DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Version 4.0<br />
EVIDENCE<br />
<strong>VA</strong>/<strong>DoD</strong> <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Guideline</strong><br />
for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus<br />
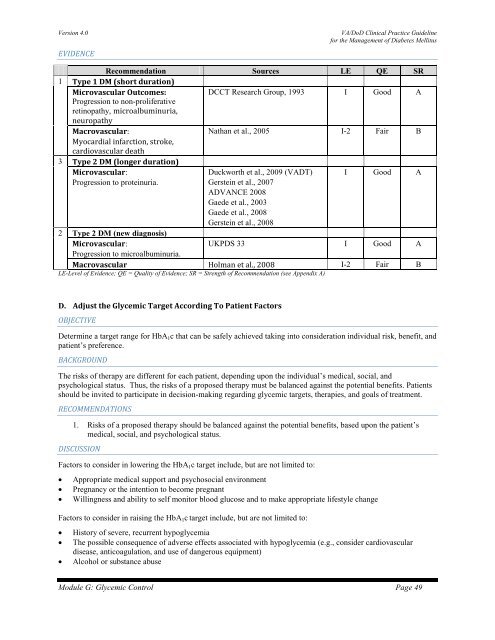
Recommendation Sources LE QE SR<br />
1 Type 1 <strong>DM</strong> (short duration)<br />
Microvascular Outcomes:<br />
DCCT Research Group, 1993 I Good A<br />
Progression to non-proliferative<br />
retinopathy, microalbuminuria,<br />
neuropathy<br />
Macrovascular:<br />
Nathan et al., 2005 I-2 Fair B<br />
Myocardial infarction, stroke,<br />
cardiovascular death<br />
3 Type 2 <strong>DM</strong> (longer duration)<br />
Microvascular:<br />
Duckworth et al., 2009 (<strong>VA</strong>DT) I Good A<br />
Progression to proteinuria.<br />
Gerstein et al., 2007<br />
AD<strong>VA</strong>NCE 2008<br />
Gaede et al., 2003<br />
Gaede et al., 2008<br />
Gerstein et al., 2008<br />
2 Type 2 <strong>DM</strong> (new diagnosis)<br />
Microvascular:<br />
UKPDS 33 I Good A<br />
Progression to microalbuminuria.<br />
Macrovascular Holman et al., 2008 I-2 Fair B<br />
LE-Level of Evidence; QE = Quality of Evidence; SR = Strength of Recommendation (see Appendix A)<br />
D. Adjust the Glycemic Target According To Patient Factors<br />
OBJECTIVE<br />
Determine a target range for HbA 1 c that can be safely achieved taking into consideration individual risk, benefit, and<br />
patient’s preference.<br />
BACKGROUND<br />
The risks of therapy are different for each patient, depending upon the individual’s medical, social, and<br />
psychological status. Thus, the risks of a proposed therapy must be balanced against the potential benefits. Patients<br />
should be invited to participate in decision-making regarding glycemic targets, therapies, and goals of treatment.<br />
RECOMMENDATIONS<br />
1. Risks of a proposed therapy should be balanced against the potential benefits, based upon the patient’s<br />
medical, social, and psychological status.<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Factors to consider in lowering the HbA 1 c target include, but are not limited to:<br />
• Appropriate medical support and psychosocial environment<br />
• Pregnancy or the intention to become pregnant<br />
• Willingness and ability to self monitor blood glucose and to make appropriate lifestyle change<br />
Factors to consider in raising the HbA 1 c target include, but are not limited to:<br />
• History of severe, recurrent hypoglycemia<br />
• The possible consequence of adverse effects associated with hypoglycemia (e.g., consider cardiovascular<br />
disease, anticoagulation, and use of dangerous equipment)<br />
• Alcohol or substance abuse<br />
Module G: Glycemic Control Page 49