D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
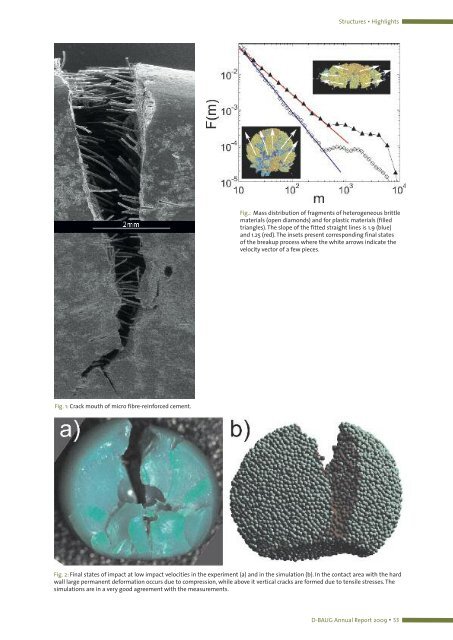
Fig. 1: Crack mouth of micro fibre-reinforced cement.<br />
Structures ▪ Highlights<br />
Fig.: Mass distribution of fragments of heterogeneous brittle<br />
materials (open diamonds) and for plastic materials (filled<br />
triangles). The slope of the fitted straight lines is 1.9 (blue)<br />
and 1.25 (red). The insets present corresponding final states<br />
of the breakup process where the white arrows indicate the<br />
velocity vector of a few pieces.<br />
Fig. 2: Final states of impact at low impact velocities in the experiment (a) and in the simulation (b). In the contact area with the hard<br />
wall large permanent deformation occurs due to compression, while above it vertical cracks are formed due to tensile stresses. The<br />
simulations are in a very good agreement with the measurements.<br />
D-<strong>BAUG</strong> Annual Report 2009 ▪ 53