WO 100 2 - ESAB
WO 100 2 - ESAB
WO 100 2 - ESAB
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
GB<br />
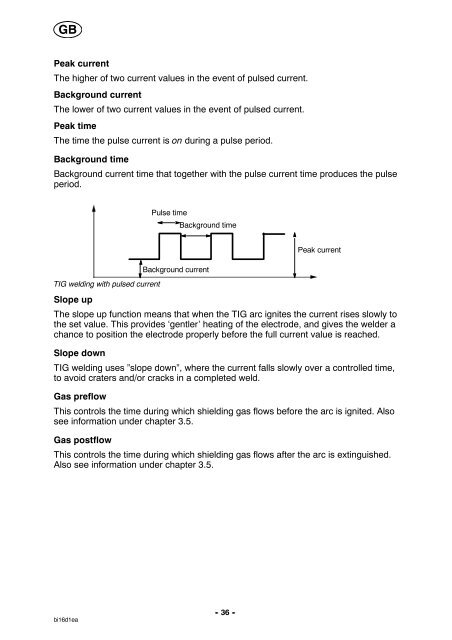
Peak current<br />
The higher of two current values in the event of pulsed current.<br />
Background current<br />
The lower of two current values in the event of pulsed current.<br />
Peak time<br />
The time the pulse current is on during a pulse period.<br />
Background time<br />
Background current time that together with the pulse current time produces the pulse<br />
period.<br />
TIG welding with pulsed current<br />
bi16d1ea<br />
Pulse time<br />
Background time<br />
Background current<br />
- 36 -<br />
Peak current<br />
Slope up<br />
The slope up function means that when the TIG arc ignites the current rises slowly to<br />
the set value. This provides ‘gentler’ heating of the electrode, and gives the welder a<br />
chance to position the electrode properly before the full current value is reached.<br />
Slope down<br />
TIG welding uses ”slope down”, where the current falls slowly over a controlled time,<br />
to avoid craters and/or cracks in a completed weld.<br />
Gas preflow<br />
This controls the time during which shielding gas flows before the arc is ignited. Also<br />
see information under chapter 3.5.<br />
Gas postflow<br />
This controls the time during which shielding gas flows after the arc is extinguished.<br />
Also see information under chapter 3.5.