PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
potential for most nuclei in spite of the attractive nature of basic neutron-nuclear interaction. The<br />
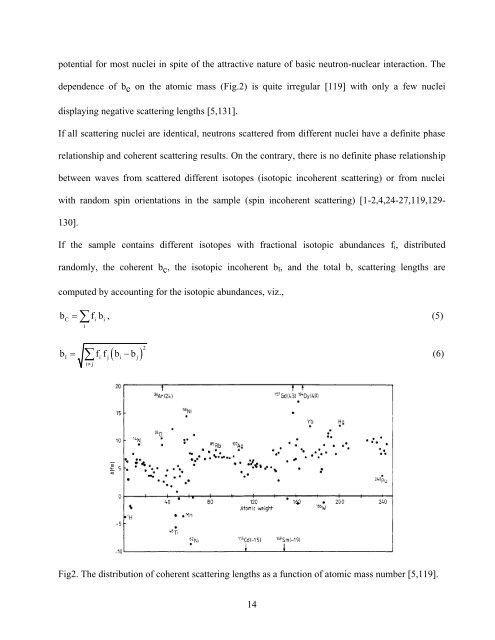
dependence of b c on the atomic mass (Fig.2) is quite irregular [119] with only a few nuclei<br />
displaying negative scattering lengths [5,131].<br />
If all scattering nuclei are identical, neutrons scattered from different nuclei have a definite phase<br />
relationship and coherent scattering results. On the contrary, there is no definite phase relationship<br />
between waves from scattered different isotopes (isotopic incoherent scattering) or from nuclei<br />
with random spin orientations in the sample (spin incoherent scattering) [1-2,4,24-27,119,129-<br />
130].<br />
If the sample contains different isotopes with fractional isotopic abundances f i , distributed<br />
randomly, the coherent b c , the isotopic incoherent b I , and the total b, scattering lengths are<br />
computed by accounting for the isotopic abundances, viz.,<br />
bC fi b<br />
i<br />
,<br />
(5)<br />
i<br />
2<br />
b f f b b<br />
(6)<br />
I i j i j<br />
i<br />
j<br />
Fig2. The distribution of coherent scattering lengths as a function of atomic mass number [5,119].<br />
14