents Part I Introduction 1 What
- Page 18:
Contents XI 2.1 Plant Compounds....
- Page 22:
Contents XIII 3.3 Influence on Phos
- Page 26:
Contents XV 5 Conclusions .........
- Page 30:
Contents XVII 9 Detection of In Sit
- Page 34:
XX Contributors Cappellazzo, G. Ist
- Page 38:
XXII Contributors Merbach, W. Marti
- Page 42:
Part I Introduction
- Page 46:
4 F. Buscot - As the soil genesis a
- Page 50:
6 F. Buscot size fractions, the san
- Page 54:
8 F. Buscot 2.4 Migration Processes
- Page 58:
10 F. Buscot 3.2 Nitrogen and Phosp
- Page 62:
12 F. Buscot life in the soil, whic
- Page 66:
14 F. Buscot the indigenous soil bi
- Page 70:
16 F. Buscot to understand the comp
- Page 74:
2 Microbial Diversity in Soils Bhoo
- Page 78:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 21 Ear
- Page 82:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 23 PRO
- Page 86:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 25 Tab
- Page 90:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 27 Dip
- Page 94:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 29 soi
- Page 98:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 31 the
- Page 102:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 33 man
- Page 106:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 35 ing
- Page 110:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 37 Bul
- Page 114:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 39 cyc
- Page 118:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 41 5.3
- Page 122:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 43 sti
- Page 126:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 45 Asp
- Page 130:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 47 7 C
- Page 134:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 49 Ref
- Page 138:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 51 Eva
- Page 142:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 53 Meh
- Page 146:
Microbial Diversity in Soils 55 Var
- Page 150:
3 Role of Microorganisms in Wear Do
- Page 154:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 158:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 162:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 166:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 170:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 174:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 178:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 182:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 186:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 190:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 194:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 198:
Role of Microorganisms in Wear Down
- Page 202:
4 Humification and Mineralization i
- Page 206:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 210:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 214:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 218:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 222:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 226:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 230:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 234:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 238:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 242:
Humification and Mineralization in
- Page 246:
5 Importance of Microorganisms for
- Page 250:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 254:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 258:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 262:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 266:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 270:
Importance of Microorganisms for So
- Page 274:
6 Microbial Energetics in Soils Oli
- Page 278:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 125 T
- Page 282:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 127 R
- Page 286:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 129 F
- Page 290:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 131 T
- Page 294:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 133 o
- Page 298:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 135 F
- Page 302:
Microbial Energetics in Soils 137 D
- Page 306:
7 Role of Microorganisms in Carbon
- Page 310:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 314:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 318:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 322:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 326:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 330:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 334:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 338:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 342:
Role of Microorganisms in Carbon Cy
- Page 346:
160 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon 2
- Page 350:
162 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon Fi
- Page 354:
164 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon of
- Page 358:
166 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon in
- Page 362:
168 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon lo
- Page 366:
170 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon In
- Page 370:
172 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon to
- Page 374:
174 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon Ge
- Page 378:
176 L. Philippot and J.C. Germon Vi
- Page 382:
178 A. Deubel and W. Merbach Table
- Page 386:
180 A. Deubel and W. Merbach Table
- Page 390:
182 A. Deubel and W. Merbach Fig. 1
- Page 394:
184 A. Deubel and W. Merbach compar
- Page 398:
186 A. Deubel and W. Merbach Fig. 2
- Page 402:
188 A. Deubel and W. Merbach Refere
- Page 406:
190 A. Deubel and W. Merbach E (200
- Page 410:
Part IV Biotic Interactions Involvi
- Page 414:
196 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 418:
198 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 422:
200 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 426:
202 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 430:
204 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 434:
206 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 438:
208 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 442:
210 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 446:
212 J.M. Barea, R. Azcón and C. Az
- Page 450:
214 B. Giri et al. tant source of c
- Page 454:
216 B. Giri et al. Fig. 2. Events i
- Page 458:
218 B. Giri et al. perhaps 345 m.y.
- Page 462:
220 B. Giri et al. Microbes also co
- Page 466:
222 B. Giri et al. from the roots.
- Page 470:
224 B. Giri et al. association by F
- Page 474:
226 B. Giri et al. mation of a shea
- Page 478:
228 B. Giri et al. because of their
- Page 482:
230 B. Giri et al. in some of the m
- Page 486:
232 B. Giri et al. Table 5. Plants
- Page 490:
234 B. Giri et al. 9.4 Arbuscular M
- Page 494:
236 B. Giri et al. Table 6. Synergi
- Page 498:
238 B. Giri et al. parasitized by o
- Page 502:
240 B. Giri et al. systems, particu
- Page 506:
242 B. Giri et al. 11.6 Interaction
- Page 510:
244 B. Giri et al. Table 9. Influen
- Page 514:
246 B. Giri et al. cause of their h
- Page 518:
248 B. Giri et al. endophyte develo
- Page 522:
250 B. Giri et al. Koide R (1993) P
- Page 526:
252 B. Giri et al. Subramanian S, C
- Page 530:
254 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 534:
256 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 538:
258 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 542:
260 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 546:
262 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 550:
264 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 554:
266 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 558:
268 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 562:
270 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 566:
272 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 570:
274 S. Scheu, L. Ruess and M. Bonko
- Page 574:
Part V Function of Microbes in Spec
- Page 578:
280 V. Bianciotto et al. plant (Coo
- Page 582:
282 V. Bianciotto et al. which prod
- Page 586:
284 V. Bianciotto et al. Fig. 1. Co
- Page 590: 286 V. Bianciotto et al. trophic fu
- Page 594: 288 V. Bianciotto et al. Curl EA, T
- Page 598: 290 V. Bianciotto et al. Vierheilig
- Page 602: 292 P. Lavelle et al. Fig. 1. A hie
- Page 606: 294 P. Lavelle et al. tohundredsofm
- Page 610: 296 P. Lavelle et al. tissue cultur
- Page 614: 298 P. Lavelle et al. ties were mor
- Page 618: 300 P. Lavelle et al. Fig. 4. Compa
- Page 622: 302 P. Lavelle et al. This has majo
- Page 626: 304 P. Lavelle et al. LavelleP,Spai
- Page 630: 15 1 Introduction Microorganisms of
- Page 634: Microorganisms of Biological Crusts
- Page 638: Microorganisms of Biological Crusts
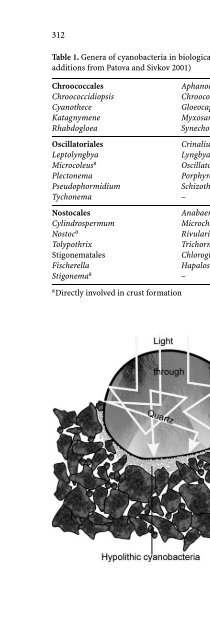
- Page 644: 314 B. Büdel that this species for
- Page 648: 316 B. Büdel Table 3. Lichen gener
- Page 652: 318 B. Büdel 1. Physical crusts; f
- Page 656: 320 B. Büdel cyanobacteria, algae,
- Page 660: 322 B. Büdel Hunt CD, Durrell LW (
- Page 664: 16 Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Po
- Page 668: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 672: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 676: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 680: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 684: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 688: Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 692:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 696:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 700:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 704:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 708:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 712:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 716:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 720:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 724:
Microorganisms in Toxic Metal-Pollu
- Page 728:
Part VI Techniques to Investigate S
- Page 732:
360 C.C. Tebbe Thehugegapbetweenvia
- Page 736:
362 C.C. Tebbe 3 Ribosomal RNA as a
- Page 740:
364 C.C. Tebbe to obtain PCR-amplif
- Page 744:
366 C.C. Tebbe Fig. 1. SSCP profile
- Page 748:
368 C.C. Tebbe Table 2. Examples of
- Page 752:
370 C.C. Tebbe 8 Recombinant Marker
- Page 756:
372 C.C. Tebbe can be intrinsic, li
- Page 760:
374 C.C. Tebbe and they detect comb
- Page 764:
376 C.C. Tebbe Amann R, Ludwig W (2
- Page 768:
378 C.C. Tebbe Fitts R, Diamond M,
- Page 772:
380 C.C. Tebbe Ogram A, Sayler GS,
- Page 776:
382 C.C. Tebbe Tourasse NJ, Gouy M
- Page 780:
384 E.A. Hobbie 2 Natural Abundance
- Page 784:
386 E.A. Hobbie 2.1.1 Carbon Isotop
- Page 788:
388 E.A. Hobbie surements are expen
- Page 792:
390 E.A. Hobbie Table 1. Isotopic f
- Page 796:
392 E.A. Hobbie 2.1.2 Nitrogen Isot
- Page 800:
394 E.A. Hobbie ectomycorrhizal fun
- Page 804:
396 E.A. Hobbie 1998; Henn and Chap
- Page 808:
398 E.A. Hobbie determined by using
- Page 812:
400 E.A. Hobbie Hayes JM (2002) Fra
- Page 816:
402 E.A. Hobbie Schmidt S, Stewart
- Page 820:
404 Subject Index Animal manure 149
- Page 824:
406 Subject Index Chaetomium 33 Cha
- Page 828:
408 Subject Index Endophytic microo
- Page 832:
410 Subject Index Green fluorescenc
- Page 836:
412 Subject Index Megaspora 316 Mel
- Page 840:
414 Subject Index Obligate anoxybio
- Page 844:
416 Subject Index Prasiococcus 313
- Page 848:
418 Subject Index Solorinaa 316 Sol