Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
Applying OLAP Pre-Aggregation Techniques to ... - Jacobs University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.2 Geo-Raster Operations 47<br />
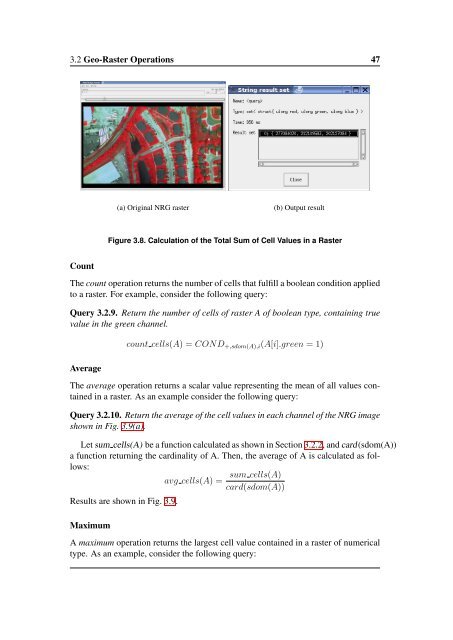
(a) Original NRG raster<br />
(b) Output result<br />
Figure 3.8. Calculation of the Total Sum of Cell Values in a Raster<br />
Count<br />
The count operation returns the number of cells that fulfill a boolean condition applied<br />
<strong>to</strong> a raster. For example, consider the following query:<br />
Query 3.2.9. Return the number of cells of raster A of boolean type, containing true<br />
value in the green channel.<br />
Average<br />
count cells(A) = COND +,sdom(A),i (A[i].green = 1)<br />
The average operation returns a scalar value representing the mean of all values contained<br />
in a raster. As an example consider the following query:<br />
Query 3.2.10. Return the average of the cell values in each channel of the NRG image<br />
shown in Fig. 3.9(a).<br />
Let sum cells(A) be a function calculated as shown in Section 3.2.2, and card(sdom(A))<br />
a function returning the cardinality of A. Then, the average of A is calculated as follows:<br />
sum cells(A)<br />
avg cells(A) =<br />
card(sdom(A))<br />
Results are shown in Fig. 3.9.<br />
Maximum<br />
A maximum operation returns the largest cell value contained in a raster of numerical<br />
type. As an example, consider the following query: