Palladium- and Copper-Catalyzed Aryl Halide Amination ...
Palladium- and Copper-Catalyzed Aryl Halide Amination ...
Palladium- and Copper-Catalyzed Aryl Halide Amination ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
REVIEW <strong>Palladium</strong>- <strong>and</strong> <strong>Copper</strong>-<strong>Catalyzed</strong> Heterocycle Synthesis 13<br />
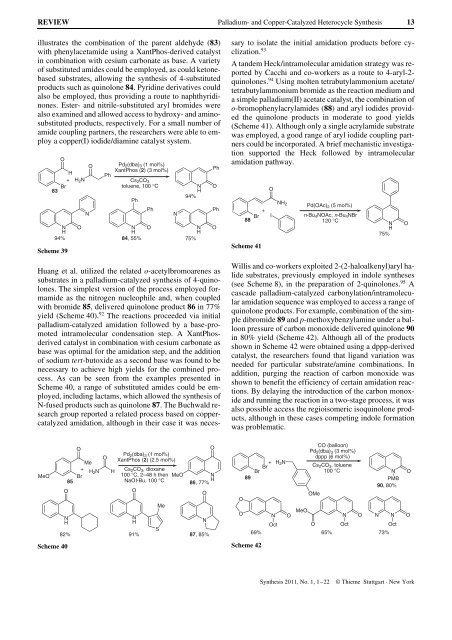
illustrates the combination of the parent aldehyde (83)<br />
with phenylacetamide using a XantPhos-derived catalyst<br />
in combination with cesium carbonate as base. A variety<br />
of substituted amides could be employed, as could ketonebased<br />
substrates, allowing the synthesis of 4-substituted<br />
products such as quinolone 84. Pyridine derivatives could<br />
also be employed, thus providing a route to naphthyridinones.<br />
Ester- <strong>and</strong> nitrile-substituted aryl bromides were<br />
also examined <strong>and</strong> allowed access to hydroxy- <strong>and</strong> aminosubstituted<br />
products, respectively. For a small number of<br />
amide coupling partners, the researchers were able to employ<br />
a copper(I) iodide/diamine catalyst system.<br />
83<br />
Scheme 39<br />
O<br />
O<br />
H<br />
+ H2N<br />
Br<br />
N<br />
H<br />
94%<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ph<br />
Pd 2(dba)3 (1 mol%)<br />
XantPhos (2) (3 mol%)<br />
Cs2CO3<br />
toluene, 100 °C<br />
N<br />
H<br />
84, 55%<br />
N<br />
H<br />
94%<br />
Huang et al. utilized the related o-acetylbromoarenes as<br />
substrates in a palladium-catalyzed synthesis of 4-quinolones.<br />
The simplest version of the process employed formamide<br />
as the nitrogen nucleophile <strong>and</strong>, when coupled<br />
with bromide 85, delivered quinolone product 86 in 77%<br />
yield (Scheme 40). 92 The reactions proceeded via initial<br />
palladium-catalyzed amidation followed by a base-promoted<br />
intramolecular condensation step. A XantPhosderived<br />
catalyst in combination with cesium carbonate as<br />
base was optimal for the amidation step, <strong>and</strong> the addition<br />
of sodium tert-butoxide as a second base was found to be<br />
necessary to achieve high yields for the combined process.<br />
As can be seen from the examples presented in<br />
Scheme 40, a range of substituted amides could be employed,<br />
including lactams, which allowed the synthesis of<br />
N-fused products such as quinolone 87. The Buchwald research<br />
group reported a related process based on coppercatalyzed<br />
amidation, although in their case it was neces-<br />
MeO<br />
N<br />
H<br />
Scheme 40<br />
85<br />
O<br />
Ph<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
Me<br />
Br H O<br />
Pd2(dba) 3 (1 mol%)<br />
XantPhos (2) (2.5 mol%)<br />
+<br />
2N H<br />
Cs2CO3, dioxane<br />
100 °C, 2–48 h then<br />
NaOt-Bu, 100 °C<br />
MeO<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
H<br />
75%<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H<br />
86, 77%<br />
S<br />
82% 91% 87, 85%<br />
Me<br />
O<br />
N<br />
sary to isolate the initial amidation products before cyclization.<br />
93<br />
A t<strong>and</strong>em Heck/intramolecular amidation strategy was reported<br />
by Cacchi <strong>and</strong> co-workers as a route to 4-aryl-2quinolones.<br />
94 Using molten tetrabutylammonium acetate/<br />
tetrabutylammonium bromide as the reaction medium <strong>and</strong><br />
a simple palladium(II) acetate catalyst, the combination of<br />
o-bromophenylacrylamides (88) <strong>and</strong> aryl iodides provided<br />
the quinolone products in moderate to good yields<br />
(Scheme 41). Although only a single acrylamide substrate<br />
was employed, a good range of aryl iodide coupling partners<br />
could be incorporated. A brief mechanistic investigation<br />
supported the Heck followed by intramolecular<br />
amidation pathway.<br />
88<br />
+<br />
Br<br />
Scheme 41<br />
Willis <strong>and</strong> co-workers exploited 2-(2-haloalkenyl)aryl halide<br />
substrates, previously employed in indole syntheses<br />
(see Scheme 8), in the preparation of 2-quinolones. 95 A<br />
cascade palladium-catalyzed carbonylation/intramolecular<br />
amidation sequence was employed to access a range of<br />
quinolone products. For example, combination of the simple<br />
dibromide 89 <strong>and</strong> p-methoxybenzylamine under a balloon<br />
pressure of carbon monoxide delivered quinolone 90<br />
in 80% yield (Scheme 42). Although all of the products<br />
shown in Scheme 42 were obtained using a dppp-derived<br />
catalyst, the researchers found that lig<strong>and</strong> variation was<br />
needed for particular substrate/amine combinations. In<br />
addition, purging the reaction of carbon monoxide was<br />
shown to benefit the efficiency of certain amidation reactions.<br />
By delaying the introduction of the carbon monoxide<br />
<strong>and</strong> running the reaction in a two-stage process, it was<br />
also possible access the regioisomeric isoquinolone products,<br />
although in these cases competing indole formation<br />
was problematic.<br />
O<br />
Scheme 42<br />
O<br />
I<br />
NH 2<br />
+<br />
H2N<br />
Br<br />
Br<br />
89<br />
Pd(OAc)2 (5 mol%)<br />
n-Bu4NOAc, n-Bu4NBr<br />
120 °C<br />
CO (balloon)<br />
Pd2(dba)3 (3 mol%)<br />
dppp (6 mol%)<br />
Cs2CO3, toluene<br />
100 °C<br />
OMe<br />
N<br />
H<br />
75%<br />
Synthesis 2011, No. 1, 1–22 © Thieme Stuttgart · New York<br />
O<br />
N O<br />
PMB<br />
90, 80%<br />
O N O<br />
MeO<br />
N O N N O<br />
Oct<br />
O Oct<br />
Oct<br />
69% 65% 73%