Il terreno e la SO - Associazione Studenti di Agraria IAAS Sassari
Il terreno e la SO - Associazione Studenti di Agraria IAAS Sassari
Il terreno e la SO - Associazione Studenti di Agraria IAAS Sassari
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
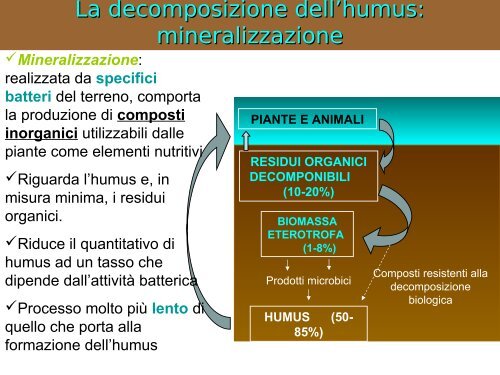
La decomposizione dell’humus:<br />
mineralizzazione<br />
Mineralizzazione:<br />
realizzata da specifici<br />
batteri del <strong>terreno</strong>, comporta<br />
<strong>la</strong> produzione <strong>di</strong> composti<br />
inorganici utilizzabili dalle<br />
piante come elementi nutritivi<br />
Riguarda l’humus e, in<br />
misura Elementi minima, nutritivi i residui<br />
organici.<br />
Riduce il quantitativo <strong>di</strong><br />
humus ad un tasso che<br />
<strong>di</strong>pende dall’attività batterica<br />
Processo molto più lento <strong>di</strong><br />
quello che porta al<strong>la</strong><br />
formazione dell’humus<br />
PIANTE E ANIMALI<br />
RESIDUI ORGANICI<br />
DECOMPONIBILI<br />
(10-20%)<br />
BIOMASSA<br />
ETEROTROFA<br />
(1-8%)<br />
Prodotti microbici<br />
HUMUS (50-<br />
85%)<br />
Composti resistenti al<strong>la</strong><br />
decomposizione<br />
biologica