network protocols handbook.pdf
network protocols handbook.pdf
network protocols handbook.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
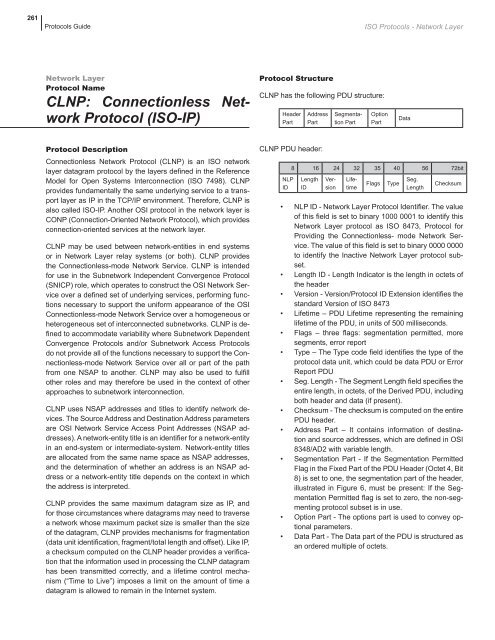
261Protocols GuideISO Protocols - Network LayerNetwork LayerProtocol NameCLNP: Connectionless NetworkProtocol (ISO-IP)Protocol StructureCLNP has the following PDU structure:HeaderPartAddressPartSegmentationPartOptionPartDataProtocol DescriptionConnectionless Network Protocol (CLNP) is an ISO <strong>network</strong>layer datagram protocol by the layers defined in the ReferenceModel for Open Systems Interconnection (ISO 7498). CLNPprovides fundamentally the same underlying service to a transportlayer as IP in the TCP/IP environment. Therefore, CLNP isalso called ISO-IP. Another OSI protocol in the <strong>network</strong> layer isCONP (Connection-Oriented Network Protocol), which providesconnection-oriented services at the <strong>network</strong> layer.CLNP may be used between <strong>network</strong>-entities in end systemsor in Network Layer relay systems (or both). CLNP providesthe Connectionless-mode Network Service. CLNP is intendedfor use in the Sub<strong>network</strong> Independent Convergence Protocol(SNICP) role, which operates to construct the OSI Network Serviceover a defined set of underlying services, performing functionsnecessary to support the uniform appearance of the OSIConnectionless-mode Network Service over a homogeneous orheterogeneous set of interconnected sub<strong>network</strong>s. CLNP is definedto accommodate variability where Sub<strong>network</strong> DependentConvergence Protocols and/or Sub<strong>network</strong> Access Protocolsdo not provide all of the functions necessary to support the Connectionless-modeNetwork Service over all or part of the pathfrom one NSAP to another. CLNP may also be used to fulfillother roles and may therefore be used in the context of otherapproaches to sub<strong>network</strong> interconnection.CLNP uses NSAP addresses and titles to identify <strong>network</strong> devices.The Source Address and Destination Address parametersare OSI Network Service Access Point Addresses (NSAP addresses).A <strong>network</strong>-entity title is an identifier for a <strong>network</strong>-entityin an end-system or intermediate-system. Network-entity titlesare allocated from the same name space as NSAP addresses,and the determination of whether an address is an NSAP addressor a <strong>network</strong>-entity title depends on the context in whichthe address is interpreted.CLNP provides the same maximum datagram size as IP, andfor those circumstances where datagrams may need to traversea <strong>network</strong> whose maximum packet size is smaller than the sizeof the datagram, CLNP provides mechanisms for fragmentation(data unit identification, fragment/total length and offset). Like IP,a checksum computed on the CLNP header provides a verificationthat the information used in processing the CLNP datagramhas been transmitted correctly, and a lifetime control mechanism(“Time to Live”) imposes a limit on the amount of time adatagram is allowed to remain in the Internet system.CLNP PDU header:NLPID8 16 24 32 35 40 56 72bitLengthIDVersionLifetimeFlagsTypeSeg.LengthChecksum• NLP ID - Network Layer Protocol Identifier. The valueof this field is set to binary 1000 0001 to identify thisNetwork Layer protocol as ISO 8473, Protocol forProviding the Connectionless- mode Network Service.The value of this field is set to binary 0000 0000to identify the Inactive Network Layer protocol subset.• Length ID - Length Indicator is the length in octets ofthe header• Version - Version/Protocol ID Extension identifies thestandard Version of ISO 8473• Lifetime – PDU Lifetime representing the remaininglifetime of the PDU, in units of 500 milliseconds.• Flags – three flags: segmentation permitted, moresegments, error report• Type – The Type code field identifies the type of theprotocol data unit, which could be data PDU or ErrorReport PDU• Seg. Length - The Segment Length field specifies theentire length, in octets, of the Derived PDU, includingboth header and data (if present).• Checksum - The checksum is computed on the entirePDU header.• Address Part – It contains information of destinationand source addresses, which are defined in OSI8348/AD2 with variable length.• Segmentation Part - If the Segmentation PermittedFlag in the Fixed Part of the PDU Header (Octet 4, Bit8) is set to one, the segmentation part of the header,illustrated in Figure 6, must be present: If the SegmentationPermitted flag is set to zero, the non-segmentingprotocol subset is in use.• Option Part - The options part is used to convey optionalparameters.• Data Part - The Data part of the PDU is structured asan ordered multiple of octets.