D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
D-BAUG - Departement Bau, Umwelt und Geomatik - ETH Zürich
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Geo-, Structural- and Environmental Data ▪ Highlights<br />
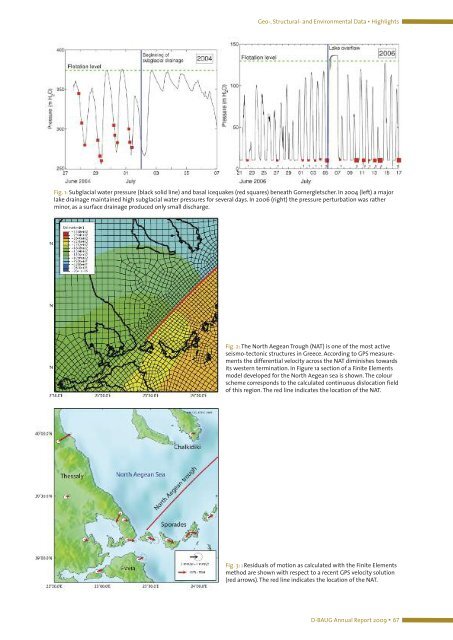
Fig. 1: Subglacial water pressure (black solid line) and basal icequakes (red squares) beneath Gornergletscher. In 2004 (left) a major<br />
lake drainage maintained high subglacial water pressures for several days. In 2006 (right) the pressure perturbation was rather<br />
minor, as a surface drainage produced only small discharge.<br />
Fig. 2: The North Aegean Trough (NAT) is one of the most active<br />
seismo-tectonic structures in Greece. According to GPS measurements<br />
the differential velocity across the NAT diminishes towards<br />
its western termination. In Figure 1a section of a Finite Elements<br />
model developed for the North Aegean sea is shown. The colour<br />
scheme corresponds to the calculated continuous dislocation field<br />
of this region. The red line indicates the location of the NAT.<br />
Fig. 3: : Residuals of motion as calculated with the Finite Elements<br />
method are shown with respect to a recent GPS velocity solution<br />
(red arrows). The red line indicates the location of the NAT.<br />
D-<strong>BAUG</strong> Annual Report 2009 ▪ 67