Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Atallah A. Shaaban<br />
75<br />
A- Anatomy<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> <strong>Urology</strong><br />
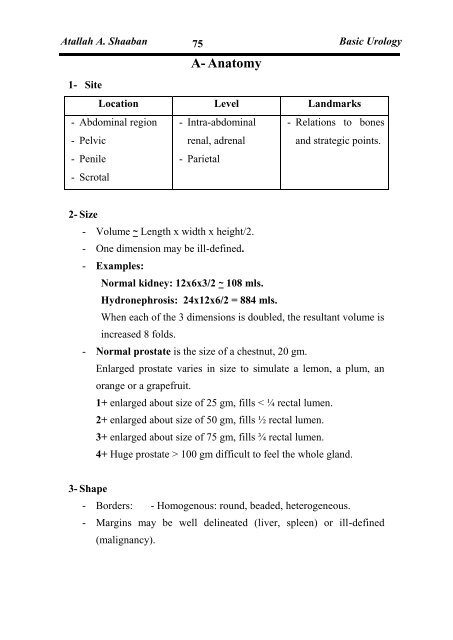
1- Site<br />
Location Level Landmarks<br />
- Abdominal region<br />
- Pelvic<br />
- Penile<br />
- Scrotal<br />
- Intra-abdominal<br />
renal, adrenal<br />
- Parietal<br />
- Relations to bones<br />
and strategic points.<br />
2- Size<br />
- Volume ~ Length x width x height/2.<br />
- One dimension may be ill-defined.<br />
- Examples:<br />
Normal kidney: 12x6x3/2 ~ 108 mls.<br />
Hydronephrosis: 24x12x6/2 = 884 mls.<br />
When each of the 3 dimensions is doubled, the resultant volume is<br />
increased 8 folds.<br />
- Normal prostate is the size of a chestnut, 20 gm.<br />
Enlarged prostate varies in size to simulate a lemon, a plum, an<br />
orange or a grapefruit.<br />
1+ enlarged about size of 25 gm, fills < ¼ rectal lumen.<br />
2+ enlarged about size of 50 gm, fills ½ rectal lumen.<br />
3+ enlarged about size of 75 gm, fills ¾ rectal lumen.<br />
4+ Huge prostate > 100 gm difficult to feel the whole gland.<br />
3- Shape<br />
- Borders: - Homogenous: round, beaded, heterogeneous.<br />
- Margins may be well delineated (liver, spleen) or ill-defined<br />
(malignancy).