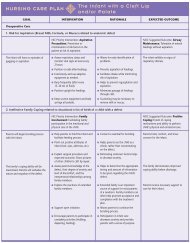
19.1 Payoff Tables and Decision Trees
19.1 Payoff Tables and Decision Trees
19.1 Payoff Tables and Decision Trees
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
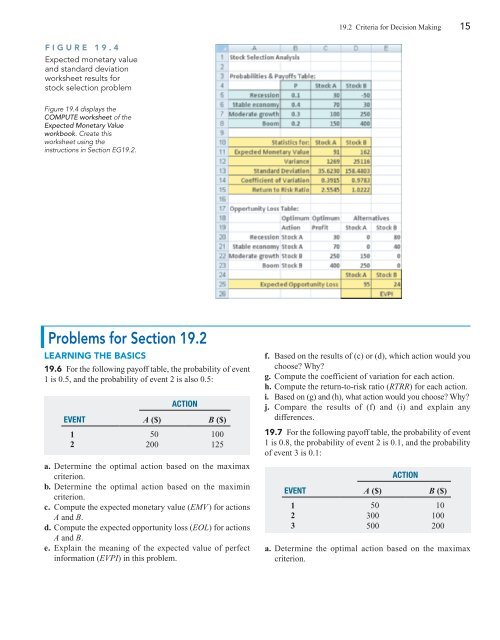
FIGURE 19.4<br />
Expected monetary value<br />
<strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation<br />
worksheet results for<br />
stock selection problem<br />
Figure 19.4 displays the<br />
COMPUTE worksheet of the<br />
Expected Monetary Value<br />
workbook. Create this<br />
worksheet using the<br />
instructions in Section EG19.2.<br />
Problems for Section 19.2<br />
LEARNING THE BASICS<br />
19.6 For the following payoff table, the probability of event<br />
1 is 0.5, <strong>and</strong> the probability of event 2 is also 0.5:<br />
ACTION<br />
EVENT A ($) B ($)<br />
1 50 100<br />
2 200 125<br />
a. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax<br />
criterion.<br />
b. Determine the optimal action based on the maximin<br />
criterion.<br />
c. Compute the expected monetary value (EMV) for actions<br />
A <strong>and</strong> B.<br />
d. Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for actions<br />
A <strong>and</strong> B.<br />
e. Explain the meaning of the expected value of perfect<br />
information (EVPI) in this problem.<br />
19.2 Criteria for <strong>Decision</strong> Making 15<br />
f. Based on the results of (c) or (d), which action would you<br />
choose? Why?<br />
g. Compute the coefficient of variation for each action.<br />
h. Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for each action.<br />
i. Based on (g) <strong>and</strong> (h), what action would you choose? Why?<br />
j. Compare the results of (f) <strong>and</strong> (i) <strong>and</strong> explain any<br />
differences.<br />
19.7 For the following payoff table, the probability of event<br />
1 is 0.8, the probability of event 2 is 0.1, <strong>and</strong> the probability<br />
of event 3 is 0.1:<br />
ACTION<br />
EVENT A ($) B ($)<br />
1 50 10<br />
2 300 100<br />
3 500 200<br />
a. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax<br />
criterion.