Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
Staff Members of the Institute of Biochemistry, TU - Institut für ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
discovering novel genes, processes and pathways that regulate lipid homeostasis in humans,<br />
mice and yeast. This is one <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> projects in <strong>the</strong> field <strong>of</strong> functional genomics (GEN-<br />
AU,GENome research in AUstria) funded by <strong>the</strong> Austrian Federal Ministry for Education,<br />
Science and Culture (bm:bwk).<br />
Green: wt Red: ko Red: wt Green: ko<br />
30<br />
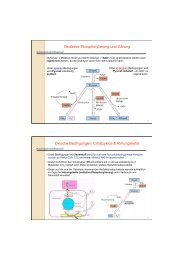
DABGE Analysis <strong>of</strong><br />
lipases and esterases<br />
in mouse adipose tissue<br />
<strong>of</strong> wt and lipase ko mice<br />
Differential activity-based gel electrophoresis (DABGE) was developed for comparative<br />
analysis <strong>of</strong> two lipolytic proteomes in one polyacrylamide gel. For this purpose, <strong>the</strong> active<br />
lipases/esterases <strong>of</strong> two different samples are labelled with fluorescent inhibitors that possess<br />
identical substrate analogous structures but carry different cyanine dyes as reporter<br />
fluorophores. After sample mixing and protein separation by 1-D or 2-D PAGE, <strong>the</strong> enzymes<br />
carrying <strong>the</strong> sample-specific colors are detected and quantified. This technique can be used<br />
for <strong>the</strong> determination <strong>of</strong> differences in enzyme patterns, e.g. due to effects <strong>of</strong> genetic<br />
background, environment, metabolic state and disease.<br />
Doctoral Thesis completed:<br />
Ute Stemmer: Toxicity, uptake and targeting <strong>of</strong> oxidized phospholipids in cultured<br />
macrophages.<br />
The uptake <strong>of</strong> oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) by <strong>the</strong> macrophages <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> arterial<br />
wall and <strong>the</strong> accumulation <strong>of</strong> apoptotic cells in a<strong>the</strong>rosclerotic lesions are hallmarks <strong>of</strong><br />
a<strong>the</strong>rosclerosis. The harmful effects <strong>of</strong> oxLDL are largely mediated by <strong>the</strong> intrinsic toxicity <strong>of</strong><br />
a great variety <strong>of</strong> lipid oxidation products that are generated in LDL under <strong>the</strong> conditions <strong>of</strong><br />
oxidative stress. These compounds comprise oxidized sterols, oxidized fatty acid derivatives<br />
and oxidized glycerophospholipids. Oxidized phospholipids may contain a modified longchain<br />
carboxylic acid or a truncated acyl residue with a polar functional group at its ω-end.<br />
Typical derivatives <strong>of</strong> truncated phospholipids are <strong>the</strong> carboxy-phospholipid 1-palmitoyl-2glutaroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine<br />
(PGPC) and <strong>the</strong> chemically reactive aldehydophosphospholipid<br />
1-palmitoyl-2-(5-oxovaleroyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POVPC),<br />
which are oxidation products <strong>of</strong> arachidonoyl-phosphatidylcholine. The latter lipid can<br />
undergo Schiff base formation with amino groups <strong>of</strong> proteins, <strong>the</strong>reby modulating <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
properties and functions. It was <strong>the</strong> aim <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> first part <strong>of</strong> this doctoral <strong>the</strong>sis to find out