INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
INAUGURAL–DISSERTATION zur Erlangung der Doktorwürde der ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4 1. Introduction<br />
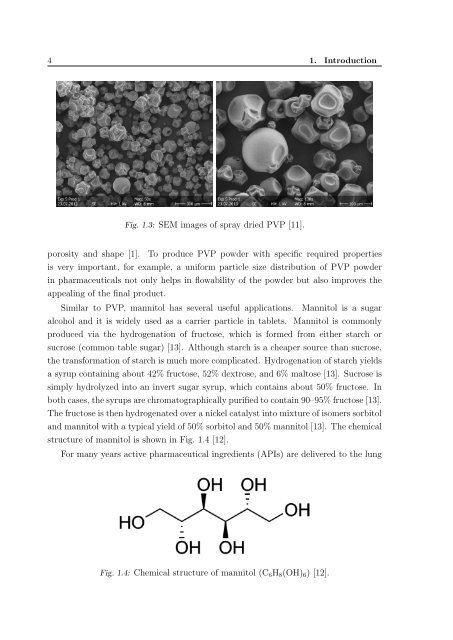
Fig. 1.3: SEM images of spray dried PVP [11].<br />
porosity and shape [1]. To produce PVP pow<strong>der</strong> with specific required properties<br />
is very important, for example, a uniform particle size distribution of PVP pow<strong>der</strong><br />
in pharmaceuticals not only helps in flowability of the pow<strong>der</strong> but also improves the<br />
appealing of the final product.<br />
Similar to PVP, mannitol has several useful applications. Mannitol is a sugar<br />
alcohol and it is widely used as a carrier particle in tablets. Mannitol is commonly<br />
produced via the hydrogenation of fructose, which is formed from either starch or<br />
sucrose (common table sugar) [13]. Although starch is a cheaper source than sucrose,<br />
the transformation of starch is much more complicated. Hydrogenation of starch yields<br />
a syrup containing about 42% fructose, 52% dextrose, and 6% maltose [13]. Sucrose is<br />
simply hydrolyzed into an invert sugar syrup, which contains about 50% fructose. In<br />
both cases, the syrups are chromatographically purified to contain 90–95% fructose [13].<br />
The fructose is then hydrogenated over a nickel catalyst into mixture of isomers sorbitol<br />
and mannitol with a typical yield of 50% sorbitol and 50% mannitol [13]. The chemical<br />
structure of mannitol is shown in Fig. 1.4 [12].<br />
For many years active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are delivered to the lung<br />
Fig. 1.4: Chemical structure of mannitol (C 6 H 8 (OH) 6 ) [12].