Solitons in Nonlocal Media
Solitons in Nonlocal Media
Solitons in Nonlocal Media
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4.4 Breath<strong>in</strong>g<br />
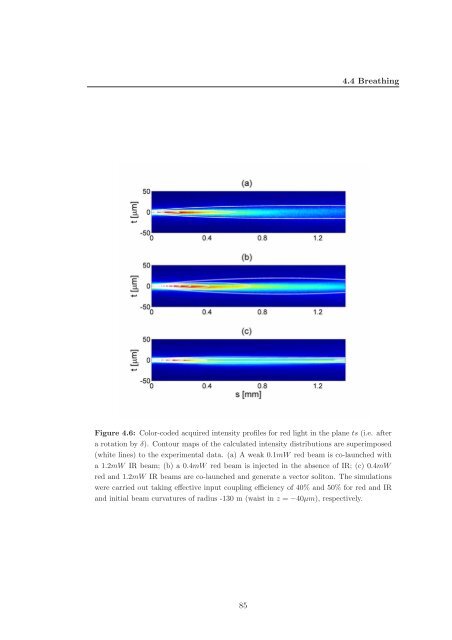
Figure 4.6: Color-coded acquired <strong>in</strong>tensity profiles for red light <strong>in</strong> the plane ts (i.e. after<br />
a rotation by δ). Contour maps of the calculated <strong>in</strong>tensity distributions are superimposed<br />
(white l<strong>in</strong>es) to the experimental data. (a) A weak 0.1mW red beam is co-launched with<br />
a 1.2mW IR beam; (b) a 0.4mW red beam is <strong>in</strong>jected <strong>in</strong> the absence of IR; (c) 0.4mW<br />
red and 1.2mW IR beams are co-launched and generate a vector soliton. The simulations<br />
were carried out tak<strong>in</strong>g effective <strong>in</strong>put coupl<strong>in</strong>g efficiency of 40% and 50% for red and IR<br />
and <strong>in</strong>itial beam curvatures of radius -130 m (waist <strong>in</strong> z = −40µm), respectively.<br />
85