Optimal integrering av energianvändningen vid ... - Gasefuels AB
Optimal integrering av energianvändningen vid ... - Gasefuels AB
Optimal integrering av energianvändningen vid ... - Gasefuels AB
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Gasholder<br />
Cooling water<br />
35˚C<br />
H 2S<br />
removal<br />
Cooling water<br />
60˚C<br />
Cooling water<br />
35˚C<br />
Scrubber<br />
Cooling water<br />
60˚C<br />
Cooling water<br />
35˚C<br />
Cooling water<br />
60˚C<br />
ix<br />
Dryer<br />
Vehicle fuel gas<br />
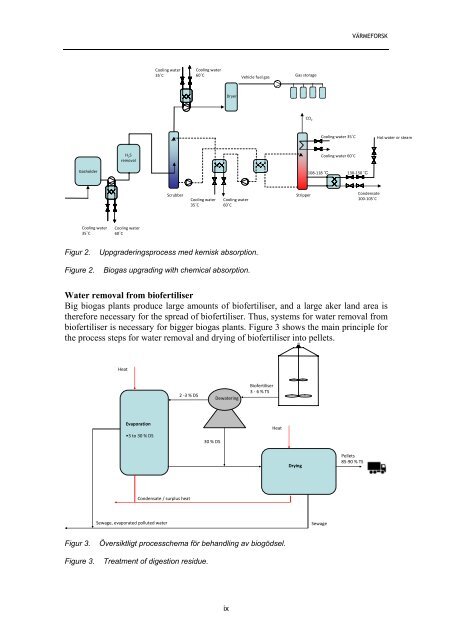
Figur 2. Uppgraderingsprocess med kemisk absorption.<br />
Figure 2. Biogas upgrading with chemical absorption.<br />
Gas storage<br />
CO 2<br />
Stripper<br />
108‐118 ˚C<br />
Cooling water 35˚C<br />
Cooling water 60˚C<br />
VÄRMEFORSK<br />
130‐150 ˚C<br />
Condensate<br />
100‐105˚C<br />
Water removal from biofertiliser<br />
Big biogas plants produce large amounts of biofertiliser, and a large aker land area is<br />
therefore necessary for the spread of biofertiliser. Thus, systems for water removal from<br />
biofertiliser is necessary for bigger biogas plants. Figure 3 shows the main principle for<br />
the process steps for water removal and drying of biofertiliser into pellets.<br />
Heat<br />
Evaporation<br />
•3 to 30 % DS<br />
2 ‐3 % DS<br />
Condensate / surplus heat<br />
Sewage, evaporated polluted water<br />
30 % DS<br />
Dewatering<br />
Biofertiliser<br />
3 ‐ 6 % TS<br />
Figur 3. Översiktligt processchema för behandling <strong>av</strong> biogödsel.<br />
Figure 3. Treatment of digestion residue.<br />
Heat<br />
Drying<br />
Sewage<br />
Pellets<br />
85‐90 % TS<br />
Hot water or steam