Imara African Cement Report Africa, the last cement frontier Angola ...
Imara African Cement Report Africa, the last cement frontier Angola ...
Imara African Cement Report Africa, the last cement frontier Angola ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
US$ Millions<br />
US$ per barrel<br />
over 100 Chinese firms were operating in <strong>Angola</strong> (over 50 of <strong>the</strong>m of significant size) and many of <strong>the</strong>se<br />
companies use Chinese workers. Officially some 40,000 Chinese work on official infrastructure projects.<br />
According to a statement by <strong>the</strong> Ministry of Finance in January 2009, <strong>the</strong> second phase of disbursements under<br />
<strong>the</strong> existing second US$ 2.5bn credit line of China‟s Exim Bank started, with a total of US$1.6bn in funds<br />
available for projects in infrastructure, transport and agriculture.<br />
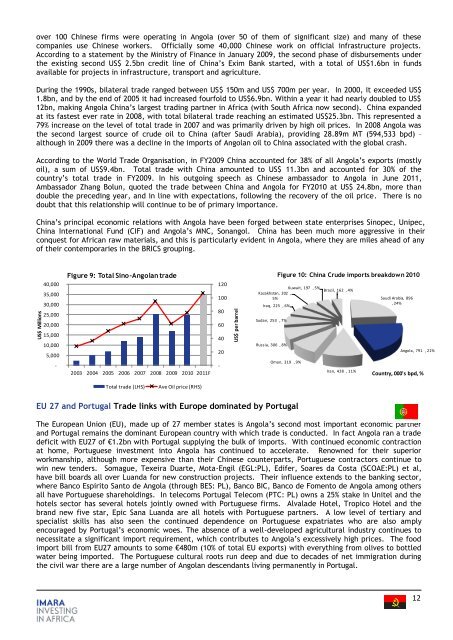
During <strong>the</strong> 1990s, bilateral trade ranged between US$ 150m and US$ 700m per year. In 2000, it exceeded US$<br />
1.8bn, and by <strong>the</strong> end of 2005 it had increased fourfold to US$6.9bn. Within a year it had nearly doubled to US$<br />
12bn, making <strong>Angola</strong> China‟s largest trading partner in <strong>Africa</strong> (with South <strong>Africa</strong> now second). China expanded<br />
at its fastest ever rate in 2008, with total bilateral trade reaching an estimated US$25.3bn. This represented a<br />
79% increase on <strong>the</strong> level of total trade in 2007 and was primarily driven by high oil prices. In 2008 <strong>Angola</strong> was<br />
<strong>the</strong> second largest source of crude oil to China (after Saudi Arabia), providing 28.89m MT (594,533 bpd) –<br />
although in 2009 <strong>the</strong>re was a decline in <strong>the</strong> imports of <strong>Angola</strong>n oil to China associated with <strong>the</strong> global crash.<br />
According to <strong>the</strong> World Trade Organisation, in FY2009 China accounted for 38% of all <strong>Angola</strong>‟s exports (mostly<br />
oil), a sum of US$9.4bn. Total trade with China amounted to US$ 11.3bn and accounted for 30% of <strong>the</strong><br />
country‟s total trade in FY2009. In his outgoing speech as Chinese ambassador to <strong>Angola</strong> in June 2011,<br />
Ambassador Zhang Bolun, quoted <strong>the</strong> trade between China and <strong>Angola</strong> for FY2010 at US$ 24.8bn, more than<br />
double <strong>the</strong> preceding year, and in line with expectations, following <strong>the</strong> recovery of <strong>the</strong> oil price. There is no<br />
doubt that this relationship will continue to be of primary importance.<br />
China‟s principal economic relations with <strong>Angola</strong> have been forged between state enterprises Sinopec, Unipec,<br />
China International Fund (CIF) and <strong>Angola</strong>‟s MNC, Sonangol. China has been much more aggressive in <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
conquest for <strong><strong>Africa</strong>n</strong> raw materials, and this is particularly evident in <strong>Angola</strong>, where <strong>the</strong>y are miles ahead of any<br />
of <strong>the</strong>ir contemporaries in <strong>the</strong> BRICS grouping.<br />
40,000<br />
35,000<br />
30,000<br />
25,000<br />
20,000<br />
Figure 9: Total Sino-<strong>Angola</strong>n trade<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
Iraq, 225 , 6%<br />
Sudan, 253 , 7%<br />
Figure 10: China Crude imports breakdown 2010<br />
Kuwait, 197 , 5% Brazil, 162 , 4%<br />
Kazakhstan, 202 ,<br />
5%<br />
Saudi Arabia, 896<br />
, 24%<br />
15,000<br />
10,000<br />
5,000<br />
-<br />
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011F<br />
40<br />
20<br />
-<br />
Russia, 306 , 8%<br />
Oman, 319 , 9%<br />
Iran, 428 , 11%<br />
<strong>Angola</strong>, 791 , 21%<br />
Country, 000's bpd, %<br />
Total trade (LHS) Ave Oil price (RHS)<br />
EU 27 and Portugal Trade links with Europe dominated by Portugal<br />
The European Union (EU), made up of 27 member states is <strong>Angola</strong>‟s second most important economic partner<br />
and Portugal remains <strong>the</strong> dominant European country with which trade is conducted. In fact <strong>Angola</strong> ran a trade<br />
deficit with EU27 of €1.2bn with Portugal supplying <strong>the</strong> bulk of imports. With continued economic contraction<br />
at home, Portuguese investment into <strong>Angola</strong> has continued to accelerate. Renowned for <strong>the</strong>ir superior<br />
workmanship, although more expensive than <strong>the</strong>ir Chinese counterparts, Portuguese contractors continue to<br />
win new tenders. Somague, Texeira Duarte, Mota-Engil (EGL:PL), Edifer, Soares da Costa (SCOAE:PL) et al,<br />
have bill boards all over Luanda for new construction projects. Their influence extends to <strong>the</strong> banking sector,<br />
where Banco Espirito Santo de <strong>Angola</strong> (through BES: PL), Banco BIC, Banco de Fomento de <strong>Angola</strong> among o<strong>the</strong>rs<br />
all have Portuguese shareholdings. In telecoms Portugal Telecom (PTC: PL) owns a 25% stake in Unitel and <strong>the</strong><br />
hotels sector has several hotels jointly owned with Portuguese firms. Alvalade Hotel, Tropico Hotel and <strong>the</strong><br />
brand new five star, Epic Sana Luanda are all hotels with Portuguese partners. A low level of tertiary and<br />
specialist skills has also seen <strong>the</strong> continued dependence on Portuguese expatriates who are also amply<br />
encouraged by Portugal‟s economic woes. The absence of a well-developed agricultural industry continues to<br />
necessitate a significant import requirement, which contributes to <strong>Angola</strong>‟s excessively high prices. The food<br />
import bill from EU27 amounts to some €480m (10% of total EU exports) with everything from olives to bottled<br />
water being imported. The Portuguese cultural roots run deep and due to decades of net immigration during<br />
<strong>the</strong> civil war <strong>the</strong>re are a large number of <strong>Angola</strong>n descendants living permanently in Portugal.<br />
12