DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Version 4.0<br />
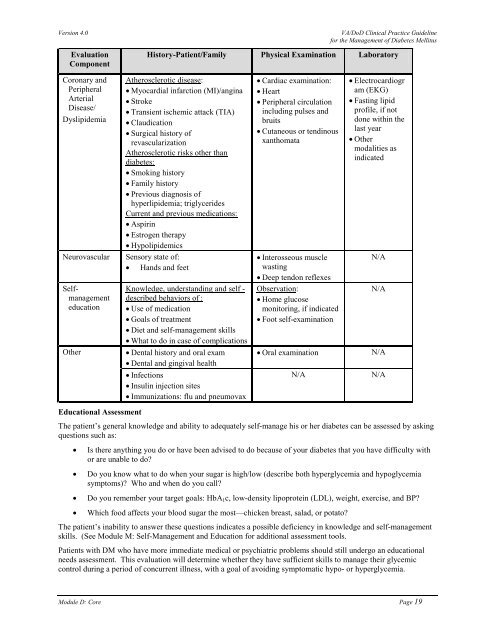
Evaluation<br />
Component<br />
<strong>VA</strong>/<strong>DoD</strong> <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Guideline</strong><br />
for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus<br />
History-Patient/Family Physical Examination Laboratory<br />
Coronary and<br />
Peripheral<br />
Arterial<br />
Disease/<br />
Dyslipidemia<br />
Neurovascular<br />
Selfmanagement<br />
education<br />
Other<br />
Educational Assessment<br />
Atherosclerotic disease:<br />
• Myocardial infarction (MI)/angina<br />
• Stroke<br />
• Transient ischemic attack (TIA)<br />
• Claudication<br />
• Surgical history of<br />
revascularization<br />
Atherosclerotic risks other than<br />
diabetes:<br />
• Smoking history<br />
• Family history<br />
• Previous diagnosis of<br />
hyperlipidemia; triglycerides<br />
Current and previous medications:<br />
• Aspirin<br />
• Estrogen therapy<br />
• Hypolipidemics<br />
Sensory state of:<br />
• Hands and feet<br />
Knowledge, understanding and self -<br />
described behaviors of :<br />
• Use of medication<br />
• Goals of treatment<br />
• Diet and self-management skills<br />
• What to do in case of complications<br />
• Dental history and oral exam<br />
• Dental and gingival health<br />
• Infections<br />
• Insulin injection sites<br />
• Immunizations: flu and pneumovax<br />
• Cardiac examination:<br />
• Heart<br />
• Peripheral circulation<br />
including pulses and<br />
bruits<br />
• Cutaneous or tendinous<br />
xanthomata<br />
• Interosseous muscle<br />
wasting<br />
• Deep tendon reflexes<br />
Observation:<br />
• <strong>Home</strong> glucose<br />
monitoring, if indicated<br />
• Foot self-examination<br />
• Oral examination<br />
• Electrocardiogr<br />
am (EKG)<br />
• Fasting lipid<br />
profile, if not<br />
done within the<br />
last year<br />
• Other<br />
modalities as<br />
indicated<br />
The patient’s general knowledge and ability to adequately self-manage his or her diabetes can be assessed by asking<br />
questions such as:<br />
• Is there anything you do or have been advised to do because of your diabetes that you have difficulty with<br />
or are unable to do?<br />
• Do you know what to do when your sugar is high/low (describe both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia<br />
symptoms)? Who and when do you call?<br />
• Do you remember your target goals: HbA 1 c, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), weight, exercise, and BP?<br />
N/A<br />
• Which food affects your blood sugar the most—chicken breast, salad, or potato?<br />
The patient’s inability to answer these questions indicates a possible deficiency in knowledge and self-management<br />
skills. (See Module M: Self-Management and Education for additional assessment tools.<br />
Patients with <strong>DM</strong> who have more immediate medical or psychiatric problems should still undergo an educational<br />
needs assessment. This evaluation will determine whether they have sufficient skills to manage their glycemic<br />
control during a period of concurrent illness, with a goal of avoiding symptomatic hypo- or hyperglycemia.<br />
N/A<br />
N/A<br />
N/A<br />
N/A<br />
Module D: Core Page 19