New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
New Approaches to in silico Design of Epitope-Based Vaccines
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
48 CHAPTER 4. EPITOPE DISCOVERY<br />
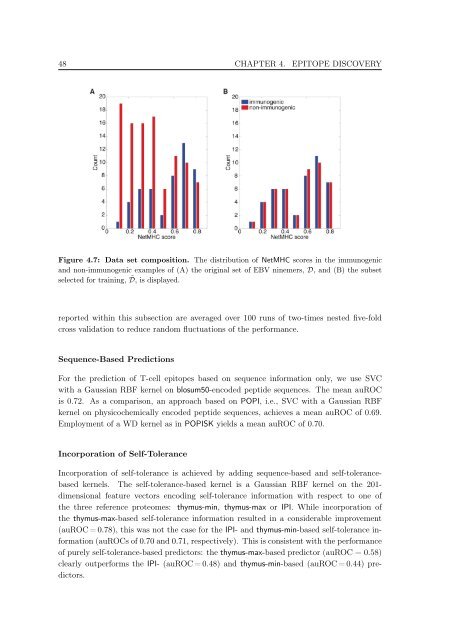
Figure 4.7: Data set composition. The distribution <strong>of</strong> NetMHC scores <strong>in</strong> the immunogenic<br />
and non-immunogenic examples <strong>of</strong> (A) the orig<strong>in</strong>al set <strong>of</strong> EBV n<strong>in</strong>emers, D, and (B) the subset<br />
selected for tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g, ˜ D, is displayed.<br />
reported with<strong>in</strong> this subsection are averaged over 100 runs <strong>of</strong> two-times nested five-fold<br />
cross validation <strong>to</strong> reduce random fluctuations <strong>of</strong> the performance.<br />
Sequence-<strong>Based</strong> Predictions<br />
For the prediction <strong>of</strong> T-cell epi<strong>to</strong>pes based on sequence <strong>in</strong>formation only, we use SVC<br />
with a Gaussian RBF kernel on blosum50-encoded peptide sequences. The mean auROC<br />
is 0.72. As a comparison, an approach based on POPI, i.e., SVC with a Gaussian RBF<br />
kernel on physicochemically encoded peptide sequences, achieves a mean auROC <strong>of</strong> 0.69.<br />
Employment <strong>of</strong> a WD kernel as <strong>in</strong> POPISK yields a mean auROC <strong>of</strong> 0.70.<br />
Incorporation <strong>of</strong> Self-Tolerance<br />
Incorporation <strong>of</strong> self-<strong>to</strong>lerance is achieved by add<strong>in</strong>g sequence-based and self-<strong>to</strong>lerancebased<br />
kernels. The self-<strong>to</strong>lerance-based kernel is a Gaussian RBF kernel on the 201dimensional<br />
feature vec<strong>to</strong>rs encod<strong>in</strong>g self-<strong>to</strong>lerance <strong>in</strong>formation with respect <strong>to</strong> one <strong>of</strong><br />
the three reference proteomes: thymus-m<strong>in</strong>, thymus-max or IPI. While <strong>in</strong>corporation <strong>of</strong><br />
the thymus-max-based self-<strong>to</strong>lerance <strong>in</strong>formation resulted <strong>in</strong> a considerable improvement<br />
(auROC = 0.78), this was not the case for the IPI- and thymus-m<strong>in</strong>-based self-<strong>to</strong>lerance <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
(auROCs <strong>of</strong> 0.70 and 0.71, respectively). This is consistent with the performance<br />
<strong>of</strong> purely self-<strong>to</strong>lerance-based predic<strong>to</strong>rs: the thymus-max-based predic<strong>to</strong>r (auROC = 0.58)<br />
clearly outperforms the IPI- (auROC = 0.48) and thymus-m<strong>in</strong>-based (auROC = 0.44) predic<strong>to</strong>rs.