psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite ...
psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite ...
psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite psikiyatrik bozukluklard obezite ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Cortex & limbic system<br />
‘Reward’<br />
Dopamine, Opioids and<br />
Endocannabinoids<br />
APD<br />
+<br />
Arcuate<br />
nucleus<br />
+<br />
Orexin NPY AGRP<br />
+<br />
+<br />
5HT 2c R Leptin R<br />
+<br />
Paraventricular<br />
nucleus<br />
Insulin<br />
+<br />
–<br />
APD?<br />
+<br />
Hypothalamus<br />
APD<br />
Food Intake<br />
POMC αMSH<br />
CART<br />
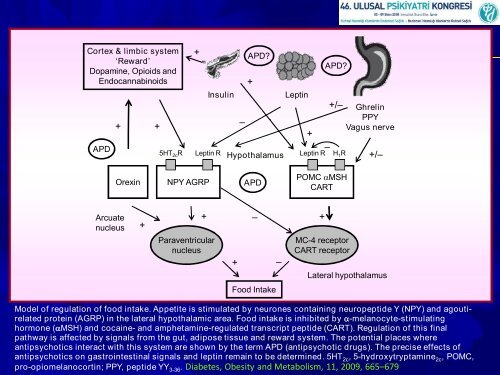
Model of regulation of food intake. Appetite is stimulated by neurones containing neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti agouti<br />
related protein (AGRP) in the lateral hypothalamic area. Food intake is inhibited by αmelanocytestimulating<br />
hormone (αMSH) and cocaine and amphetamineregulated regulated transcript peptide (CART). Regulation of this final<br />
pathway is affected by signals from the gut, adipose tissue and reward system. The potential places where<br />
antipsychotics interact with this system are shown by the term APD (antipsychotic drugs). The precise effects of<br />
antipsychotics on gastrointestinal signals and leptin remain to be determined. 5HT 2c , 5hydroxytryptamine 2c , POMC,<br />
proopiomelanocortin; PPY, peptide YY 336 . Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 11, 2009, 665 665–679<br />
–<br />
–<br />
Leptin<br />
+<br />
+<br />
APD?<br />
–<br />
+/–<br />
Leptin R H 1 R<br />
MC4 receptor<br />
CART receptor<br />
Ghrelin<br />
PPY<br />
Vagus nerve<br />
+/–<br />
Lateral hypothalamus