Apixaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in people ...
Apixaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in people ...
Apixaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in people ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
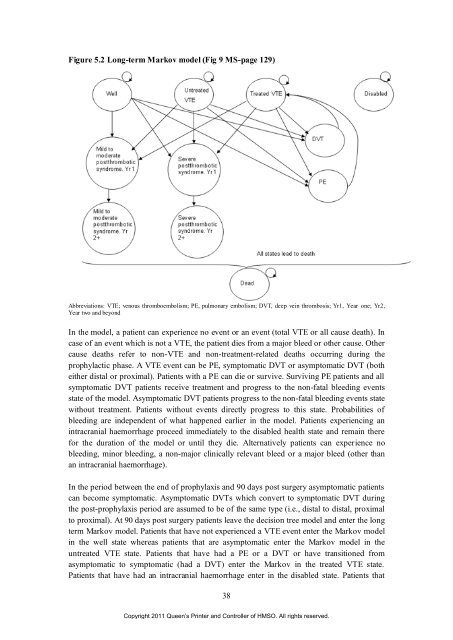
Figure 5.2 Long-term Markov model (Fig 9 MS-page 129)<br />
Abbreviations: VTE; <strong>venous</strong> <strong>thromboembolism</strong>; PE, pulmonary embolism; DVT, deep ve<strong>in</strong> thrombosis; Yr1, Year one; Yr2,<br />
Year two and beyond<br />
In <strong>the</strong> model, a patient can experience no event or an event (total VTE or all cause death). In<br />
case <strong>of</strong> an event which is not a VTE, <strong>the</strong> patient dies from a major bleed or o<strong>the</strong>r cause. O<strong>the</strong>r<br />
cause deaths refer to non-VTE and non-treatment-related deaths occurr<strong>in</strong>g dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong><br />
prophylactic phase. A VTE event can be PE, symptomatic DVT or asymptomatic DVT (both<br />
ei<strong>the</strong>r distal or proximal). Patients with a PE can die or survive. Surviv<strong>in</strong>g PE patients and all<br />
symptomatic DVT patients receive treatment and progress to <strong>the</strong> non-fatal bleed<strong>in</strong>g events<br />
state <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> model. Asymptomatic DVT patients progress to <strong>the</strong> non-fatal bleed<strong>in</strong>g events state<br />
without treatment. Patients without events directly progress to this state. Probabilities <strong>of</strong><br />
bleed<strong>in</strong>g are <strong>in</strong>dependent <strong>of</strong> what happened earlier <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> model. Patients experienc<strong>in</strong>g an<br />
<strong>in</strong>tracranial haemorrhage proceed immediately to <strong>the</strong> disabled health state and rema<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>re<br />
<strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> duration <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> model or until <strong>the</strong>y die. Alternatively patients can experience no<br />
bleed<strong>in</strong>g, m<strong>in</strong>or bleed<strong>in</strong>g, a non-major cl<strong>in</strong>ically relevant bleed or a major bleed (o<strong>the</strong>r than<br />
an <strong>in</strong>tracranial haemorrhage).<br />
In <strong>the</strong> period between <strong>the</strong> end <strong>of</strong> prophylaxis and 90 days post surgery asymptomatic patients<br />
can become symptomatic. Asymptomatic DVTs which convert to symptomatic DVT dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>the</strong> post-prophylaxis period are assumed to be <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> same type (i.e., distal to distal, proximal<br />
to proximal). At 90 days post surgery patients leave <strong>the</strong> decision tree model and enter <strong>the</strong> long<br />
term Markov model. Patients that have not experienced a VTE event enter <strong>the</strong> Markov model<br />
<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> well state whereas patients that are asymptomatic enter <strong>the</strong> Markov model <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
untreated VTE state. Patients that have had a PE or a DVT or have transitioned from<br />
asymptomatic to symptomatic (had a DVT) enter <strong>the</strong> Markov <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> treated VTE state.<br />
Patients that have had an <strong>in</strong>tracranial haemorrhage enter <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> disabled state. Patients that<br />
38<br />
Copyright 2011 Queen’s Pr<strong>in</strong>ter and Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO. All rights reserved.