network protocols handbook.pdf
network protocols handbook.pdf
network protocols handbook.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
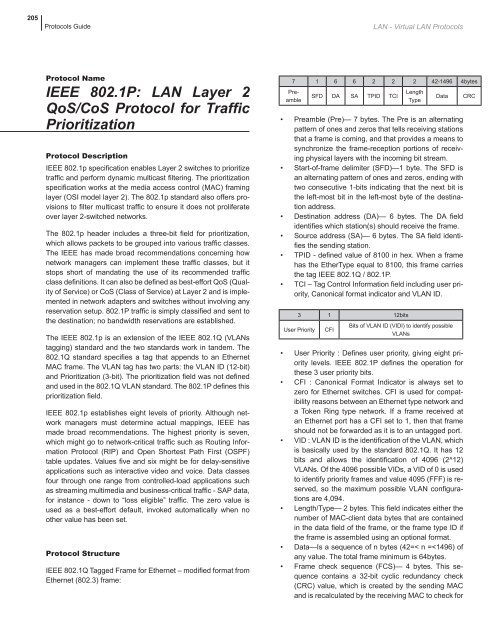
205Protocols GuideLAN - Virtual LAN ProtocolsProtocol NameIEEE 802.1P: LAN Layer 2QoS/CoS Protocol for TrafficPrioritizationProtocol DescriptionIEEE 802.1p specification enables Layer 2 switches to prioritizetraffic and perform dynamic multicast filtering. The prioritizationspecification works at the media access control (MAC) framinglayer (OSI model layer 2). The 802.1p standard also offers provisionsto filter multicast traffic to ensure it does not proliferateover layer 2-switched <strong>network</strong>s.The 802.1p header includes a three-bit field for prioritization,which allows packets to be grouped into various traffic classes.The IEEE has made broad recommendations concerning how<strong>network</strong> managers can implement these traffic classes, but itstops short of mandating the use of its recommended trafficclass definitions. It can also be defined as best-effort QoS (Qualityof Service) or CoS (Class of Service) at Layer 2 and is implementedin <strong>network</strong> adapters and switches without involving anyreservation setup. 802.1P traffic is simply classified and sent tothe destination; no bandwidth reservations are established.The IEEE 802.1p is an extension of the IEEE 802.1Q (VLANstagging) standard and the two standards work in tandem. The802.1Q standard specifies a tag that appends to an EthernetMAC frame. The VLAN tag has two parts: the VLAN ID (12-bit)and Prioritization (3-bit). The prioritization field was not definedand used in the 802.1Q VLAN standard. The 802.1P defines thisprioritization field.IEEE 802.1p establishes eight levels of priority. Although <strong>network</strong>managers must determine actual mappings, IEEE hasmade broad recommendations. The highest priority is seven,which might go to <strong>network</strong>-critical traffic such as Routing InformationProtocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)table updates. Values five and six might be for delay-sensitiveapplications such as interactive video and voice. Data classesfour through one range from controlled-load applications suchas streaming multimedia and business-critical traffic - SAP data,for instance - down to “loss eligible” traffic. The zero value isused as a best-effort default, invoked automatically when noother value has been set.Protocol StructureIEEE 802.1Q Tagged Frame for Ethernet – modified format fromEthernet (802.3) frame:7 1 6 6 2 2 2 42-1496 4bytesPreambleSFD DA SA TPID TCILengthTypeData• Preamble (Pre)— 7 bytes. The Pre is an alternatingpattern of ones and zeros that tells receiving stationsthat a frame is coming, and that provides a means tosynchronize the frame-reception portions of receivingphysical layers with the incoming bit stream.• Start-of-frame delimiter (SFD)—1 byte. The SFD isan alternating pattern of ones and zeros, ending withtwo consecutive 1-bits indicating that the next bit isthe left-most bit in the left-most byte of the destinationaddress.• Destination address (DA)— 6 bytes. The DA fieldidentifies which station(s) should receive the frame.• Source address (SA)— 6 bytes. The SA field identifiesthe sending station.• TPID - defined value of 8100 in hex. When a framehas the EtherType equal to 8100, this frame carriesthe tag IEEE 802.1Q / 802.1P.• TCI – Tag Control Information field including user priority,Canonical format indicator and VLAN ID.3 1 12bitsUser PriorityCFIBits of VLAN ID (VIDI) to identify possibleVLANs• User Priority : Defines user priority, giving eight prioritylevels. IEEE 802.1P defines the operation forthese 3 user priority bits.• CFI : Canonical Format Indicator is always set tozero for Ethernet switches. CFI is used for compatibilityreasons between an Ethernet type <strong>network</strong> anda Token Ring type <strong>network</strong>. If a frame received atan Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frameshould not be forwarded as it is to an untagged port.• VID : VLAN ID is the identification of the VLAN, whichis basically used by the standard 802.1Q. It has 12bits and allows the identification of 4096 (2^12)VLANs. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is usedto identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved,so the maximum possible VLAN configurationsare 4,094.• Length/Type— 2 bytes. This field indicates either thenumber of MAC-client data bytes that are containedin the data field of the frame, or the frame type ID ifthe frame is assembled using an optional format.• Data—Is a sequence of n bytes (42=< n =