DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
DM Full Guideline (2010) - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines Home
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Version 4.0<br />
<strong>VA</strong>/<strong>DoD</strong> <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Guideline</strong><br />
for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus<br />
• Kruger et al. (2003) determined that there was no significant difference in glycemic control among women<br />
with gestational diabetes who transmitted SMBG data telephonically versus electronically. However, the<br />
electronic transfer was shown to be more convenient and efficient for both patients and providers.<br />
• An RCT by Kwon et al. (2004) studied the effects of Internet recording of SMBG with feedback and no<br />
outpatient visits versus patients without Internet recordings but with monthly outpatient visits. There was a<br />
small decrease in SMBG with the Internet recordings group and a small increase in SMBG with the non-<br />
Internet recordings group.<br />
• An RCT by Laffel et al. (2007) compared the effectiveness of using an integrated glucose meter and<br />
electronic logbook and conventional meters and paper logbooks in a group of insulin treated patients. The<br />
use of the integrated meter and electronic logbook resulted in small but significant improvement in HbA 1 c<br />
up to one year<br />
• In a meta-analysis by St. John et al. (<strong>2010</strong>), the results of five RCTs in patients with non–insulin-treated<br />
type 2 diabetes were combined with two earlier RCTs which yielded a significant pooled SMBG-related<br />
decrease in HbA 1 c of −0.22 (95% CI −0.34% to −0.11%).<br />
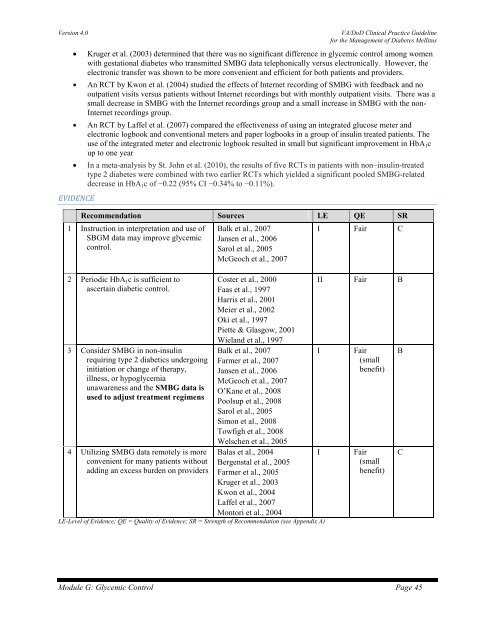
EVIDENCE<br />
Recommendation Sources LE QE SR<br />
1 Instruction in interpretation and use of<br />
SBGM data may improve glycemic<br />
control.<br />
Balk et al., 2007<br />
Jansen et al., 2006<br />
Sarol et al., 2005<br />
McGeoch et al., 2007<br />
I Fair C<br />
2 Periodic HbA 1 c is sufficient to<br />
ascertain diabetic control.<br />
3 Consider SMBG in non-insulin<br />
requiring type 2 diabetics undergoing<br />
initiation or change of therapy,<br />
illness, or hypoglycemia<br />
unawareness and the SMBG data is<br />
used to adjust treatment regimens<br />
4 Utilizing SMBG data remotely is more<br />
convenient for many patients without<br />
adding an excess burden on providers<br />
Coster et al., 2000<br />
Faas et al., 1997<br />
Harris et al., 2001<br />
Meier et al., 2002<br />
Oki et al., 1997<br />
Piette & Glasgow, 2001<br />
Wieland et al., 1997<br />
Balk et al., 2007<br />
Farmer et al., 2007<br />
Jansen et al., 2006<br />
McGeoch et al., 2007<br />
O’Kane et al., 2008<br />
Poolsup et al., 2008<br />
Sarol et al., 2005<br />
Simon et al., 2008<br />
Towfigh et al., 2008<br />
Welschen et al., 2005<br />
Balas et al., 2004<br />
Bergenstal et al., 2005<br />
Farmer et al., 2005<br />
Kruger et al., 2003<br />
Kwon et al., 2004<br />
Laffel et al., 2007<br />
Montori et al., 2004<br />
LE-Level of Evidence; QE = Quality of Evidence; SR = Strength of Recommendation (see Appendix A)<br />
II Fair B<br />
I<br />
I<br />
Fair<br />
(small<br />
benefit)<br />
Fair<br />
(small<br />
benefit)<br />
B<br />
C<br />
Module G: Glycemic Control Page 45