You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
THE KETO THEORY<br />
The keto diet changes metabolism by<br />
shifting the human body’s fuel source<br />
from blood glucose to ketones, chemicals<br />
the liver makes when fat is burned to<br />
generate energy. A perfectly healthy<br />
human body could switch from one<br />
fuel to the other as needed, much like a<br />
hybrid car that uses either gas or electrical<br />
power. However, the large amount of<br />
carbohydrates that most people eat has<br />
broken that switch, blocking fat from<br />
being used as an energy source. The keto<br />
diet forces the switch to turn on.<br />
“You’re burning fat, which is in your<br />
diet, but you’re also opening up pathways<br />
that allow you to eat yourself—you<br />
can liberate and mobilize fat, and your<br />
brain senses that energy,” says Dominic<br />
D’Agostino, PhD, a neuroscientist at<br />
the University of South Florida who<br />
has been researching keto diets and<br />
supplements for over 10 years. “If you’re<br />
on a really high-carbohydrate diet and<br />
you go four or five hours without food,”<br />
he adds, “your brain senses an energetic<br />
crisis because it doesn’t have quick or<br />
easy access to the fat.” If it did, there<br />
wouldn’t be a problem.<br />
Fat burning and keto production<br />
are also triggered by fasting, which<br />
is why people can survive without<br />
food for weeks. Intense or prolonged<br />
exercise can also trigger temporary<br />
ketone production.<br />
WHY KETO TRIGGERS<br />
WEIGHT LOSS<br />
Scores of dramatic before-and-after<br />
photos, shared online by keto adherents,<br />
might give you the idea that there’s<br />
something magical about eating a lot<br />
of fat. But this isn’t why the keto diet<br />
works. “It helps you lose weight, but it<br />
does it by calorie restriction, because it<br />
helps you regulate your appetite,” says<br />
D’Agostino. “It’s really changing brain<br />
chemistry,” he adds. “Instead of your<br />
appetite controlling you, the diet allows<br />
you to control your appetite, to moderate<br />
your intake, and to really control what<br />
you eat.”<br />
Keto Benefits Beyond Weight Loss<br />
The keto diet originated in 1921 as a treatment for type 1 diabetes (before the<br />
invention of diabetes drugs) and seizures among children with epilepsy. Since then,<br />
studies have found that it may assist in the treatment of certain diseases, including:<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Type 2 diabetes<br />
Prediabetes<br />
Seizure disorders<br />
Acne and eczema<br />
Polycystic ovary<br />
syndrome (PCOS)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Cancer<br />
Amyotrophic lateral<br />
sclerosis (ALS)<br />
Alzheimer’s disease<br />
Traumatic brain<br />
injury<br />
KETO DIET BASICS<br />
The carb content of keto diets is typically counted as net carbs: the amount of total<br />
carbs in a food minus its fiber content. Total net carbs per day range between 20 and<br />
50 grams, much lower than the typical American diet, which contains between<br />
200 and 300 grams of total carbs.<br />
No one officially tracks the nation’s net carb consumption, but it’s estimated that<br />
we eat an average of 15 grams of fiber daily. Subtracting the fiber from total carbs,<br />
average daily net carbs would be around 185 to 285 grams—dramatically higher<br />
than keto diet levels.<br />
The carb calories are replaced mostly by fat, as in healthy fat. Protein levels don’t<br />
dramatically change and shouldn’t be too high, as too much protein can prevent fat<br />
burning. Although we don’t usually turn protein into blood glucose, it can happen<br />
on a low-carb, high-protein diet.<br />
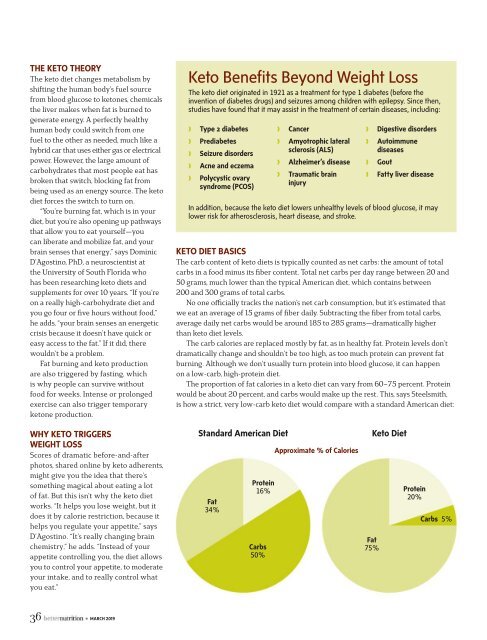
The proportion of fat calories in a keto diet can vary from 60–75 percent. Protein<br />
would be about 20 percent, and carbs would make up the rest. This, says Steelsmith,<br />
is how a strict, very low-carb keto diet would compare with a standard American diet:<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Digestive disorders<br />
Autoimmune<br />
diseases<br />
Gout<br />
Fatty liver disease<br />
In addition, because the keto diet lowers unhealthy levels of blood glucose, it may<br />
lower risk for atherosclerosis, heart disease, and stroke.<br />
Standard American Diet<br />
Fat<br />
34%<br />
Approximate % of Calories<br />
Keto Diet<br />
Protein<br />
16% Protein<br />
20%<br />
Carbs<br />
50%<br />
Fat<br />
75%<br />
Carbs 5%<br />
36 • MARCH <strong>2019</strong>