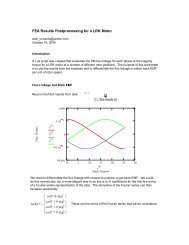
1 Introduction - Finite Element Method Magnetics
1 Introduction - Finite Element Method Magnetics
1 Introduction - Finite Element Method Magnetics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Figure 5: Grid Properties dialog.<br />
The Grid Properties dialog has an edit box for the user to enter the desired grid sizing. When<br />
the box appears, the number in this edit box is the current grid size. The edit box also contains<br />
a drop list that allows the user to select between Cartesian and Polar coordinates. If Cartesian<br />
is selected, points are specified by their (x,y) coordinates for a planar problem, or by their (r,z)<br />
coordinates for an axisymmetric problem. If Polar is selected, points are specified by an angle and<br />
a radial distance from the origin. The default is Cartesian coordinates.<br />
3.5 Edit<br />
Several useful tasks can be performed via the Edit menu off of the main menu.<br />
Perhaps the most frequently used is the Undo command. Choosing this selection undoes the<br />
last addition or deletion that the user has made to the model’s geometry.<br />
For selecting many objects quickly, the Select Group command is useful. This command<br />
allows the user to select objects of the current type located in an arbitrary rectangular box. When<br />
this command is selected, move the mouse pointer to one corner of the region that is to be selected.<br />
Press and hold the left mouse button. Then, drag the mouse pointer to the opposite diagonal<br />
corner of the region. A red box will appear, outlining the region to be selected. When the desired<br />
region has been specified, release the left mouse button. All objects of the current type completely<br />
contained within the box will become selected.<br />
Any objects that are currently selected can be moved, copied, or pasted. To move or copy<br />
selected objects, simply choose the corresponding selection off of the main menu’s Edit menu. A<br />
dialog will appear prompting for an amount of displacement or rotation.<br />
3.6 Problem Definition<br />
The definition of problem type is specified by choosing the Problem selection off of the main<br />
menu. Selecting this option brings up the Problem Definition dialog, shown in Figure 6<br />
The first selection is the Problem Type drop list. This drop box allows the user to choose from<br />
a 2-D planar problem (the Planar selection), or an axisymmetric problem (the Axisymmetric<br />
selection).<br />
Next is the Length Units drop list. This box identifies what unit is associated with the dimensions<br />
prescribed in the model’s geometry. Currently, the program supports inches, millimeters,<br />
centimeters, meters, mils, and µmeters.<br />
14