Synthèse de CF2-carbasucres par cyclisation radicalaire et ... - TEL
Synthèse de CF2-carbasucres par cyclisation radicalaire et ... - TEL
Synthèse de CF2-carbasucres par cyclisation radicalaire et ... - TEL
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
tel-00559649, version 1 - 26 Jan 2011<br />
<strong>Synthèse</strong> <strong>de</strong> 5-désoxy-<strong>CF2</strong>-<strong>carbasucres</strong><br />
HO<br />
32<br />
O<br />
HO OH<br />
OH<br />
HCl, MeOH,<br />
Acétone<br />
78%<br />
HO<br />
O<br />
O O<br />
OMe<br />
I 2, PPh 3,<br />
Imidazole, Δ<br />
99%<br />
I<br />
O<br />
O O<br />
OMe<br />
Zn,<br />
MeOH, Δ<br />
82%<br />
O O<br />
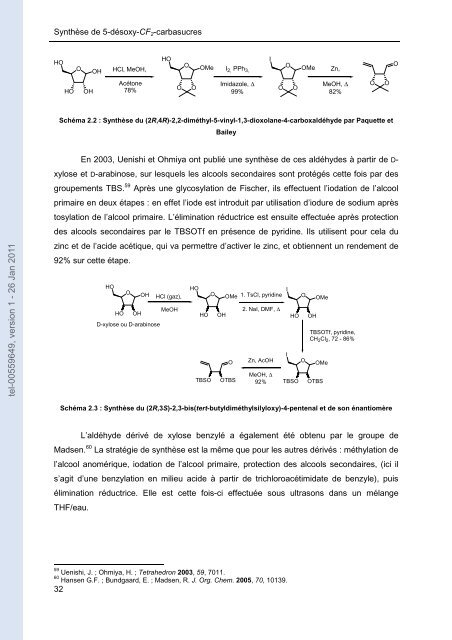
Schéma 2.2 : <strong>Synthèse</strong> du (2R,4R)-2,2-diméthyl-5-vinyl-1,3-dioxolane-4-carboxaldéhy<strong>de</strong> <strong>par</strong> Paqu<strong>et</strong>te <strong>et</strong><br />
Bailey<br />
En 2003, Uenishi <strong>et</strong> Ohmiya ont publié une synthèse <strong>de</strong> ces aldéhy<strong>de</strong>s à <strong>par</strong>tir <strong>de</strong> D-<br />
xylose <strong>et</strong> D-arabinose, sur lesquels les alcools secondaires sont protégés c<strong>et</strong>te fois <strong>par</strong> <strong>de</strong>s<br />
groupements TBS. 59 Après une glycosylation <strong>de</strong> Fischer, ils effectuent l’iodation <strong>de</strong> l’alcool<br />
primaire en <strong>de</strong>ux étapes : en eff<strong>et</strong> l’io<strong>de</strong> est introduit <strong>par</strong> utilisation d’iodure <strong>de</strong> sodium après<br />
tosylation <strong>de</strong> l’alcool primaire. L’élimination réductrice est ensuite effectuée après protection<br />
<strong>de</strong>s alcools secondaires <strong>par</strong> le TBSOTf en présence <strong>de</strong> pyridine. Ils utilisent pour cela du<br />
zinc <strong>et</strong> <strong>de</strong> l’aci<strong>de</strong> acétique, qui va perm<strong>et</strong>tre d’activer le zinc, <strong>et</strong> obtiennent un ren<strong>de</strong>ment <strong>de</strong><br />
92% sur c<strong>et</strong>te étape.<br />
HO<br />
O<br />
HO OH<br />
OH<br />
D-xylose ou D-arabinose<br />
HCl (gaz),<br />
MeOH<br />
HO<br />
O<br />
HO OH<br />
I<br />
OMe 1. TsCl, pyridine<br />
O<br />
TBSO OTBS<br />
2. NaI, DMF, Δ<br />
Zn, AcOH<br />
MeOH, Δ<br />
92%<br />
I<br />
O<br />
HO OH<br />
O<br />
OMe<br />
TBSOTf, pyridine,<br />
CH 2Cl 2, 72 - 86%<br />
OMe<br />
TBSO OTBS<br />
Schéma 2.3 : <strong>Synthèse</strong> du (2R,3S)-2,3-bis(tert-butyldiméthylsilyloxy)-4-pentenal <strong>et</strong> <strong>de</strong> son énantiomère<br />
L’aldéhy<strong>de</strong> dérivé <strong>de</strong> xylose benzylé a également été obtenu <strong>par</strong> le groupe <strong>de</strong><br />
Madsen. 60 La stratégie <strong>de</strong> synthèse est la même que pour les autres dérivés : méthylation <strong>de</strong><br />
l’alcool anomérique, iodation <strong>de</strong> l’alcool primaire, protection <strong>de</strong>s alcools secondaires, (ici il<br />
s’agit d’une benzylation en milieu aci<strong>de</strong> à <strong>par</strong>tir <strong>de</strong> trichloroacétimidate <strong>de</strong> benzyle), puis<br />
élimination réductrice. Elle est c<strong>et</strong>te fois-ci effectuée sous ultrasons dans un mélange<br />
THF/eau.<br />
59 Uenishi, J. ; Ohmiya, H. ; T<strong>et</strong>rahedron 2003, 59, 7011.<br />
60 Hansen G.F. ; Bundgaard, E. ; Madsen, R. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 10139.<br />
O