INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2 1. Introduction<br />
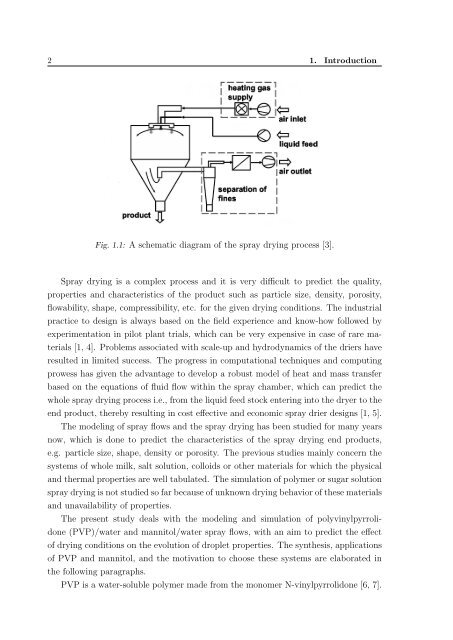
Fig. 1.1: A schematic diagram of the spray drying process [3].<br />
Spray drying is a complex process and it is very difficult to predict the quality,<br />
properties and characteristics of the product such as particle size, density, porosity,<br />
flowability, shape, compressibility, etc. for the given drying conditions. The industrial<br />
practice to design is always based on the field experience and know-how followed by<br />
experimentation in pilot plant trials, which can be very expensive in case of rare materials<br />
[1, 4]. Problems associated with scale-up and hydrodynamics of the driers have<br />
resulted in limited success. The progress in computational techniques and computing<br />
prowess has given the advantage to develop a robust model of heat and mass transfer<br />
based on the equations of fluid flow within the spray chamber, which can predict the<br />
whole spray drying process i.e., from the liquid feed stock entering into the dryer to the<br />
end product, thereby resulting in cost effective and economic spray drier designs [1, 5].<br />
The modeling of spray flows and the spray drying has been studied for many years<br />
now, which is done to predict the characteristics of the spray drying end products,<br />
e.g. particle size, shape, density or porosity. The previous studies mainly concern the<br />
systems of whole milk, salt solution, colloids or other materials for which the physical<br />
and thermal properties are well tabulated. The simulation of polymer or sugar solution<br />
spray drying is not studied so far because of unknown drying behavior of these materials<br />
and unavailability of properties.<br />
The present study deals with the modeling and simulation of polyvinylpyrrolidone<br />
(PVP)/water and mannitol/water spray flows, with an aim to predict the effect<br />
of drying conditions on the evolution of droplet properties. The synthesis, applications<br />
of PVP and mannitol, and the motivation to choose these systems are elaborated in<br />
the following paragraphs.<br />
PVP is a water-soluble polymer made from the monomer N-vinylpyrrolidone [6, 7].