AUDIT ANALYTICS AUDIT
1JWn3ix
1JWn3ix
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>AUDIT</strong> <strong>ANALYTICS</strong> AND CONTINUOUS <strong>AUDIT</strong>:LOOKING TOWARD THE FUTURE<br />
business processes have become too complex to be efficiently addressed<br />
through pure human assurance. Layers of data, software, and the<br />
interconnection with upstream and downstream systems (and processes)<br />
make observation and evaluation very complex.<br />
In general an entirely new family of audit analytics is emerging 15 that can<br />
affect all parts of the audit engagement and can allow the use of an<br />
expanded data framework that includes external big data to support<br />
audit assertions in an unorthodox manner. Table 1-9 illustrates the<br />
number of potential changes and improvements to assurance<br />
methodologies. It should be considered together with table 1-10 in which<br />
the emphasis is more on procedures.<br />
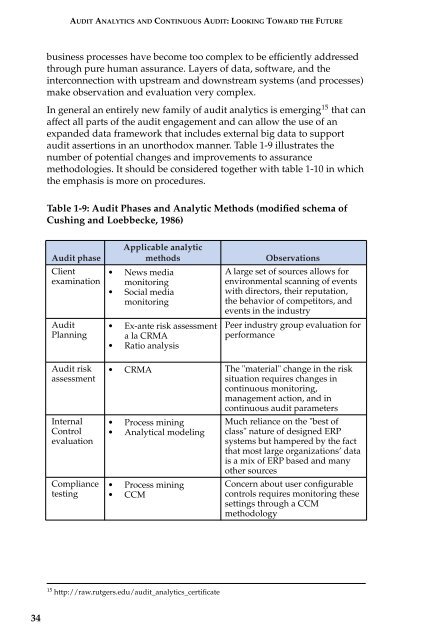
Table 1-9: Audit Phases and Analytic Methods (modified schema of<br />
Cushing and Loebbecke, 1986)<br />
Audit phase<br />
Applicable analytic<br />
methods<br />
Client<br />
examination • News media<br />
monitoring<br />
• Social media<br />
monitoring<br />
Audit<br />
Planning<br />
• Ex-ante risk assessment<br />
alaCRMA<br />
• Ratio analysis<br />
Observations<br />
A large set of sources allows for<br />
environmental scanning of events<br />
with directors, their reputation,<br />
the behavior of competitors, and<br />
events in the industry<br />
Peer industry group evaluation for<br />
performance<br />
Audit risk<br />
assessment<br />
Internal<br />
Control<br />
evaluation<br />
Compliance<br />
testing<br />
• CRMA The "material" change in the risk<br />
situation requires changes in<br />
continuous monitoring,<br />
management action, and in<br />
continuous audit parameters<br />
• Process mining<br />
• Analytical modeling<br />
• Process mining<br />
• CCM<br />
Much reliance on the "best of<br />
class" nature of designed ERP<br />
systems but hampered by the fact<br />
that most large organizations’ data<br />
is a mix of ERP based and many<br />
other sources<br />
Concern about user configurable<br />
controls requires monitoring these<br />
settings through a CCM<br />
methodology<br />
15 http://raw.rutgers.edu/audit_analytics_certificate<br />
34