New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 6<br />
Epi<strong>to</strong>pe Assembly<br />
The mathematical framework presented <strong>in</strong> the previous chapter yields an optimal set <strong>of</strong><br />
epi<strong>to</strong>pes with respect <strong>to</strong> a given def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>of</strong> a good vacc<strong>in</strong>e. Str<strong>in</strong>g-<strong>of</strong>-beads type vacc<strong>in</strong>es<br />
require these epi<strong>to</strong>pes <strong>to</strong> be comb<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> one long polypeptide. In the follow<strong>in</strong>g, we will<br />
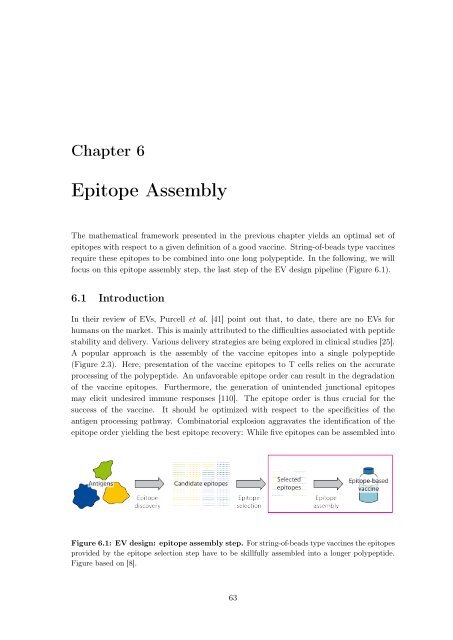
focus on this epi<strong>to</strong>pe assembly step, the last step <strong>of</strong> the EV design pipel<strong>in</strong>e (Figure 6.1).<br />
6.1 Introduction<br />
In their review <strong>of</strong> EVs, Purcell et al. [41] po<strong>in</strong>t out that, <strong>to</strong> date, there are no EVs for<br />
humans on the market. This is ma<strong>in</strong>ly attributed <strong>to</strong> the difficulties associated with peptide<br />
stability and delivery. Various delivery strategies are be<strong>in</strong>g explored <strong>in</strong> cl<strong>in</strong>ical studies [25].<br />
A popular approach is the assembly <strong>of</strong> the vacc<strong>in</strong>e epi<strong>to</strong>pes <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle polypeptide<br />
(Figure 2.3). Here, presentation <strong>of</strong> the vacc<strong>in</strong>e epi<strong>to</strong>pes <strong>to</strong> T cells relies on the accurate<br />
process<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the polypeptide. An unfavorable epi<strong>to</strong>pe order can result <strong>in</strong> the degradation<br />
<strong>of</strong> the vacc<strong>in</strong>e epi<strong>to</strong>pes. Furthermore, the generation <strong>of</strong> un<strong>in</strong>tended junctional epi<strong>to</strong>pes<br />
may elicit undesired immune responses [110]. The epi<strong>to</strong>pe order is thus crucial for the<br />
success <strong>of</strong> the vacc<strong>in</strong>e. It should be optimized with respect <strong>to</strong> the specificities <strong>of</strong> the<br />
antigen process<strong>in</strong>g pathway. Comb<strong>in</strong>a<strong>to</strong>rial explosion aggravates the identification <strong>of</strong> the<br />
epi<strong>to</strong>pe order yield<strong>in</strong>g the best epi<strong>to</strong>pe recovery: While five epi<strong>to</strong>pes can be assembled <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong><br />
Figure 6.1: EV design: epi<strong>to</strong>pe assembly step. For str<strong>in</strong>g-<strong>of</strong>-beads type vacc<strong>in</strong>es the epi<strong>to</strong>pes<br />
provided by the epi<strong>to</strong>pe selection step have <strong>to</strong> be skillfully assembled <strong>in</strong><strong>to</strong> a longer polypeptide.<br />
Figure based on [8].<br />
63