Oceans of noise - Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society
Oceans of noise - Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society
Oceans of noise - Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
2<br />
4<br />
5<br />
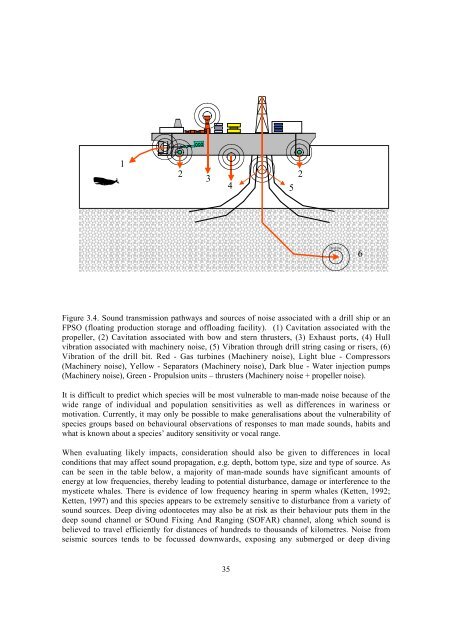
Figure 3.4. Sound transmission pathways <strong>and</strong> sources <strong>of</strong> <strong>noise</strong> associated with a drill ship or an<br />
FPSO (floating production storage <strong>and</strong> <strong>of</strong>floading facility). (1) Cavitation associated with the<br />
propeller, (2) Cavitation associated with bow <strong>and</strong> stern thrusters, (3) Exhaust ports, (4) Hull<br />
vibration associated with machinery <strong>noise</strong>, (5) Vibration through drill string casing or risers, (6)<br />
Vibration <strong>of</strong> the drill bit. Red - Gas turbines (Machinery <strong>noise</strong>), Light blue - Compressors<br />
(Machinery <strong>noise</strong>), Yellow - Separators (Machinery <strong>noise</strong>), Dark blue - Water injection pumps<br />
(Machinery <strong>noise</strong>), Green - Propulsion units – thrusters (Machinery <strong>noise</strong> + propeller <strong>noise</strong>).<br />
It is difficult to predict which species will be most vulnerable to man-made <strong>noise</strong> because <strong>of</strong> the<br />
wide range <strong>of</strong> individual <strong>and</strong> population sensitivities as well as differences in wariness or<br />
motivation. Currently, it may only be possible to make generalisations about the vulnerability <strong>of</strong><br />
species groups based on behavioural observations <strong>of</strong> responses to man made sounds, habits <strong>and</strong><br />
what is known about a species’ auditory sensitivity or vocal range.<br />
When evaluating likely impacts, consideration should also be given to differences in local<br />
conditions that may affect sound propagation, e.g. depth, bottom type, size <strong>and</strong> type <strong>of</strong> source. As<br />
can be seen in the table below, a majority <strong>of</strong> man-made sounds have significant amounts <strong>of</strong><br />
energy at low frequencies, thereby leading to potential disturbance, damage or interference to the<br />
mysticete whales. There is evidence <strong>of</strong> low frequency hearing in sperm whales (Ketten, 1992;<br />
Ketten, 1997) <strong>and</strong> this species appears to be extremely sensitive to disturbance from a variety <strong>of</strong><br />
sound sources. Deep diving odontocetes may also be at risk as their behaviour puts them in the<br />
deep sound channel or SOund Fixing And Ranging (SOFAR) channel, along which sound is<br />
believed to travel efficiently for distances <strong>of</strong> hundreds to thous<strong>and</strong>s <strong>of</strong> kilometres. Noise from<br />
seismic sources tends to be focussed downwards, exposing any submerged or deep diving<br />
35<br />
Drill bit<br />
6