English version - Fit for Work Europe
English version - Fit for Work Europe
English version - Fit for Work Europe
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
According to the MHLW Estimates of National Medical Expenditure Survey, MSDs account<br />
<strong>for</strong> 7.5 per cent of Japan’s total general medical costs, or nearly JPY 2 trillion in 2009 (MHLW,<br />
2009). Total expenditure on MSDs has risen throughout the last decade, from JPY 1.6 trillion in<br />
2003, although the proportion of medical expenditure allocated to these diseases has remained<br />
relatively stable.<br />
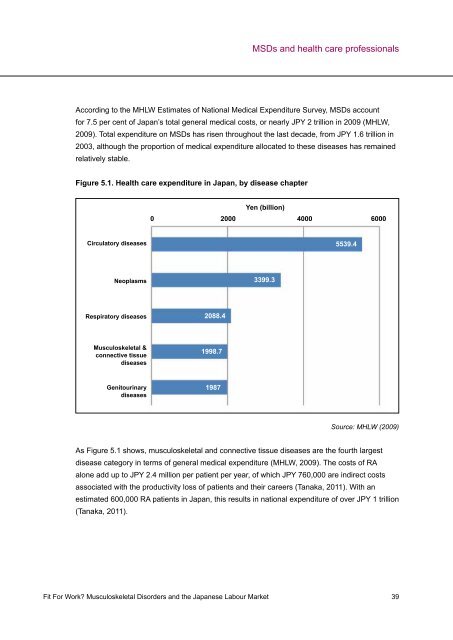
Figure 5.1. Health care expenditure in Japan, by disease chapter<br />
Circulatory diseases<br />
Neoplasms<br />
Respiratory diseases<br />
Musculoskeletal &<br />
connective tissue<br />
diseases<br />
Genitourinary<br />
diseases<br />
Yen (billion)<br />
0 2000 4000 6000<br />
2088.4<br />
1998.7<br />
1987<br />
MSDs and health care professionals<br />
3399.3<br />
5539.4<br />
Source: MHLW (2009)<br />
As Figure 5.1 shows, musculoskeletal and connective tissue diseases are the fourth largest<br />
disease category in terms of general medical expenditure (MHLW, 2009). The costs of RA<br />
alone add up to JPY 2.4 million per patient per year, of which JPY 760,000 are indirect costs<br />
associated with the productivity loss of patients and their careers (Tanaka, 2011). With an<br />
estimated 600,000 RA patients in Japan, this results in national expenditure of over JPY 1 trillion<br />
(Tanaka, 2011).<br />
<strong>Fit</strong> For <strong>Work</strong>? Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Japanese Labour Market 39