- Page 1 and 2:
Lotus® Domino Version 7 Domino Adm
- Page 3 and 4:
Contents Chapter 1. Deploying Domin
- Page 5 and 6:
Upgrading from a beta release to Do
- Page 7 and 8:
Adding a hosted organization to an
- Page 9 and 10:
Configuring Domino to send and rece
- Page 11 and 12:
Interoperability issues . . . . . .
- Page 13 and 14:
Setting up automatic diagnostic dat
- Page 15 and 16:
To start the cconsole program . . .
- Page 17 and 18:
Max_NSDInfo_Files . . . . . . . . .
- Page 19 and 20:
ImailLogout command . . . . . . . .
- Page 21 and 22:
Chapter 1. Deploying Domino This ch
- Page 23 and 24:
Looking at Acme’s diagram, you ca
- Page 25 and 26:
For more information on installing
- Page 27 and 28:
Example of how certifier IDs mirror
- Page 29 and 30:
Name Characters Tips Organizational
- Page 31 and 32:
Chapter 2. Setting Up the Domino Ne
- Page 33 and 34:
The Notes Name Service resolves Dom
- Page 35 and 36:
equester. A proxy can provide detai
- Page 37 and 38:
Planning the TCP/IP network The def
- Page 39 and 40:
Tip: Use policies to automate the s
- Page 41 and 42:
3. Create an A record (or, for IPv6
- Page 43 and 44:
To modify the Server Connection doc
- Page 45 and 46:
Using IPv6 address formats with Dom
- Page 47 and 48:
v If connecting or listening with a
- Page 49 and 50:
Example 7 -- Microsoft Windows/Linu
- Page 51 and 52:
Partitioned servers and IP addresse
- Page 53 and 54:
Where serverportname is the name of
- Page 55 and 56:
v For NetBIOS over TCP/IP, the syst
- Page 57 and 58:
1. From the Domino Administrator or
- Page 59 and 60:
Field Action Notes Network Enter th
- Page 61 and 62:
destination server, the server obta
- Page 63 and 64:
Setting up a secondary name server
- Page 65 and 66:
Where TCPIPportname is the port nam
- Page 67 and 68:
1. Add one entry in the local host
- Page 69 and 70:
Note: Because Internet protocols ca
- Page 71 and 72:
Confirming that TCP/IP is configure
- Page 73 and 74:
v Associate each Notes network port
- Page 75 and 76:
Chapter 3. Installing and Setting U
- Page 77 and 78:
v Before running any Domino setup c
- Page 79 and 80:
Concurrent I/O and Direct I/O not s
- Page 81 and 82:
v Creates the Reports file, names i
- Page 83 and 84:
For more information on Internet Si
- Page 85 and 86:
6. Click ″Save & Close.″ 7. Rep
- Page 87 and 88:
3. Enter the Secrets database filen
- Page 89 and 90:
For complete information on working
- Page 91 and 92:
By default, server setup is set to
- Page 93 and 94:
4. On the client system, choose Sta
- Page 95 and 96:
4. Continue through the setup progr
- Page 97 and 98:
To use a setup profile from a Windo
- Page 99 and 100:
v On a UNIX server, enter server -l
- Page 101 and 102:
Create a replica of the Certificati
- Page 103 and 104:
Field Action Expiration date (Optio
- Page 105 and 106:
Field Action Certifier password Ent
- Page 107 and 108:
The Domino server is configured to
- Page 109 and 110:
3. Click the Basics tab, and comple
- Page 111 and 112:
Field Enter Anonymous (Applies to a
- Page 113 and 114:
Note: If the server program is runn
- Page 115 and 116:
Chapter 4. Setting Up Server-to-Ser
- Page 117 and 118:
For information about connecting se
- Page 119 and 120:
can use a combination of topologies
- Page 121 and 122:
Example of hub-and-spoke topology I
- Page 123 and 124:
Example of mail and directory serve
- Page 125 and 126:
A LAN Connection document can also
- Page 127 and 128:
To gather information, the requesti
- Page 129 and 130:
To connect a Domino server to an In
- Page 131 and 132:
2. List the destination servers tha
- Page 133 and 134:
Field Description Cause calling Spe
- Page 135 and 136:
After you set up a hunt group, crea
- Page 137 and 138:
Modem command files, which have the
- Page 139 and 140:
To create a Network dialup connecti
- Page 141 and 142:
5. Choose File - Document Propertie
- Page 143 and 144:
Tab Field Description Replication/R
- Page 145 and 146:
Tab Field Description Connect at ti
- Page 147 and 148:
Field Description Port number Speci
- Page 149 and 150:
DESC A one line description of the
- Page 151 and 152:
Type of client and connection to Do
- Page 153 and 154:
Chapter 5. Setting up Domino and DB
- Page 155 and 156:
The DAV makes the data available di
- Page 157 and 158:
v Domino with DB2 supports Domino s
- Page 159 and 160:
Task Command to run task Descriptio
- Page 161 and 162:
Domino and DB2 supported platforms
- Page 163 and 164:
v DB2 UDB Enterprise Server Edition
- Page 165 and 166:
Mixed platforms are supported for D
- Page 167 and 168:
Domino server enablement and mappin
- Page 169 and 170:
You are now ready to create views.
- Page 171 and 172:
Note: When you create file systems
- Page 173 and 174:
12. Determine whether your DB2 conf
- Page 175 and 176:
18. From the Domino Administrator,
- Page 177 and 178:
Setting up DB2 on Microsoft Windows
- Page 179 and 180:
12. From the AIX OS or from the AIX
- Page 181 and 182:
5. Logged in as the Domino user, st
- Page 183 and 184:
Performing the DB2 Access server in
- Page 185 and 186:
Note: If you are using Microsoft Wi
- Page 187 and 188:
Field Action DB2 Node Name This fie
- Page 189 and 190:
NOTES.INI setting Description DB2UD
- Page 191 and 192:
Mapping the DB2 ID to a Notes ID in
- Page 193 and 194:
Example For example, you can create
- Page 195 and 196:
v Rename a DB2 class v Create a new
- Page 197 and 198:
Procedure - Upgrading when you have
- Page 199 and 200:
Upgrading to DB2 8.2.2 if you have
- Page 201 and 202:
Copying a local copy of a database
- Page 203 and 204:
5. Click Set. 6. (Optional) Select
- Page 205 and 206:
2. Choose the server for which you
- Page 207 and 208:
Domino Directory on the DB2 Access
- Page 209 and 210:
Chapter 6. Setting Up Notes Users a
- Page 211 and 212:
Alan Jones works in the Sales depar
- Page 213 and 214:
The method you use to register peop
- Page 215 and 216:
Field Default Set warning threshold
- Page 217 and 218:
Information that does not replicate
- Page 219 and 220:
If you create roaming users and do
- Page 221 and 222:
Field Enter Mail system Choose one
- Page 223 and 224:
Field Enter Location for storing us
- Page 225 and 226:
Registering users with the Web Admi
- Page 227 and 228:
Field Action Mail System Choose one
- Page 229 and 230:
Field Action Mail System Choose one
- Page 231 and 232:
11. Click the Address tab, and ente
- Page 233 and 234:
Field Action Clean-up options Choos
- Page 235 and 236:
Order Parameter Enter 11 Location D
- Page 237 and 238:
4. If the server name that is shown
- Page 239 and 240:
For information on multi-user insta
- Page 241 and 242:
Running a silent install provides u
- Page 243 and 244:
1. Invoke the InstallShield Tuner p
- Page 245 and 246:
3. Use the InstallShield Tuner (6)
- Page 247 and 248:
Using the SETUP.INI file setting to
- Page 249 and 250:
Setting Description IM.Port IBM Lot
- Page 251 and 252:
For more information about using sc
- Page 253 and 254:
v Extract the language pack on a wo
- Page 255 and 256:
Delaying the deployment of welcome
- Page 257 and 258:
Chapter 7. Managing Notes Users Thi
- Page 259 and 260:
Troubleshooting name changes The pu
- Page 261 and 262:
New Alternate Name Information Avai
- Page 263 and 264:
1. Make sure you have the following
- Page 265 and 266:
is never prompted as to whether the
- Page 267 and 268:
To verify the change The procedure
- Page 269 and 270:
You can also move a user to another
- Page 271 and 272:
4. To complete the move, in the Cho
- Page 273 and 274:
7. Click Next. A message displays i
- Page 275 and 276:
6. If you are working with clustere
- Page 277 and 278:
To recertify a user ID Follow these
- Page 279 and 280:
3. In the ″Choose a Certifier″
- Page 281 and 282:
By default, administrators have Man
- Page 283 and 284:
Chapter 8. Setting Up and Managing
- Page 285 and 286:
Field Action Mail Domain Enter the
- Page 287 and 288:
6. (Optional) Click the Comments ta
- Page 289 and 290:
4. Complete these fields: Field Act
- Page 291 and 292:
Field Action Members Add or remove
- Page 293 and 294:
To find a group name with the Domin
- Page 295 and 296:
Chapter 9. Creating Replicas and Sc
- Page 297 and 298:
Note: If the server initiating the
- Page 299 and 300:
particular privilege for a server e
- Page 301 and 302:
Table of replication settings By de
- Page 303 and 304:
v Users can’t categorize or edit
- Page 305 and 306:
Specifying replication settings for
- Page 307 and 308:
7. In the ″Repeat interval of″
- Page 309 and 310:
To set up Connection documents for
- Page 311 and 312:
You can also specify replication di
- Page 313 and 314:
If you do not enable multiple repli
- Page 315 and 316:
Each server, network, cluster, and
- Page 317 and 318:
Chapter 10. Setting Up Calendars an
- Page 319 and 320:
v If the Free Time system finds a N
- Page 321 and 322:
The Resource Reservations database
- Page 323 and 324:
v Room -- Typically a conference ro
- Page 325 and 326:
6. Complete these fields Field Ente
- Page 327 and 328:
If you delete a resource from the R
- Page 329 and 330:
9. A message appears notifying you
- Page 331 and 332:
Field Action Repeat until (Displays
- Page 333 and 334:
Chapter 11. Using Policies Using po
- Page 335 and 336:
In organizational policies, the hie
- Page 337 and 338:
Planning and assigning policies Bef
- Page 339 and 340:
1. Make sure that you have Editor a
- Page 341 and 342:
v Check the field to create Notes I
- Page 343 and 344:
6. On the Dial-up Connections tab,
- Page 345 and 346:
Many of the tabs on the desktop pol
- Page 347 and 348:
Field Action If running this versio
- Page 349 and 350:
Field Enter SSL protocol version Ch
- Page 351 and 352:
To create Security settings: 1. Mak
- Page 353 and 354:
For more information, see the chapt
- Page 355 and 356:
Field Action Earliest Allowable Key
- Page 357 and 358:
Field Action Delete/Remove preferen
- Page 359 and 360:
Field Action For new meetings, the
- Page 361 and 362:
Field Action The following people o
- Page 363 and 364:
If you choose not to include archiv
- Page 365 and 366:
6. Under Archive locations, choose
- Page 367 and 368:
Field Action Use customer-generated
- Page 369 and 370:
Creating a policy document When you
- Page 371 and 372:
Editing policies Use this procedure
- Page 373 and 374:
v In the top right pane, selects on
- Page 375 and 376:
v Open the Groups view, select one
- Page 377 and 378:
Chapter 12. Setting Up Domain Searc
- Page 379 and 380:
Tip: You can use replication events
- Page 381 and 382:
10. Make sure the Catalog task is i
- Page 383 and 384:
For more information, see the chapt
- Page 385 and 386:
CAUTION: The security checking work
- Page 387 and 388:
By default, the indexing server use
- Page 389 and 390:
Manual setup from a Notes workstati
- Page 391 and 392:
4. Click Browse Catalog. 5. In the
- Page 393 and 394:
Chapter 13. Setting Up Domino Off-L
- Page 395 and 396:
Name of Field Action Interval Speci
- Page 397 and 398:
Syc Options Halt Conditions v Limit
- Page 399 and 400:
Name of field Action Network Settin
- Page 401 and 402:
If the application is DOLS-enabled,
- Page 403 and 404:
When the user wants to open the app
- Page 405 and 406:
6. Fill out the following fields in
- Page 407 and 408:
Option Description Tighten security
- Page 409 and 410:
Viewing DOLS download information T
- Page 411 and 412:
SELECT From=@UserName|Form="DOLSOff
- Page 413 and 414:
Chapter 14. Planning the Service Pr
- Page 415 and 416:
For more information on setting up
- Page 417 and 418:
Combination of IP address configura
- Page 419 and 420:
Combined configuration You can use
- Page 421 and 422:
Name Protocol The domain portion of
- Page 423 and 424:
1. Reads the topic ″Installing th
- Page 425 and 426:
Chapter 15. Setting Up the Service
- Page 427 and 428:
To meet the requirements for creati
- Page 429 and 430:
Where to store data for hosted orga
- Page 431 and 432:
7. Complete these fields on the ID
- Page 433 and 434:
For more information on extended AC
- Page 435 and 436:
3. Chooses Tools - Hosted Organizat
- Page 437 and 438:
For more information on Internet Si
- Page 439 and 440:
Field Action Log checkpoint at midn
- Page 441 and 442:
Chapter 16. Managing a Hosted Envir
- Page 443 and 444:
The Domino service provider softwar
- Page 445 and 446:
Moving a hosted organization that h
- Page 447 and 448:
For more information on the Interne
- Page 449 and 450:
v Add the hosted organization admin
- Page 451 and 452:
Chapter 17. Setting Up the Administ
- Page 453 and 454:
v Using a multifunction server as t
- Page 455 and 456:
Administration Process support of s
- Page 457 and 458:
Creating a Cross-domain Configurati
- Page 459 and 460:
Task Administrator needs this acces
- Page 461 and 462:
Task Rename users and convert users
- Page 463 and 464:
New Processing Option Description R
- Page 465 and 466:
Adminstration Request Documents: Ic
- Page 467 and 468:
Using Selective Replication formula
- Page 469 and 470:
Forcing an administration process r
- Page 471 and 472:
Field Enter Store Admin Process log
- Page 473 and 474:
Setting up an extended administrati
- Page 475 and 476:
Message Occurs during Corrective ac
- Page 477 and 478:
Message Occurs during Corrective ac
- Page 479 and 480:
Chapter 18. Setting Up and Using Do
- Page 481 and 482:
To update a server list The first t
- Page 483 and 484:
4. Click the up or down arrows to c
- Page 485 and 486:
Field Action Advanced Options Click
- Page 487 and 488:
If you change the foreground or bac
- Page 489 and 490:
Domino Administrator tools Most tab
- Page 491 and 492:
Access control list: Default name A
- Page 493 and 494:
Role Tab ServerAnalysis Server - An
- Page 495 and 496:
about creating and modifying groups
- Page 497 and 498:
Starting and stopping the Server Co
- Page 499 and 500:
Chapter 19. Using Domino with Windo
- Page 501 and 502:
Field Action User/group registratio
- Page 503 and 504:
Field Action Registration Options C
- Page 505 and 506:
hierarchy of organizational units a
- Page 507 and 508:
Fields Action First name, Middle na
- Page 509 and 510:
4. Choose one of these options: Fie
- Page 511 and 512:
document for that Domino Directory
- Page 513 and 514:
Chapter 20. Planning Directory Serv
- Page 515 and 516:
v Should you use an extended ACL to
- Page 517 and 518:
Planning new entries in the Domino
- Page 519 and 520:
type-ahead addressing does not sear
- Page 521 and 522:
Comparison of directory catalogs an
- Page 523 and 524:
3. The primary Domino Directory on
- Page 525 and 526:
Condensed Directory Catalog A direc
- Page 527 and 528:
Chapter 21. Setting Up the Domino D
- Page 529 and 530:
You can set up a Domino Directory a
- Page 531 and 532:
A server that stores a Configuratio
- Page 533 and 534:
You might want to customize the dat
- Page 535 and 536:
You can assign a user to up to six
- Page 537 and 538:
5. Complete any of these fields, an
- Page 539 and 540:
Chapter 22. Setting Up the LDAP Ser
- Page 541 and 542:
For example, if the distinguished n
- Page 543 and 544:
Note: A server that runs the LDAP s
- Page 545 and 546:
Setting Description For more inform
- Page 547 and 548:
Field Enter Authentication options:
- Page 549 and 550:
directory tree, but allow access to
- Page 551 and 552:
To convert the default anonymous se
- Page 553 and 554:
enable directory changes to be made
- Page 555 and 556:
Examples of the ″Rules to follow.
- Page 557 and 558:
Configuring the LDAP service to all
- Page 559 and 560:
v If you see the prompt ″Unable t
- Page 561 and 562:
xxx represents the text string to s
- Page 563 and 564:
Statistic Description Sessions.Inbo
- Page 565 and 566:
Chapter 23. Managing the LDAP Schem
- Page 567 and 568:
How an LDAP attribute relates to a
- Page 569 and 570:
Note: If the schema daemon finds th
- Page 571 and 572:
For information about the fields in
- Page 573 and 574:
A registered OID prefix begins with
- Page 575 and 576:
Using the Schema database to add a
- Page 577 and 578:
Extended Directory Catalog for whic
- Page 579 and 580:
Chapter 24. Using the ldapsearch Ut
- Page 581 and 582:
Using search filters with ldapsearc
- Page 583 and 584:
Search Command Search the host ldap
- Page 585 and 586:
Chapter 25. Setting Up Directory As
- Page 587 and 588:
Note: A server’s primary Domino D
- Page 589 and 590:
The following figure illustrates lo
- Page 591 and 592:
For more information on creating ac
- Page 593 and 594:
v A null character (nothing or a si
- Page 595 and 596:
How naming rules relate to director
- Page 597 and 598:
Directory assistance and failover f
- Page 599 and 600:
5. To trust all the directories agg
- Page 601 and 602:
Using directory assistance to contr
- Page 603 and 604:
. Enter the name of the server on w
- Page 605 and 606:
Field Enter Domain name The name of
- Page 607 and 608:
Field Enter Replica# The server nam
- Page 609 and 610:
Field Enter Attribute to be used as
- Page 611 and 612:
Field Enter Dereference alias on se
- Page 613 and 614:
Specifying a name and password for
- Page 615 and 616:
To define custom search filters, yo
- Page 617 and 618:
Once you have set up this feature,
- Page 619 and 620:
Change Detection Mechanism Tested P
- Page 621 and 622:
Basics tab Contents Comments Group
- Page 623 and 624:
Basics tab Contents Comments Option
- Page 625 and 626:
Chapter 26. Setting Up Directory Ca
- Page 627 and 628:
v Users can flag mail for encryptio
- Page 629 and 630:
a name hierarchy, and so forth. An
- Page 631 and 632:
Assistance document for each Extend
- Page 633 and 634:
Directory catalogs and Notes mail e
- Page 635 and 636:
Types of documents the Dircat task
- Page 637 and 638:
All groups aggregated as Multi-purp
- Page 639 and 640:
v In a condensed Directory Catalog,
- Page 641 and 642:
You can set up a server to use more
- Page 643 and 644:
Setting the view sort order Unlike
- Page 645 and 646:
Setting up Notes clients to use mor
- Page 647 and 648:
2. Next to Server, select the Dirca
- Page 649 and 650:
Note: See the topic ″Planning iss
- Page 651 and 652:
Document/Database Field(s)/Tab(s) P
- Page 653 and 654:
For information, see the topic ″E
- Page 655 and 656:
Or you can do a full rebuild by cli
- Page 657 and 658:
Chapter 27. Setting Up Extended ACL
- Page 659 and 660:
v To delete a document, a Notes or
- Page 661 and 662:
Note: The Administer access setting
- Page 663 and 664:
Examples of precedence rules: Subje
- Page 665 and 666:
Anonymous as subject As in the data
- Page 667 and 668:
field called FullName, ListName, or
- Page 669 and 670:
Example of using ″This container
- Page 671 and 672:
Extended ACL: example 2 The Acme co
- Page 673 and 674:
v Use names that represent groups o
- Page 675 and 676:
v Click Add - Default to add the su
- Page 677 and 678:
8. The Modified Forms section shows
- Page 679 and 680:
Chapter 28. Overview of the Domino
- Page 681 and 682:
POP3 and IMAP clients, which always
- Page 683 and 684:
How mail routes in a Domino system
- Page 685 and 686:
To help manage disk space, you can
- Page 687 and 688:
Working with other mail systems in
- Page 689 and 690:
Documents Description Adjacent and
- Page 691 and 692:
Connection documents for mail routi
- Page 693 and 694:
servers in the same Notes named net
- Page 695 and 696:
mail1.acme.com or mail2.acme.com. I
- Page 697 and 698:
Chapter 29. Setting Up Mail Routing
- Page 699 and 700:
4. Click Yes when prompted to confi
- Page 701 and 702:
Example of using one server for all
- Page 703 and 704:
Example of using two servers to bal
- Page 705 and 706:
If a user sends a MIME message to a
- Page 707 and 708:
and have smarthost.acme.com listed
- Page 709 and 710:
Configuration document or an All Se
- Page 711 and 712:
In small Domino networks, you can m
- Page 713 and 714:
Adjacent Domain documents do not pr
- Page 715 and 716:
v Restricts mail from other domains
- Page 717 and 718:
Restrictions that you set on this F
- Page 719 and 720:
can set up a single relay host that
- Page 721 and 722:
2. Choose Connections and click Add
- Page 723 and 724:
1. Make sure that you prepared your
- Page 725 and 726:
v Enable Domino to accept mail for
- Page 727 and 728:
To create a Global Domain document:
- Page 729 and 730:
6. Complete these fields, and then
- Page 731 and 732:
6. Complete the following and click
- Page 733 and 734:
To ensure that every user has a sta
- Page 735 and 736:
can split external SMTP mail routin
- Page 737 and 738:
For more information about Notes Di
- Page 739 and 740:
7. For outbound SMTP connections, c
- Page 741 and 742:
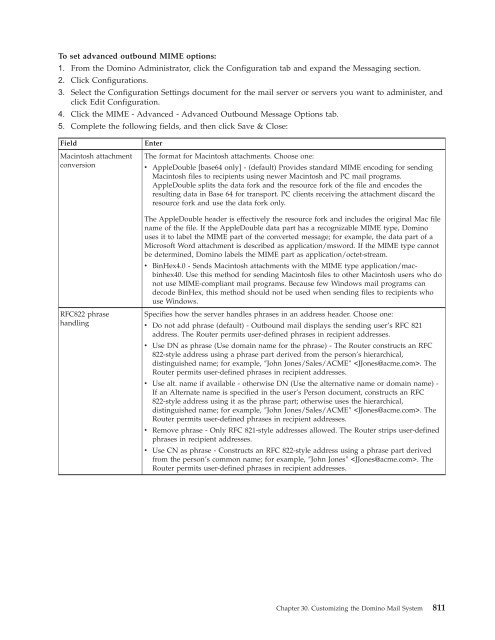
Chapter 30. Customizing the Domino
- Page 743 and 744:
naming convention used when multipl
- Page 745 and 746:
6. Complete this field in the Misce
- Page 747 and 748:
set a warning threshold of 25MB on
- Page 749 and 750:
Method for enforcing quotas Descrip
- Page 751 and 752:
ased on usage, rather than file siz
- Page 753 and 754:
Setting server mail rules You can c
- Page 755 and 756:
Condition component Description Mes
- Page 757 and 758:
How mail rules handle encrypted mes
- Page 759 and 760:
Priority level Default Notes routin
- Page 761 and 762:
1. From the Domino Administrator, c
- Page 763 and 764:
Named Network (NNN). When using Not
- Page 765 and 766:
6. Complete these fields in the Adv
- Page 767 and 768:
You can use the following tools to
- Page 769 and 770:
3. Click Configurations. 4. Select
- Page 771 and 772:
Customizing Notes routing To custom
- Page 773 and 774:
Changing the routing cost for a con
- Page 775 and 776:
Field Enter Deny mail from domains
- Page 777 and 778:
To determine whether the use of Int
- Page 779 and 780: Field Enter Enforce server access s
- Page 781 and 782: For information about enabling supp
- Page 783 and 784: have to enable the SSL port. If the
- Page 785 and 786: 6. Complete these fields in the Inb
- Page 787 and 788: commonly referred to as electronic
- Page 789 and 790: Inbound Relay Controls Deny message
- Page 791 and 792: elay host or firewall to receive In
- Page 793 and 794: 5. If the relay controls still appl
- Page 795 and 796: variable SMTPExpandDNSBLStats in th
- Page 797 and 798: Field Action Desired action when a
- Page 799 and 800: Whitelists can be used independentl
- Page 801 and 802: Inbound Sender Controls Deny messag
- Page 803 and 804: Field Description Allow messages in
- Page 805 and 806: Field Enter SSL negotiated over TCP
- Page 807 and 808: Outbound Sender Controls Deny messa
- Page 809 and 810: 1. Make sure you already have a Con
- Page 811 and 812: disclaimers with combinations of ma
- Page 813 and 814: You can use Domino mail journaling
- Page 815 and 816: The change takes effect after the n
- Page 817 and 818: Size management method Description
- Page 819 and 820: You can specify settings for the fo
- Page 821 and 822: For a list of character set groups
- Page 823 and 824: Configuring how Domino converts out
- Page 825 and 826: Field Description Message Content S
- Page 827 and 828: 7. Complete the following fields an
- Page 829: Field Choose Body - Encoding The en
- Page 833 and 834: For information on how to reload th
- Page 835 and 836: By default, the File Identification
- Page 837 and 838: Chapter 31. Setting Up Shared Mail
- Page 839 and 840: How Domino maintains the security o
- Page 841 and 842: Field name Enter Availability Speci
- Page 843 and 844: v Restore a shared mail database v
- Page 845 and 846: Note: The Domino Administrator main
- Page 847 and 848: To determine which mail files use s
- Page 849 and 850: Use these steps on each cluster mem
- Page 851 and 852: Note: Before you unlink a shared ma
- Page 853 and 854: Chapter 32. Setting Up the POP3 Ser
- Page 855 and 856: If the server uses Internet Site do
- Page 857 and 858: For more information on using the D
- Page 859 and 860: 5. After Domino creates and opens t
- Page 861 and 862: Chapter 33. Setting Up the IMAP Ser
- Page 863 and 864: Note: The Domino Release 6, and mor
- Page 865 and 866: For information on configuring an I
- Page 867 and 868: 3. Click Configurations. 4. Select
- Page 869 and 870: In addition to the personal namespa
- Page 871 and 872: 5. Select the Configuration Setting
- Page 873 and 874: The session thread communicates dir
- Page 875 and 876: Field Enter Default IMAP SSL redire
- Page 877 and 878: Field Enter When receiving unencryp
- Page 879 and 880: 1. From the Domino Administrator, o
- Page 881 and 882:
This prevents Domino from routing m
- Page 883 and 884:
adding RFC 822 phrases to users’
- Page 885 and 886:
Field Description Incoming mail (IM
- Page 887 and 888:
Chapter 34. Setting Up Domino Web A
- Page 889 and 890:
Creating Portal URLs A portal is a
- Page 891 and 892:
1. From the Domino Administrator, c
- Page 893 and 894:
6. Save the document and restart th
- Page 895 and 896:
Setting Action Directory type used
- Page 897 and 898:
Setting Action Default cache scrubb
- Page 899 and 900:
Browser Cache Management, this pref
- Page 901 and 902:
4. Change the Target Form to DWALog
- Page 903 and 904:
For example, to compress all text:
- Page 905 and 906:
mail database. For users who access
- Page 907 and 908:
v An alternative method is to use t
- Page 909 and 910:
Part 1 -- Configure Microsoft Outlo
- Page 911 and 912:
Chapter 35. Monitoring Mail This ch
- Page 913 and 914:
To create the Reports database 1. F
- Page 915 and 916:
MTC operation Description and Comma
- Page 917 and 918:
Field Enter Sent Choose one: v Toda
- Page 919 and 920:
Field Description Run this report S
- Page 921 and 922:
You can open the Reports database (
- Page 923 and 924:
Chapter 36. Setting Up the Domino W
- Page 925 and 926:
Setting up a Domino server as a Web
- Page 927 and 928:
3. (Optional) Click Internet Protoc
- Page 929 and 930:
Example configuration Settings Comm
- Page 931 and 932:
Field Action Port number Indicate t
- Page 933 and 934:
There are some restrictions when us
- Page 935 and 936:
Hosting Web sites using Web Server
- Page 937 and 938:
Field Action Java URL path Enter th
- Page 939 and 940:
To specify GIF conversion: Field En
- Page 941 and 942:
For information on the Redirect URL
- Page 943 and 944:
Field Enter Meta character set Choo
- Page 945 and 946:
Character set group Mapping choices
- Page 947 and 948:
The most important use of response
- Page 949 and 950:
Field Action Custom header (HTTP Re
- Page 951 and 952:
File protection documents provide l
- Page 953 and 954:
If there is no realm specification
- Page 955 and 956:
authentication, see the chapter ″
- Page 957 and 958:
Improving Web server performance Af
- Page 959 and 960:
Field Action Maximum requests per p
- Page 961 and 962:
Chapter 37. Setting Up Domino to Wo
- Page 963 and 964:
To install the WebSphere plug-in on
- Page 965 and 966:
Setting up security for Microsoft I
- Page 967 and 968:
v If you want to match the Windows
- Page 969 and 970:
Chapter 38. Setting Up the Web Navi
- Page 971 and 972:
Field Enter No proxy for these host
- Page 973 and 974:
2. Click the Server Tasks - Web Ret
- Page 975 and 976:
Agents The Web Navigator database c
- Page 977 and 978:
Field Enter Font for text in the ,
- Page 979 and 980:
4. Click Schedule and then specify
- Page 981 and 982:
Using the Averaging agent to calcul
- Page 983 and 984:
Chapter 39. Planning Security This
- Page 985 and 986:
Plan and deliver employee training
- Page 987 and 988:
For more information on securing de
- Page 989 and 990:
For more information on setting up
- Page 991 and 992:
Task Use Authenticate Web clients f
- Page 993 and 994:
For more information on Smartcards,
- Page 995 and 996:
Using both types of Domino Internet
- Page 997 and 998:
Chapter 40. Controlling Access to D
- Page 999 and 1000:
3. In the Server Access section, co
- Page 1001 and 1002:
You do not need to list a user indi
- Page 1003 and 1004:
v Manager access, with all access p
- Page 1005 and 1006:
v Log key mismatches for all Notes
- Page 1007 and 1008:
Controlling the use of headline mon
- Page 1009 and 1010:
Field Action Cause calling Enter an
- Page 1011 and 1012:
Field Action Run restricted Java/Ja
- Page 1013 and 1014:
1. On the Domino server workstation
- Page 1015 and 1016:
Chapter 41. Protecting and Managing
- Page 1017 and 1018:
For more information on using Inter
- Page 1019 and 1020:
CAUTION: In order for Notes users t
- Page 1021 and 1022:
Each time a user changes a password
- Page 1023 and 1024:
To lock out an individual user’s
- Page 1025 and 1026:
v Administrators export recovery in
- Page 1027 and 1028:
v If you are not using a server-bas
- Page 1029 and 1030:
Use the Notes.ini variable ID_Recov
- Page 1031 and 1032:
Note: This is done in addition to t
- Page 1033 and 1034:
Adding a Notes public key to the Do
- Page 1035 and 1036:
Note: The archived keys remain in t
- Page 1037 and 1038:
Adding cross-certificates to the Do
- Page 1039 and 1040:
Your local Domino Directory does no
- Page 1041 and 1042:
3. Select whether to use a CA-enabl
- Page 1043 and 1044:
Displaying cross-certificates To vi
- Page 1045 and 1046:
Chapter 42. Controlling User Access
- Page 1047 and 1048:
Types of ACL entries Wildcard entri
- Page 1049 and 1050:
For more information about alternat
- Page 1051 and 1052:
Anonymous not listed in database AC
- Page 1053 and 1054:
10. (Optional) Enforce a consistent
- Page 1055 and 1056:
To view ACL entries by access level
- Page 1057 and 1058:
For more information, see the chapt
- Page 1059 and 1060:
Roles list box on the Basics panel
- Page 1061 and 1062:
Setting up the Administration Proce
- Page 1063 and 1064:
Using the ACL log You can display a
- Page 1065 and 1066:
The set of URLs that gets restricte
- Page 1067 and 1068:
Chapter 43. Protecting User Worksta
- Page 1069 and 1070:
Access option If enabled, allows fo
- Page 1071 and 1072:
with default settings that are code
- Page 1073 and 1074:
For more information, see the topic
- Page 1075 and 1076:
as an entry in the Admin ECL. You t
- Page 1077 and 1078:
Chapter 44. Setting Up Name-and-Pas
- Page 1079 and 1080:
v If you set up SSL on the server a
- Page 1081 and 1082:
owswer, and the browser sends the c
- Page 1083 and 1084:
1. In the Domino Directory, create
- Page 1085 and 1086:
6. Enter the name of the custom log
- Page 1087 and 1088:
Example Description alan_jones@acme
- Page 1089 and 1090:
then the custom password policy wil
- Page 1091 and 1092:
Be sure that your client location d
- Page 1093 and 1094:
c. Enter the password (specified wh
- Page 1095 and 1096:
4. In the Web SSO Configuration fie
- Page 1097 and 1098:
v Any appropriate LDAP attribute, a
- Page 1099 and 1100:
Validation and authentication for I
- Page 1101 and 1102:
Chapter 45. Encryption and Electron
- Page 1103 and 1104:
shouldn’t create only North Ameri
- Page 1105 and 1106:
v The user selects ″MIME format
- Page 1107 and 1108:
4. Notes or the mail application co
- Page 1109 and 1110:
Chapter 46. Setting Up a Domino Ser
- Page 1111 and 1112:
3. Add certifiers to the CA process
- Page 1113 and 1114:
3. (Optional) In the Administrators
- Page 1115 and 1116:
Option Security level Password requ
- Page 1117 and 1118:
Key usage extension Description Dat
- Page 1119 and 1120:
Field Action Extended key usages Ch
- Page 1121 and 1122:
v Open the Administrator’s mail f
- Page 1123 and 1124:
8. The time period in which the Adm
- Page 1125 and 1126:
5. Click Save and Close. CAUTION: I
- Page 1127 and 1128:
Chapter 47. Setting Up SSL on a Dom
- Page 1129 and 1130:
Every server certificate includes a
- Page 1131 and 1132:
From a Domino CA using a Web browse
- Page 1133 and 1134:
For more information, see the topic
- Page 1135 and 1136:
6. Do one of the following: v If yo
- Page 1137 and 1138:
Field Enter Client certificate Choo
- Page 1139 and 1140:
Changing the password for the serve
- Page 1141 and 1142:
v In an Internet Site document. If
- Page 1143 and 1144:
Chapter 48. Setting Up Clients for
- Page 1145 and 1146:
To obtain a trusted root certificat
- Page 1147 and 1148:
5. Check to make sure that the name
- Page 1149 and 1150:
Note: The client cannot use the cer
- Page 1151 and 1152:
For information on creating cross-c
- Page 1153 and 1154:
signatures to the Contact document.
- Page 1155 and 1156:
5. Save the document. Tip: If the c
- Page 1157 and 1158:
Chapter 49. Rolling Out Databases T
- Page 1159 and 1160:
Mandatory tasks Perform these tasks
- Page 1161 and 1162:
You can assign ACL settings (includ
- Page 1163 and 1164:
3. Choose Tools - Database - Sign.
- Page 1165 and 1166:
Chapter 50. Organizing Databases on
- Page 1167 and 1168:
7. Click OK. 8. To verify that the
- Page 1169 and 1170:
Chapter 51. Setting Up and Managing
- Page 1171 and 1172:
Indexing option Description Index a
- Page 1173 and 1174:
3. Choose File - Database - Access
- Page 1175 and 1176:
Chapter 52. Setting Up Database Lib
- Page 1177 and 1178:
5. Choose Edit - Delete. Database c
- Page 1179 and 1180:
Chapter 53. Monitoring the Domino S
- Page 1181 and 1182:
Monitoring events on the Domino sys
- Page 1183 and 1184:
Field Action Trigger the event when
- Page 1185 and 1186:
5. Click the Probe tab, and complet
- Page 1187 and 1188:
1. Make sure that the ISpy task is
- Page 1189 and 1190:
Event handlers An event handler def
- Page 1191 and 1192:
Passing event parameters using the
- Page 1193 and 1194:
Creating an event handler When you
- Page 1195 and 1196:
v By Type 4. Double-click the Event
- Page 1197 and 1198:
6. Do one to restart the Domino Adm
- Page 1199 and 1200:
Field Action Collection alarm inter
- Page 1201 and 1202:
v Fixed -- Statistic values that do
- Page 1203 and 1204:
The information in these reports pr
- Page 1205 and 1206:
Exporting statistics to a spreadshe
- Page 1207 and 1208:
To change the color of a statistic:
- Page 1209 and 1210:
Chapter 54. Using the Domino SNMP a
- Page 1211 and 1212:
The text message of the Domino even
- Page 1213 and 1214:
For additional information, refer t
- Page 1215 and 1216:
There are several different ways to
- Page 1217 and 1218:
Note: The Domino SNMP Agent is set
- Page 1219 and 1220:
If you are not using the NET-SNMP M
- Page 1221 and 1222:
The pw.src should resemble the foll
- Page 1223 and 1224:
Manually starting and stopping the
- Page 1225 and 1226:
Creating and Configuring your own N
- Page 1227 and 1228:
ovstart Removing traps To remove th
- Page 1229 and 1230:
Chapter 55. Using Server Health Mon
- Page 1231 and 1232:
Statistic Rating Explanation Health
- Page 1233 and 1234:
Selecting server components to incl
- Page 1235 and 1236:
To display a current health report:
- Page 1237 and 1238:
However, the Server Health Monitor
- Page 1239 and 1240:
Chapter 56. Monitoring Domino Domai
- Page 1241 and 1242:
v Replication probes v Security pro
- Page 1243 and 1244:
6. Complete these fields, and then
- Page 1245 and 1246:
Field Action Severity Choose the se
- Page 1247 and 1248:
Directory Probe name Description Di
- Page 1249 and 1250:
Field Action Should this probe run
- Page 1251 and 1252:
Field Action Timeout for open attem
- Page 1253 and 1254:
the probe runs on Server A (origina
- Page 1255 and 1256:
Field Action Should this probe run
- Page 1257 and 1258:
Field Action Which servers should r
- Page 1259 and 1260:
Server probes There is one server p
- Page 1261 and 1262:
Field Action Probe Description Type
- Page 1263 and 1264:
Deleting a DDM Probe document When
- Page 1265 and 1266:
Example of a DDM server collection
- Page 1267 and 1268:
Adding subordinate servers to the D
- Page 1269 and 1270:
The first time that an event is log
- Page 1271 and 1272:
Changing the state of an event in D
- Page 1273 and 1274:
administrator names that displays i
- Page 1275 and 1276:
Chapter 57. Transaction Logging and
- Page 1277 and 1278:
If the database is not yet complete
- Page 1279 and 1280:
Field Action Logging style** Choose
- Page 1281 and 1282:
Fault recovery You can set up fault
- Page 1283 and 1284:
7. Click Create. Collecting diagnos
- Page 1285 and 1286:
Field Action Maximum size of NSD ou
- Page 1287 and 1288:
NOTES.INI setting MAX_NSDINFO_FILES
- Page 1289 and 1290:
Chapter 58. Using Log Files This ch
- Page 1291 and 1292:
View Contains information about Rep
- Page 1293 and 1294:
Analyzing Domino log files using an
- Page 1295 and 1296:
When you log to a text file, the fo
- Page 1297 and 1298:
Field Enter Referer log The prefix
- Page 1299 and 1300:
Chapter 59. Setting Up Activity Log
- Page 1301 and 1302:
as a result of the request, the amo
- Page 1303 and 1304:
v Open records, which log when a se
- Page 1305 and 1306:
If a session ends before authentica
- Page 1307 and 1308:
1. From the Domino Administrator, o
- Page 1309 and 1310:
Chapter 60. Maintaining Databases T
- Page 1311 and 1312:
v Quota v Warning v Created v Last
- Page 1313 and 1314:
For more information on the Databas
- Page 1315 and 1316:
For information on designing forms
- Page 1317 and 1318:
Tip: To track usage over a period o
- Page 1319 and 1320:
Indexer tasks: Update and Updall Th
- Page 1321 and 1322:
Updall: Updall is similar to Update
- Page 1323 and 1324:
Updall - Rebuild options: Option in
- Page 1325 and 1326:
Shortcut Description When to use SH
- Page 1327 and 1328:
Note: When views are being rebuilt
- Page 1329 and 1330:
v Run Fixup using a console command
- Page 1331 and 1332:
4. Enter the following command in o
- Page 1333 and 1334:
5. From the Domino Administrator, i
- Page 1335 and 1336:
6. In the Tools pane on the right,
- Page 1337 and 1338:
Running a database analysis 1. From
- Page 1339 and 1340:
Chapter 61. Maintaining Domino Serv
- Page 1341 and 1342:
For more information on policy sett
- Page 1343 and 1344:
Each item is represented by a docum
- Page 1345 and 1346:
Database comparison Explanation Rep
- Page 1347 and 1348:
v Skip -- if you are recertifying m
- Page 1349 and 1350:
Chapter 62. Using Activity Trends T
- Page 1351 and 1352:
Field Action Days of the week to co
- Page 1353 and 1354:
1. From the Domino Administrator, c
- Page 1355 and 1356:
3. Select the statistic you want to
- Page 1357 and 1358:
1. From the Domino Administrator, c
- Page 1359 and 1360:
5. Complete these fields to specify
- Page 1361 and 1362:
server, 10 databases may account fo
- Page 1363 and 1364:
v Change the layout of the Activity
- Page 1365 and 1366:
v Light -- The light bin is the top
- Page 1367 and 1368:
Field Action Type Choose one: Role
- Page 1369 and 1370:
5. The field ″Submit to″ displa
- Page 1371 and 1372:
Option Action reset Resets the inte
- Page 1373 and 1374:
The workflow for processing a plan
- Page 1375 and 1376:
To view database moves in the resou
- Page 1377 and 1378:
Field Action Category (Optional) Se
- Page 1379 and 1380:
5. On the Basics tab, complete thes
- Page 1381 and 1382:
Chapter 63. Improving Server Perfor
- Page 1383 and 1384:
v Use multiple I/O controllers to d
- Page 1385 and 1386:
Default is 30 minutes. A longer int
- Page 1387 and 1388:
For more information on database pe
- Page 1389 and 1390:
Improving Windows 2000 server perfo
- Page 1391 and 1392:
Chapter 64. Improving Database Perf
- Page 1393 and 1394:
If you select or deselect the ″Do
- Page 1395 and 1396:
v The database contains many docume
- Page 1397 and 1398:
Database cache size By default, the
- Page 1399 and 1400:
v Use replication settings to limit
- Page 1401 and 1402:
If you have specified a value for t
- Page 1403 and 1404:
Compact - Style Option Command-line
- Page 1405 and 1406:
Running Compact using a console com
- Page 1407 and 1408:
Deleting inactive documents Regular
- Page 1409 and 1410:
6. (Optional) To archive deleted do
- Page 1411 and 1412:
Chapter 65. Using Server.Load This
- Page 1413 and 1414:
Statistic Description Database.NIFP
- Page 1415 and 1416:
Messaging Statistic Description Tot
- Page 1417 and 1418:
To see the actual code of each scri
- Page 1419 and 1420:
2. Set the Thread Creation Interval
- Page 1421 and 1422:
3. Choose File - Save Settings. 4.
- Page 1423 and 1424:
Running the test: 1. Start Server.L
- Page 1425 and 1426:
7. In the ″Build Recipient List u
- Page 1427 and 1428:
Variable Action IMAPHost Enter the
- Page 1429 and 1430:
v System under test (SUT) Test Init
- Page 1431 and 1432:
3. At the end of the test, Issue a
- Page 1433 and 1434:
Setting Use this value Number of Ma
- Page 1435 and 1436:
Access rights: The user that you de
- Page 1437 and 1438:
Initial or subsequent disk requirem
- Page 1439 and 1440:
v Log_MailRouting. Set to 20 for mi
- Page 1441 and 1442:
5. Click the Script Variables tab,
- Page 1443 and 1444:
11. Click Start Test. Idle workload
- Page 1445 and 1446:
To read the code in the test script
- Page 1447 and 1448:
Initial or subsequent disk requirem
- Page 1449 and 1450:
script loop count = 1 Note: This se
- Page 1451 and 1452:
Chapter 66. Troubleshooting Even wi
- Page 1453 and 1454:
Required information Your system Op
- Page 1455 and 1456:
Insufficient memory - Admin’s req
- Page 1457 and 1458:
The following two statistics record
- Page 1459 and 1460:
1. If the agent runs to completion
- Page 1461 and 1462:
The Cluster Database Directory incl
- Page 1463 and 1464:
Server backup is occurring during w
- Page 1465 and 1466:
6. Paste or enter the Note ID or UN
- Page 1467 and 1468:
v db2 => Import from F:\TEST\NSFOBJ
- Page 1469 and 1470:
Resolving the problem: Complete the
- Page 1471 and 1472:
table "DWA1.NSFOBJNAM" from having
- Page 1473 and 1474:
For instructions on creating the se
- Page 1475 and 1476:
Directories -- Troubleshooting Thes
- Page 1477 and 1478:
″Directory assistance could not a
- Page 1479 and 1480:
2. If you are trusting all the aggr
- Page 1481 and 1482:
must also allow anonymous read acce
- Page 1483 and 1484:
The Target box doesn’t show docum
- Page 1485 and 1486:
4. Complete these fields, and then
- Page 1487 and 1488:
1. Check the replication history of
- Page 1489 and 1490:
6. Check for problems with modem co
- Page 1491 and 1492:
18. Refresh the view so that all of
- Page 1493 and 1494:
3. Make sure the communication port
- Page 1495 and 1496:
(Platform.System.PctCombinedCpuUtil
- Page 1497 and 1498:
Even if you can use the ping utilit
- Page 1499 and 1500:
For more information about setting
- Page 1501 and 1502:
v Edit the Port_MaxSessions setting
- Page 1503 and 1504:
For Notes and Domino to work proper
- Page 1505 and 1506:
After you finish checking name reso
- Page 1507 and 1508:
Note: When setting the NOTES.INI va
- Page 1509 and 1510:
Replication history: The replicatio
- Page 1511 and 1512:
3. Check the log file for a ″Repl
- Page 1513 and 1514:
Somebody modified the access contro
- Page 1515 and 1516:
CA process takes a long time to mak
- Page 1517 and 1518:
2. Make sure the Server document is
- Page 1519 and 1520:
v System level patches v Server har
- Page 1521 and 1522:
Code Meaning Cause 0 Divide error T
- Page 1523 and 1524:
v Debug_Smart_Upgrade -- Use this v
- Page 1525 and 1526:
Users are prompted multiple times f
- Page 1527 and 1528:
Domino server name IP Host name IP
- Page 1529 and 1530:
procedures, back up files directly
- Page 1531 and 1532:
Appendix A Server Commands You can
- Page 1533 and 1534:
Description: Sends a message to spe
- Page 1535 and 1536:
Description: Displays a list of ser
- Page 1537 and 1538:
To check the status of the Replicat
- Page 1539 and 1540:
To optimize resources Domino only r
- Page 1541 and 1542:
Route Marketing\Acme -- Sends mail
- Page 1543 and 1544:
v To clear a password, select ″Cl
- Page 1545 and 1546:
Description: Displays the current v
- Page 1547 and 1548:
Description: The Show Memory server
- Page 1549 and 1550:
Description: Shows single copy obje
- Page 1551 and 1552:
server console to display statistic
- Page 1553 and 1554:
Description: Displays a list of all
- Page 1555 and 1556:
Start Port Syntax: Start Port portn
- Page 1557 and 1558:
v Agent Manager v Certificate Autho
- Page 1559 and 1560:
Command Result Tell Amgr Schedule S
- Page 1561 and 1562:
Command Result Tell Clrepl Quit Sto
- Page 1563 and 1564:
Command Result Tell Router Compact
- Page 1565 and 1566:
Command Result Tell HTTP Refresh Re
- Page 1567 and 1568:
Arguments Set -- Sets DB2 access fo
- Page 1569 and 1570:
GROUP GROUP SIZE STATUS PATH NSF SI
- Page 1571 and 1572:
The Domino server’s DB2 purge tas
- Page 1573 and 1574:
Controller command Description Disa
- Page 1575 and 1576:
Adding commands to the Commands men
- Page 1577 and 1578:
Switch Result -f Lets you enter the
- Page 1579 and 1580:
Appendix B Server Tasks This chapte
- Page 1581 and 1582:
Task Command to run task Descriptio
- Page 1583 and 1584:
Appendix C NOTES.INI Settings Appen
- Page 1585 and 1586:
asterisk represents everyone listed
- Page 1587 and 1588:
Description: By default, a mail-tri
- Page 1589 and 1590:
UI equivalent: None, although you c
- Page 1591 and 1592:
UI equivalent: None, although you c
- Page 1593 and 1594:
Applies to: Servers Default: None,
- Page 1595 and 1596:
This setting can be changed at any
- Page 1597 and 1598:
Applies to: Server Default: None UI
- Page 1599 and 1600:
DB2UDFPath Syntax: DB2Path=pathname
- Page 1601 and 1602:
Applies to: Servers Default: None U
- Page 1603 and 1604:
sets the lifetime of indexes to 60
- Page 1605 and 1606:
Default: The default value is 10 mi
- Page 1607 and 1608:
0 - Show Errors & Warnings only 1 -
- Page 1609 and 1610:
UI equivalent: None DisabledPorts S
- Page 1611 and 1612:
Description: If the Domino Web serv
- Page 1613 and 1614:
Description: If this variable is se
- Page 1615 and 1616:
is observed in the United States.)
- Page 1617 and 1618:
1 - Always empty the Trash folder b
- Page 1619 and 1620:
FaultRecoveryFromINI Syntax: FaultR
- Page 1621 and 1622:
Applies to: Workstations Default: N
- Page 1623 and 1624:
Description: (Domino 7 only) Use th
- Page 1625 and 1626:
Description: Prior to Domino 7, if
- Page 1627 and 1628:
IMAPDisableMsgCache Syntax: IMAPDis
- Page 1629 and 1630:
Description: Use this variable when
- Page 1631 and 1632:
iNotes_WA_DisableBothFormats Syntax
- Page 1633 and 1634:
UI equivalent: none iNotes_WA_Logou
- Page 1635 and 1636:
iNotes_WA_NamePickerSearchAccentIns
- Page 1637 and 1638:
FORMS7.nsf. You can use the style r
- Page 1639 and 1640:
messages sent S/MIME signed or encr
- Page 1641 and 1642:
Description: Specifies the maximum-
- Page 1643 and 1644:
KeyFileName Syntax: KeyFileName=pat
- Page 1645 and 1646:
for the GroupType attribute can be
- Page 1647 and 1648:
UI equivalent: None LDAPName_Update
- Page 1649 and 1650:
T:64 E:1: S:64:22 A:4:1 L:N:I:N Aut
- Page 1651 and 1652:
Log_Replication Syntax: Log_Replica
- Page 1653 and 1654:
1 - Log messages when views are reb
- Page 1655 and 1656:
Default: In the absence of the sett
- Page 1657 and 1658:
Mail_Skip_NoKey_Dialog Syntax: Mail
- Page 1659 and 1660:
Applies to: Servers Default: 10 UI
- Page 1661 and 1662:
UI equivalent: None MTMaxResponses
- Page 1663 and 1664:
NetWareSocket Syntax: NetWareSocket
- Page 1665 and 1666:
NoMailMenu Syntax: NoMailMenu=value
- Page 1667 and 1668:
Description: This variable reflects
- Page 1669 and 1670:
5 - Full trace information plus dri
- Page 1671 and 1672:
Default: None UI equivalent: None P
- Page 1673 and 1674:
ProgramMode Syntax: ProgramMode=val
- Page 1675 and 1676:
Description: Use this setting to en
- Page 1677 and 1678:
Default: 7 UI equivalent: None Sche
- Page 1679 and 1680:
Schema_Daemon_Resynctime Syntax: Sc
- Page 1681 and 1682:
Default: 0 UI equivalent: None, alt
- Page 1683 and 1684:
ServerNoReplRequests Syntax: Server
- Page 1685 and 1686:
Server_Show_Performance Syntax: Ser
- Page 1687 and 1688:
Description: Identifies the setup d
- Page 1689 and 1690:
RC2_56 RC2_64 RC2_80 RC2_128 RC5_5
- Page 1691 and 1692:
Default: In the absence of this set
- Page 1693 and 1694:
0 - Entries in the Allow field of t
- Page 1695 and 1696:
2 - Require the RFC822 From header
- Page 1697 and 1698:
TCP_EnableIPV6 Syntax: TCP_EnableIP
- Page 1699 and 1700:
Applies to: Servers and workstation
- Page 1701 and 1702:
TransLog_UseAll Syntax: TransLog_Us
- Page 1703 and 1704:
Updaters Syntax: Updaters=number of
- Page 1705 and 1706:
Parameter Enter value4 Not currentl
- Page 1707 and 1708:
Window_Title Syntax: Window_Title=t
- Page 1709 and 1710:
Appendix D System and Application T
- Page 1711 and 1712:
Template title and file name Templa
- Page 1713 and 1714:
Template title and file name Templa
- Page 1715 and 1716:
Appendix E Customizing the Domino D
- Page 1717 and 1718:
The only reason to use the Domino D
- Page 1719 and 1720:
v Create a new LDAP structural obje
- Page 1721 and 1722:
Note: You can use a backslash (\) i
- Page 1723 and 1724:
For more information, see the topic
- Page 1725 and 1726:
4. Open the $xxxInheritableSchema s
- Page 1727 and 1728:
To add the auxiliary object class t
- Page 1729 and 1730:
Upgrading to a new Domino Directory
- Page 1731 and 1732:
Appendix F Administration Process R
- Page 1733 and 1734:
Recertify users Register hosted org
- Page 1735 and 1736:
Create replica Create a Roaming Use
- Page 1737 and 1738:
Update domain catalog configuration
- Page 1739 and 1740:
Triggered by: A user initiating an
- Page 1741 and 1742:
Result: A new replica of the databa
- Page 1743 and 1744:
Carried out on: Server on which the
- Page 1745 and 1746:
Carried out: According to the ″In
- Page 1747 and 1748:
Result: The Administration Process
- Page 1749 and 1750:
Carried out on: The deleted person
- Page 1751 and 1752:
Carried out on: The administration
- Page 1753 and 1754:
Request Replica Deletion: This requ
- Page 1755 and 1756:
Result: Each server in the domain d
- Page 1757 and 1758:
For more information on this reques
- Page 1759 and 1760:
Result: Creates a replica copy of t
- Page 1761 and 1762:
Result: The old mail file is delete
- Page 1763 and 1764:
Carried out on: The destination ser
- Page 1765 and 1766:
v Source database is full-text inde
- Page 1767 and 1768:
moving roaming files are listed her
- Page 1769 and 1770:
Carried out: According to the ″In
- Page 1771 and 1772:
Carried out: According to the ″In
- Page 1773 and 1774:
Carried out on: The administration
- Page 1775 and 1776:
For information on renaming a Web u
- Page 1777 and 1778:
Carried out on: Each server in the
- Page 1779 and 1780:
Carried out: When you approve or re
- Page 1781 and 1782:
Carried out on: Each server in the
- Page 1783 and 1784:
Result: Updates the password and us
- Page 1785 and 1786:
Result: Updates the Certifier docum
- Page 1787 and 1788:
Carried out: Immediately Result: Up
- Page 1789 and 1790:
Carried out on: On the administrati
- Page 1791 and 1792:
Web set Soft Deletion Expire Time T
- Page 1793 and 1794:
Carried out: According to the ″De
- Page 1795 and 1796:
Result: The Administration Process
- Page 1797 and 1798:
Result: Creates the replica on the
- Page 1799 and 1800:
Result: The server name is removed
- Page 1801 and 1802:
Delete in Reader / Author fields: T
- Page 1803 and 1804:
Result: Updates the person’s name
- Page 1805 and 1806:
Rename server in Domino Directory:
- Page 1807 and 1808:
Check access for non-cluster move r
- Page 1809 and 1810:
Appendix G Accessibility and Keyboa
- Page 1811 and 1812:
Keyboard shortcuts for databases Yo
- Page 1813 and 1814:
Press To do this RIGHT ARROW Move t
- Page 1815 and 1816:
Press To do this DELETE Delete sele
- Page 1817 and 1818:
Appendix H Server.Load Command Lang
- Page 1819 and 1820:
Note: You need to add a value for t
- Page 1821 and 1822:
Example 2 Using changeto to create
- Page 1823 and 1824:
Drop command Use in a Server.Load s
- Page 1825 and 1826:
Syntax If [Value] [Command] Where:
- Page 1827 and 1828:
Index command Used in a Server.Load
- Page 1829 and 1830:
NEXT_EXPANDED_SELECTED, NEXT_EXPAND
- Page 1831 and 1832:
Quit command Used in a Server.Load
- Page 1833 and 1834:
Message Body Size Attachment size (
- Page 1835 and 1836:
Syntax Web Mail workload usage of W
- Page 1837 and 1838:
v If nthiteration = 1, the command
- Page 1839 and 1840:
Appendix I Server.Load Scripts This
- Page 1841 and 1842:
To issue remote console commands Th
- Page 1843 and 1844:
**Pause 10 to 20 seconds** Pause 10
- Page 1845 and 1846:
**Reset initial document count by d
- Page 1847 and 1848:
Open **Close the view** close EndCr
- Page 1849 and 1850:
pause 0 - 180000 **Start the part o
- Page 1851 and 1852:
Appendix J Setting Up a Domino 5 Ce
- Page 1853 and 1854:
3. Enter the old password, and then
- Page 1855 and 1856:
3. Click Dump CA Key Ring to Text.
- Page 1857 and 1858:
Appendix K Upgrading Notes Clients
- Page 1859 and 1860:
Notes Client Feature Instant Messag
- Page 1861 and 1862:
Mail Rules: Formula rewrite to impr
- Page 1863 and 1864:
UI Indicator for LotusScript debugg
- Page 1865 and 1866:
options for further delay. If the s
- Page 1867 and 1868:
Note: Lotus Notes Smart Upgrade fir
- Page 1869 and 1870:
In this field Do this Destination v
- Page 1871 and 1872:
Running a silent upgrade using opti
- Page 1873 and 1874:
A user who is not assigned to the L
- Page 1875 and 1876:
Index Special characters $AdminP Vi
- Page 1877 and 1878:
Archiving agents for 1388, 1389 dat
- Page 1879 and 1880:
Compound document format. See Notes
- Page 1881 and 1882:
DDM Probes (continued) scheduling a
- Page 1883 and 1884:
Domains (continued) mail routing 69
- Page 1885 and 1886:
Error messages (continued) OS/2 150
- Page 1887 and 1888:
Host names (continued) specifying i
- Page 1889 and 1890:
Internet passwords (continued) user
- Page 1891 and 1892:
Loopback addresses creating 413 Lot
- Page 1893 and 1894:
Monitoring (continued) performance
- Page 1895 and 1896:
Passthru connections activity loggi
- Page 1897 and 1898:
R6IMAP Initialization workload sett
- Page 1899 and 1900:
Sametime (continued) and scriptable
- Page 1901 and 1902:
Server-based certification authorit
- Page 1903 and 1904:
SMTPGreeting setting described 1671
- Page 1905 and 1906:
Transform files applying 226 for en
- Page 1907 and 1908:
Web sites (continued) authenticatio
- Page 1909 and 1910:
Licensees of this program who wish