New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.2. MACHINE LEARNING 27<br />
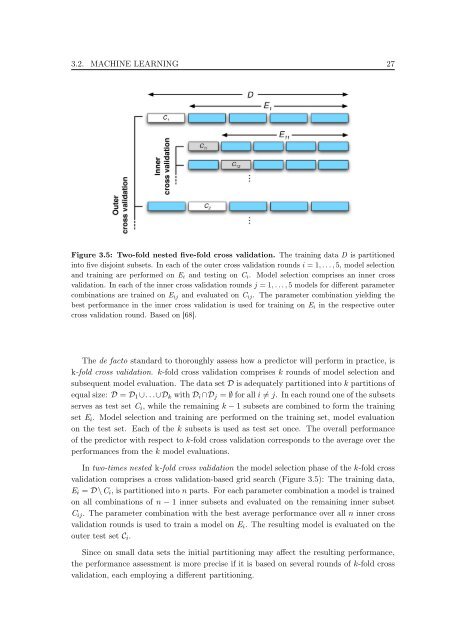
Figure 3.5: Two-fold nested five-fold cross validation. The tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g data D is partitioned<br />
<strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> five disjo<strong>in</strong>t subsets. In each <strong>of</strong> the outer cross validation rounds i = 1, . . . , 5, model selection<br />
and tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g are performed on Ei and test<strong>in</strong>g on Ci. Model selection comprises an <strong>in</strong>ner cross<br />
validation. In each <strong>of</strong> the <strong>in</strong>ner cross validation rounds j = 1, . . . , 5 models for different parameter<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>ations are tra<strong>in</strong>ed on Eij and evaluated on Cij. The parameter comb<strong>in</strong>ation yield<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
best performance <strong>in</strong> the <strong>in</strong>ner cross validation is used for tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g on Ei <strong>in</strong> the respective outer<br />
cross validation round. <strong>Based</strong> on [68].<br />
The de fac<strong>to</strong> standard <strong>to</strong> thoroughly assess how a predic<strong>to</strong>r will perform <strong>in</strong> practice, is<br />
k-fold cross validation. k-fold cross validation comprises k rounds <strong>of</strong> model selection and<br />
subsequent model evaluation. The data set D is adequately partitioned <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> k partitions <strong>of</strong><br />
equal size: D = D1∪. . .∪Dk with Di∩Dj = ∅ for all i = j. In each round one <strong>of</strong> the subsets<br />
serves as test set Ci, while the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g k − 1 subsets are comb<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>to</strong> form the tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
set Ei. Model selection and tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g are performed on the tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g set, model evaluation<br />
on the test set. Each <strong>of</strong> the k subsets is used as test set once. The overall performance<br />
<strong>of</strong> the predic<strong>to</strong>r with respect <strong>to</strong> k-fold cross validation corresponds <strong>to</strong> the average over the<br />
performances from the k model evaluations.<br />
In two-times nested k-fold cross validation the model selection phase <strong>of</strong> the k-fold cross<br />
validation comprises a cross validation-based grid search (Figure 3.5): The tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g data,<br />
Ei = D\Ci, is partitioned <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> n parts. For each parameter comb<strong>in</strong>ation a model is tra<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
on all comb<strong>in</strong>ations <strong>of</strong> n − 1 <strong>in</strong>ner subsets and evaluated on the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>ner subset<br />
Cij. The parameter comb<strong>in</strong>ation with the best average performance over all n <strong>in</strong>ner cross<br />
validation rounds is used <strong>to</strong> tra<strong>in</strong> a model on Ei. The result<strong>in</strong>g model is evaluated on the<br />
outer test set Ci.<br />
S<strong>in</strong>ce on small data sets the <strong>in</strong>itial partition<strong>in</strong>g may affect the result<strong>in</strong>g performance,<br />
the performance assessment is more precise if it is based on several rounds <strong>of</strong> k-fold cross<br />
validation, each employ<strong>in</strong>g a different partition<strong>in</strong>g.