Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
16 2. Background and Related Work<br />
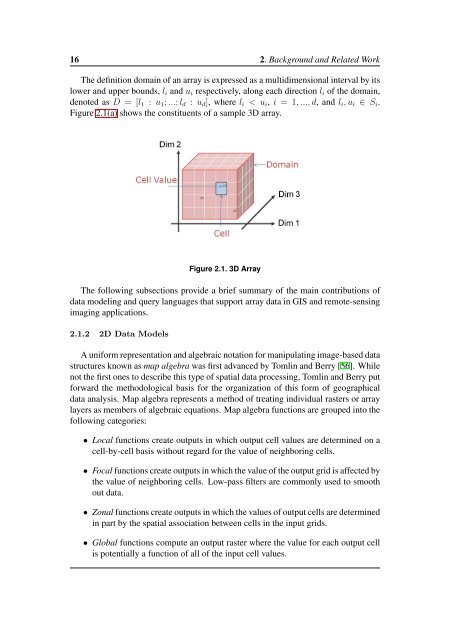
The definition domain of an array is expressed as a multidimensional interval by its<br />
lower and upper bounds, l i and u i respectively, along each direction l i of the domain,<br />
denoted as D = [l 1 : u 1 ; ...; l d : u d ], where l i < u i , i = 1, ..., d, and l i , u i ∈ S i .<br />
Figure 2.1(a) shows the constituents of a sample 3D array.<br />
Figure 2.1. 3D Array<br />
The following subsections provide a brief summary of the main contributions of<br />
data modeling and query languages that support array data in GIS and remote-sensing<br />
imaging applications.<br />
2.1.2 2D Data Models<br />
A uniform representation and algebraic notation for manipulating image-based data<br />
structures known as map algebra was first advanced by Tomlin and Berry [56]. While<br />
not the first ones <strong>to</strong> describe this type of spatial data processing, Tomlin and Berry put<br />
forward the methodological basis for the organization of this form of geographical<br />
data analysis. Map algebra represents a method of treating individual rasters or array<br />
layers as members of algebraic equations. Map algebra functions are grouped in<strong>to</strong> the<br />
following categories:<br />
• Local functions create outputs in which output cell values are determined on a<br />
cell-by-cell basis without regard for the value of neighboring cells.<br />
• Focal functions create outputs in which the value of the output grid is affected by<br />
the value of neighboring cells. Low-pass filters are commonly used <strong>to</strong> smooth<br />
out data.<br />
• Zonal functions create outputs in which the values of output cells are determined<br />
in part by the spatial association between cells in the input grids.<br />
• Global functions compute an output raster where the value for each output cell<br />
is potentially a function of all of the input cell values.