Arūnas Diškus - VPU biblioteka - Vilniaus pedagoginis universitetas
Arūnas Diškus - VPU biblioteka - Vilniaus pedagoginis universitetas
Arūnas Diškus - VPU biblioteka - Vilniaus pedagoginis universitetas
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
16<br />
Species number<br />
IV(1)<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
IV(2)<br />
V(1)<br />
V(2)<br />
VI(1)<br />
VI(2)<br />
VII(1)<br />
VII(2)<br />
VIII(1)<br />
VIII(2)<br />
IX(1)<br />
IX(2)<br />
X(1)<br />
X(2)<br />
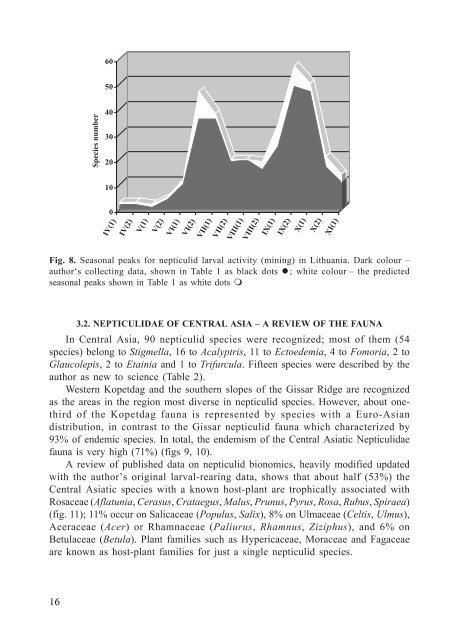
Fig. 8. Seasonal peaks for nepticulid larval activity (mining) in Lithuania. Dark colour –<br />
author‘s collecting data, shown in Table 1 as black dots l; white colour – the predicted<br />
seasonal peaks shown in Table 1 as white dots m<br />
3.2. NEPTICULIDAE OF CENTRAL ASIA – A REVIEW OF THE FAUNA<br />
In Central Asia, 90 nepticulid species were recognized; most of them (54<br />
species) belong to Stigmella, 16 to Acalyptris, 11 to Ectoedemia, 4 to Fomoria, 2 to<br />
Glaucolepis, 2 to Etainia and 1 to Trifurcula. Fifteen species were described by the<br />
author as new to science (Table 2).<br />
Western Kopetdag and the southern slopes of the Gissar Ridge are recognized<br />
as the areas in the region most diverse in nepticulid species. However, about onethird<br />
of the Kopetdag fauna is represented by species with a Euro-Asian<br />
distribution, in contrast to the Gissar nepticulid fauna which characterized by<br />
93% of endemic species. In total, the endemism of the Central Asiatic Nepticulidae<br />
fauna is very high (71%) (figs 9, 10).<br />
A review of published data on nepticulid bionomics, heavily modified updated<br />
with the author’s original larval-rearing data, shows that about half (53%) the<br />
Central Asiatic species with a known host-plant are trophically associated with<br />
Rosaceae (Aflatunia, Cerasus, Crataegus, Malus, Prunus, Pyrus, Rosa, Rubus, Spiraea)<br />
(fig. 11); 11% occur on Salicaceae (Populus, Salix), 8% on Ulmaceae (Celtis, Ulmus),<br />
Aceraceae (Acer) or Rhamnaceae (Paliurus, Rhamnus, Ziziphus), and 6% on<br />
Betulaceae (Betula). Plant families such as Hypericaceae, Moraceae and Fagaceae<br />
are known as host-plant families for just a single nepticulid species.<br />
XI(1)