English version - Fit for Work Europe
English version - Fit for Work Europe
English version - Fit for Work Europe
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
MSDs and employers<br />
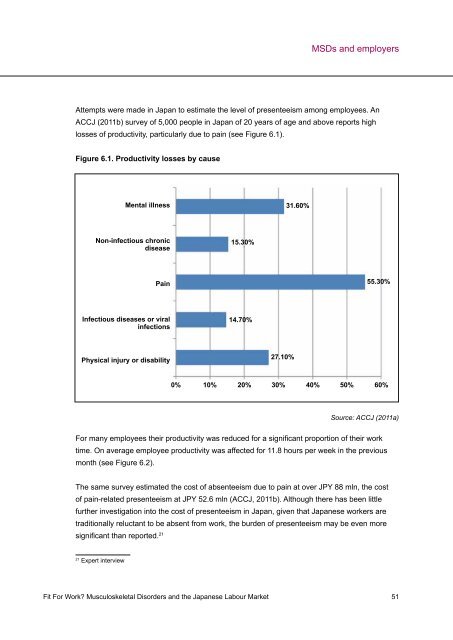
Attempts were made in Japan to estimate the level of presenteeism among employees. An<br />
ACCJ (2011b) survey of 5,000 people in Japan of 20 years of age and above reports high<br />
losses of productivity, particularly due to pain (see Figure 6.1).<br />
Figure 6.1. Productivity losses by cause<br />
Mental illness<br />
Non-infectious chronic<br />
disease<br />
Pain<br />
Infectious diseases or viral<br />
infections<br />
Physical injury or disability<br />
15.30%<br />
14.70%<br />
27.10%<br />
31.60%<br />
55.30%<br />
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60%<br />
Source: ACCJ (2011a)<br />
For many employees their productivity was reduced <strong>for</strong> a significant proportion of their work<br />
time. On average employee productivity was affected <strong>for</strong> 11.8 hours per week in the previous<br />
month (see Figure 6.2).<br />
The same survey estimated the cost of absenteeism due to pain at over JPY 88 mln, the cost<br />
of pain-related presenteeism at JPY 52.6 mln (ACCJ, 2011b). Although there has been little<br />
further investigation into the cost of presenteeism in Japan, given that Japanese workers are<br />
traditionally reluctant to be absent from work, the burden of presenteeism may be even more<br />
significant than reported. 21<br />
21 Expert interview<br />
<strong>Fit</strong> For <strong>Work</strong>? Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Japanese Labour Market 51