and Music
Omega-Book
Omega-Book
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
32<br />
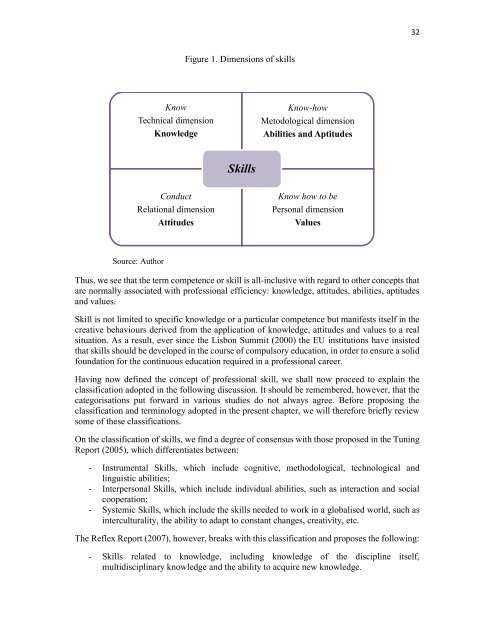
Figure 1. Dimensions of skills<br />
Know<br />
Technical dimension<br />
Knowledge<br />
Know-how<br />
Metodological dimension<br />
Abilities <strong>and</strong> Aptitudes<br />
Skills<br />
Conduct<br />
Relational dimension<br />
Attitudes<br />
Know how to be<br />
Personal dimension<br />
Values<br />
Source: Author<br />
Thus, we see that the term competence or skill is all-inclusive with regard to other concepts that<br />
are normally associated with professional efficiency: knowledge, attitudes, abilities, aptitudes<br />
<strong>and</strong> values.<br />
Skill is not limited to specific knowledge or a particular competence but manifests itself in the<br />
creative behaviours derived from the application of knowledge, attitudes <strong>and</strong> values to a real<br />
situation. As a result, ever since the Lisbon Summit (2000) the EU institutions have insisted<br />
that skills should be developed in the course of compulsory education, in order to ensure a solid<br />
foundation for the continuous education required in a professional career.<br />
Having now defined the concept of professional skill, we shall now proceed to explain the<br />
classification adopted in the following discussion. It should be remembered, however, that the<br />
categorisations put forward in various studies do not always agree. Before proposing the<br />
classification <strong>and</strong> terminology adopted in the present chapter, we will therefore briefly review<br />
some of these classifications.<br />
On the classification of skills, we find a degree of consensus with those proposed in the Tuning<br />
Report (2005), which differentiates between:<br />
- Instrumental Skills, which include cognitive, methodological, technological <strong>and</strong><br />
linguistic abilities;<br />
- Interpersonal Skills, which include individual abilities, such as interaction <strong>and</strong> social<br />
cooperation;<br />
- Systemic Skills, which include the skills needed to work in a globalised world, such as<br />
interculturality, the ability to adapt to constant changes, creativity, etc.<br />
The Reflex Report (2007), however, breaks with this classification <strong>and</strong> proposes the following:<br />
- Skills related to knowledge, including knowledge of the discipline itself,<br />
multidisciplinary knowledge <strong>and</strong> the ability to acquire new knowledge.