PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
PHYS01200804001 Sohrab Abbas - Homi Bhabha National Institute
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
other with a compression factor limit of 47.62 (Fig.31) adding up to a single large peak. Thus by<br />
increasing A, we achieve stronger and narrower diffraction peaks due to better compression and<br />
hence superior collimation.<br />
By a judicious optimisation of the Bragg reflection, the asymmetry of the Bragg configuration and<br />
apex angle A, the angular profile of the diffracted beam emerging from the side face can be<br />
narrowed down to the sub-arcsec domain. For 5.26 Å neutrons and Si {111} reflection, the optimal<br />
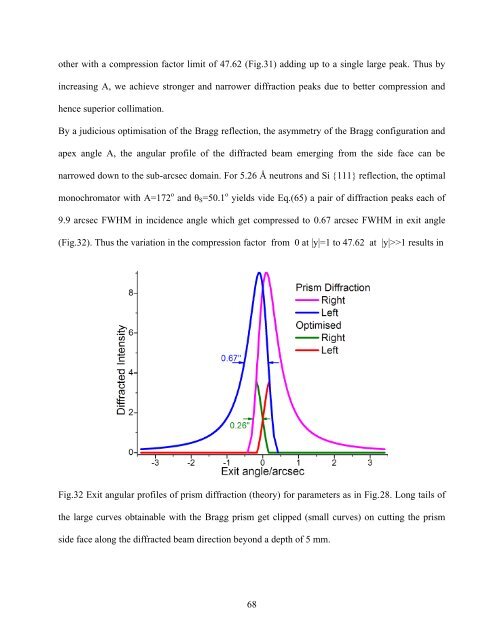
monochromator with A=172 o and θ S =50.1 o yields vide Eq.(65) a pair of diffraction peaks each of<br />
9.9 arcsec FWHM in incidence angle which get compressed to 0.67 arcsec FWHM in exit angle<br />
(Fig.32). Thus the variation in the compression factor from 0 at |y|=1 to 47.62 at |y|>>1 results in<br />
Fig.32 Exit angular profiles of prism diffraction (theory) for parameters as in Fig.28. Long tails of<br />
the large curves obtainable with the Bragg prism get clipped (small curves) on cutting the prism<br />
side face along the diffracted beam direction beyond a depth of 5 mm.<br />
68