Part 1 – A Rapid Participatory Biodiversity Assessment - IUCN
Part 1 – A Rapid Participatory Biodiversity Assessment - IUCN
Part 1 – A Rapid Participatory Biodiversity Assessment - IUCN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
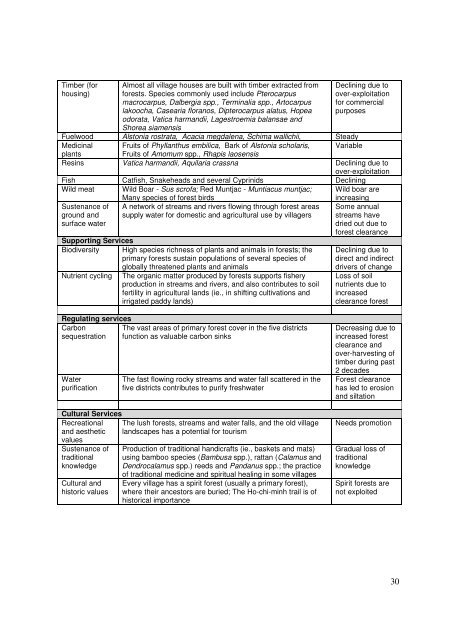
Timber (for<br />
housing)<br />
Almost all village houses are built with timber extracted from<br />
forests. Species commonly used include Pterocarpus<br />
macrocarpus, Dalbergia spp., Terminalia spp., Artocarpus<br />
lakoocha, Casearia floranos, Dipterocarpus alatus, Hopea<br />
odorata, Vatica harmandii, Lagestroemia balansae and<br />
Shorea siamensis<br />
Declining due to<br />
over-exploitation<br />
for commercial<br />
purposes<br />
Fuelwood Alstonia rostrata, Acacia megdalena, Schima wallichii, Steady<br />
Medicinal Fruits of Phyllanthus embilica, Bark of Alstonia scholaris, Variable<br />
plants Fruits of Amomum spp., Rhapis laosensis<br />
Resins Vatica harmandii, Aquilaria crassna Declining due to<br />
over-exploitation<br />
Fish Catfish, Snakeheads and several Cyprinids Declining<br />
Wild meat Wild Boar - Sus scrofa; Red Muntjac - Muntiacus muntjac; Wild boar are<br />
Many species of forest birds<br />
increasing<br />
Sustenance of A network of streams and rivers flowing through forest areas Some annual<br />
ground and supply water for domestic and agricultural use by villagers streams have<br />
surface water<br />
dried out due to<br />
forest clearance<br />
Supporting Services<br />
<strong>Biodiversity</strong> High species richness of plants and animals in forests; the Declining due to<br />
primary forests sustain populations of several species of direct and indirect<br />
globally threatened plants and animals<br />
drivers of change<br />
Nutrient cycling The organic matter produced by forests supports fishery Loss of soil<br />
production in streams and rivers, and also contributes to soil nutrients due to<br />
fertility in agricultural lands (ie., in shifting cultivations and increased<br />
irrigated paddy lands)<br />
clearance forest<br />
Regulating services<br />
Carbon<br />
sequestration<br />
Water<br />
purification<br />
Cultural Services<br />
Recreational<br />
and aesthetic<br />
values<br />
Sustenance of<br />
traditional<br />
knowledge<br />
Cultural and<br />
historic values<br />
The vast areas of primary forest cover in the five districts<br />
function as valuable carbon sinks<br />
The fast flowing rocky streams and water fall scattered in the<br />
five districts contributes to purify freshwater<br />
The lush forests, streams and water falls, and the old village<br />
landscapes has a potential for tourism<br />
Production of traditional handicrafts (ie., baskets and mats)<br />
using bamboo species (Bambusa spp.), rattan (Calamus and<br />
Dendrocalamus spp.) reeds and Pandanus spp.; the practice<br />
of traditional medicine and spiritual healing in some villages<br />
Every village has a spirit forest (usually a primary forest),<br />
where their ancestors are buried; The Ho-chi-minh trail is of<br />
historical importance<br />
Decreasing due to<br />
increased forest<br />
clearance and<br />
over-harvesting of<br />
timber during past<br />
2 decades<br />
Forest clearance<br />
has led to erosion<br />
and siltation<br />
Needs promotion<br />
Gradual loss of<br />
traditional<br />
knowledge<br />
Spirit forests are<br />
not exploited<br />
30