End-of-life decision-making for children with severe developmental disabilities
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
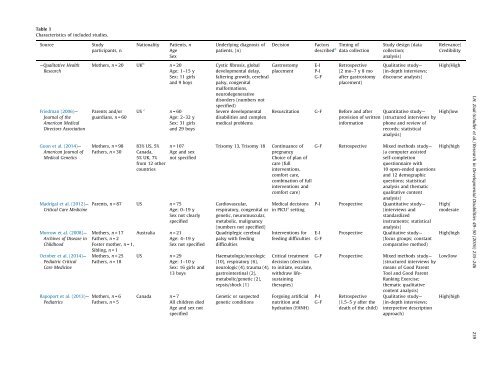
Table 1<br />
Characteristics <strong>of</strong> included studies.<br />
Source<br />
Study<br />
participants, n<br />
Nationality<br />
Patients, n<br />
Age<br />
Sex<br />
Underlying diagnosis <strong>of</strong><br />
patients, (n)<br />
Decision<br />
Factors<br />
described d Timing <strong>of</strong><br />
data collection<br />
Study design (data<br />
collection;<br />
analysis)<br />
Relevance/<br />
Credibility<br />
—Qualitative Health<br />
Research<br />
Friedman (2006)—<br />
Journal <strong>of</strong> the<br />
American Medical<br />
Directors Association<br />
Guon et al. (2014)—<br />
American Journal <strong>of</strong><br />
Medical Genetics<br />
Madrigal et al. (2012)—<br />
Critical Care Medicine<br />
Morrow et al. (2008)—<br />
Archives <strong>of</strong> Disease in<br />
Childhood<br />
October et al. (2014)—<br />
Pediatric Critical<br />
Care Medicine<br />
Rapoport et al. (2013)—<br />
Pediatrics<br />
Mothers, n =20 UK b n =20<br />
Age: 1–15 y<br />
Sex: 11 girls<br />
and 9 boys<br />
Parents and/or<br />
guardians, n =60<br />
Mothers, n =98<br />
Fathers, n =30<br />
US c n =60<br />
Age: 2–32 y<br />
Sex: 31 girls<br />
and 29 boys<br />
83% US, 5%<br />
Canada,<br />
5% UK, 7%<br />
from 12 other<br />
countries<br />
n = 107<br />
Age and sex<br />
not specified<br />
Parents, n =87 US n =75<br />
Age: 0–19 y<br />
Sex not clearly<br />
specified<br />
Mothers, n =17<br />
Fathers, n =2<br />
Foster mother, n =1,<br />
Sibling, n =1<br />
Mothers, n =25<br />
Fathers, n =18<br />
Mothers, n =6<br />
Fathers, n =5<br />
Australia n =21<br />
Age: 4–19 y<br />
Sex not specified<br />
US n =29<br />
Age: 1–10 y<br />
Sex: 16 girls and<br />
13 boys<br />
Canada n =7<br />
All <strong>children</strong> died<br />
Age and sex not<br />
specified<br />
Cystic fibrosis, global Gastrostomy<br />
<strong>developmental</strong> delay, placement<br />
faltering growth, cerebral<br />
palsy, congenital<br />
mal<strong>for</strong>mations,<br />
neurodegenerative<br />
disorders (numbers not<br />
specified)<br />
Severe <strong>developmental</strong><br />
<strong>disabilities</strong> and complex<br />
medical problems<br />
Trisomy 13, Trisomy 18<br />
E-I<br />
P-I<br />
G-F<br />
Retrospective<br />
(2 mo–7 y 8 mo<br />
after gastrostomy<br />
placement)<br />
Qualitative study—<br />
(in-depth interviews;<br />
discourse analysis)<br />
Resuscitation G-F Be<strong>for</strong>e and after Quantitative study—<br />
provision <strong>of</strong> written (structured interviews by<br />
in<strong>for</strong>mation phone and review <strong>of</strong><br />
records; statistical<br />
analysis)<br />
Continuance <strong>of</strong><br />
pregnancy<br />
Choice <strong>of</strong> plan <strong>of</strong><br />
care (full<br />
interventions,<br />
com<strong>for</strong>t care,<br />
combination <strong>of</strong> full<br />
interventions and<br />
com<strong>for</strong>t care)<br />
Cardiovascular,<br />
Medical <strong>decision</strong>s<br />
respiratory, congenital or in PICU a setting<br />
genetic, neuromuscular,<br />
metabolic, malignancy<br />
(numbers not specified)<br />
Quadriplegic cerebral<br />
palsy <strong>with</strong> feeding<br />
difficulties<br />
Haematologic/oncologic<br />
(10), respiratory (6),<br />
neurologic (4), trauma (4),<br />
gastrointestinal (2),<br />
metabolic/genetic (2),<br />
sepsis/shock (1)<br />
Genetic or suspected<br />
genetic conditions<br />
Interventions <strong>for</strong><br />
feeding difficulties<br />
Critical treatment<br />
<strong>decision</strong> (<strong>decision</strong><br />
to initiate, escalate,<br />
<strong>with</strong>draw <strong>life</strong>sustaining<br />
therapies)<br />
Forgoing artificial<br />
nutrition and<br />
hydration (FANH)<br />
G-F Retrospective Mixed methods study—<br />
(a computer assisted<br />
self-completion<br />
questionnaire <strong>with</strong><br />
10 open-ended questions<br />
and 12 demographic<br />
questions; statistical<br />
analysis and thematic<br />
qualitative content<br />
analysis)<br />
P-I Prospective Quantitative study—<br />
(interviews and<br />
standardized<br />
instruments; statistical<br />
analysis)<br />
E-I<br />
G-F<br />
Prospective<br />
Qualitative study—<br />
(focus groups; constant<br />
comparative method)<br />
G-F Prospective Mixed methods study—<br />
(structured interviews by<br />
means <strong>of</strong> Good Parent<br />
Tool and Good Parent<br />
Ranking Exercise;<br />
thematic qualitative<br />
content analysis)<br />
P-I<br />
G-F<br />
Retrospective<br />
(1.5–5 y after the<br />
death <strong>of</strong> the child)<br />
Qualitative study—<br />
(in-depth interviews;<br />
interpretive description<br />
approach)<br />
High/High<br />
High/low<br />
High/high<br />
High/<br />
moderate<br />
High/high<br />
Low/low<br />
High/high<br />
I.H. Zaal-Schuller et al. / Research in Developmental Disabilities 49–50 (2016) 235–246 239