Abstracts (poster) - Wissenschaft Online
Abstracts (poster) - Wissenschaft Online
Abstracts (poster) - Wissenschaft Online
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Wibke Peters, Thomas Macherey, Mike Duisken, Sophie Willnow, Bernhard Lüscher,<br />
Elmar Weinhold<br />
New S-Adenosyl-L-methionine Analogues to Investigate the<br />
Methylome<br />
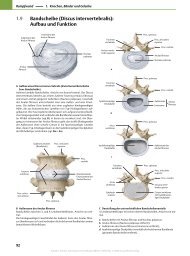
DNA and protein methyltransferases (MTases) play crucial roles in setting epigenetic<br />
marks on DNA and histone proteins. They catalyse the transfer of the activated methyl<br />
group from the ubiquitous cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet or SAM) to specific<br />
residues within their substrates. Since the methyl group is not an attractive reporter<br />
group, we have synthesised two new classes of AdoMet analogues which serve as<br />
efficient cofactors for sequence-specific DNA functionalisation and labelling.<br />
In the first class of cofactor analogues the amino acid side chain of AdoMet is replaced<br />
with an aziridinyl residue and reporter groups are attached to the adenine ring.[1,2]<br />
DNA MTase-catalysed nucleophilic aziridine ring opening leads to sequence-specific<br />
coupling of the whole aziridine cofactor with DNA and hence to covalent DNA labelling. In<br />
the second class of cofactor analogues the methyl group of AdoMet is replaced with<br />
extended carbon chains carrying an unsaturated bond in beta-position to the sulfonium<br />
center.[3,4] The unsaturared bond is essential and leads to efficient transfer of the<br />
extended side chain to DNA.<br />
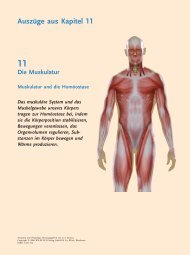
We have extended this work to protein MTases and find that the latter AdoMet analogues<br />
also function as cofactors for histone MTases. These analogues are used to transfer<br />
bioorthogonal chemical groups for modification by click chemistry and provide a new<br />
chemical tool to label proteins and identify targets of protein MTases.<br />
Literature<br />
[1] Pljevaljcic, F. Schmidt, E. Weinhold, Sequence-specific Methyltransferase-Induced<br />
Labeling of DNA (SMILing DNA), ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 265–269.<br />
[2] Pljevaljcic, F. Schmidt, A. J. Scheidig, R. Lurz, E. Weinhold, Quantitative labeling of<br />
long plasmid DNA with nanometer precision, ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1516–1519.<br />
[3] C. Dalhoff, G. Lukinavicius, S. Klimasauskas, E. Weinhold, Direct transfer of<br />
extended groups from synthetic cofactors by DNA methyltransferases, Nat. Chem. Biol.<br />
2006, 2, 31–32.<br />
[4] G. Lukinavicius, V. Lapiene, Z. Stasevskij, C. Dalhoff, E. Weinhold, S. Klimasauskas,<br />
Targeted labeling of DNA by methyltransferase-directed Transfer of Activated Groups<br />
(mTAG), J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2758–2759.<br />
contact:<br />
Professor Elmar Weinhold<br />
RWTH Aachen University<br />
Institute of Organic Chemistry<br />
elmar.weinhold@oc.rwth-aachen.de<br />
Landoltweg 1<br />
52056 Aachen (Germany)<br />
additional information<br />
Mike Duisken, LECO Instrumente GmbH, 41199 Mönchengladbach, Germany; Bernhard Lüscher,<br />
Institute of Biochemistry, Division of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, RWTH Aachen University<br />
Hospital, 52074 Aachen, Germany.