ch01-03 stress & strain & properties
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
01 Solutions 46060 5/6/10 2:43 PM Page 43<br />
© 2010 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently<br />
exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.<br />
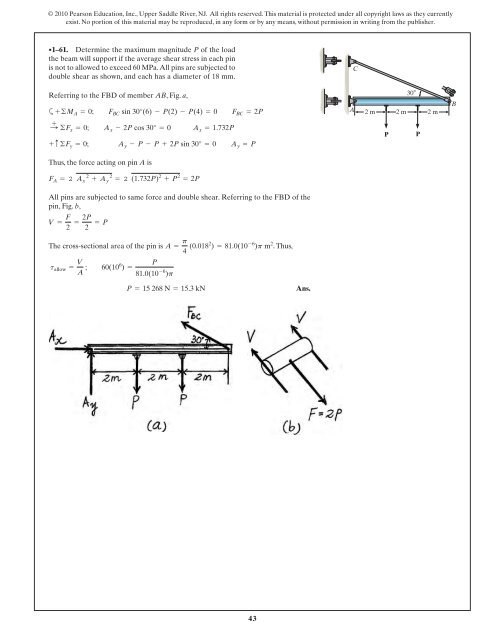
•1–61. Determine the maximum magnitude P of the load<br />
the beam will support if the average shear <strong>stress</strong> in each pin<br />
is not to allowed to exceed 60 MPa.All pins are subjected to<br />
double shear as shown, and each has a diameter of 18 mm.<br />
C<br />
Referring to the FBD of member AB,Fig.a,<br />
a+©M A = 0; F BC sin 30°(6) - P(2) - P(4) = 0 F BC = 2P<br />
A<br />
2 m<br />
2 m<br />
30<br />
2 m<br />
B<br />
: + ©F x = 0; A x - 2P cos 30° = 0 A x = 1.732P<br />
+ c ©F y = 0; A y - P - P + 2P sin 30° = 0 A y = P<br />
Thus, the force acting on pin A is<br />
F A = 2 A x 2 + A y 2 = 2 (1.732P) 2 + P 2 = 2P<br />
All pins are subjected to same force and double shear. Referring to the FBD of the<br />
pin, Fig. b,<br />
P<br />
P<br />
V = F 2 = 2P 2<br />
= P<br />
The cross-sectional area of the pin is A = p . Thus,<br />
4 (0.0182 ) = 81.0(10 - 6 )p m 2<br />
t allow = V A ; 60(106 ) =<br />
P<br />
81.0(10 - 6 )p<br />
P = 15 268 N = 15.3 kN<br />
Ans.<br />
43