Sensoren - Lehrstuhls für Elektrische Antriebssysteme und ...
Sensoren - Lehrstuhls für Elektrische Antriebssysteme und ...
Sensoren - Lehrstuhls für Elektrische Antriebssysteme und ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
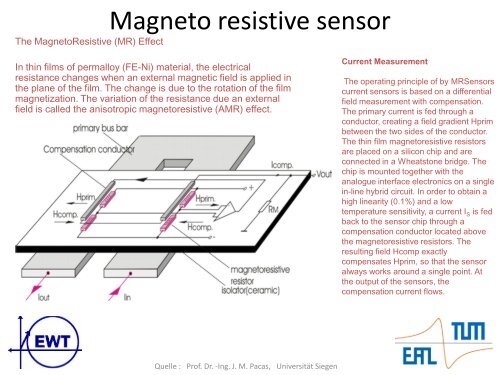
The MagnetoResistive (MR) Effect<br />
Magneto resistive sensor<br />
In thin films of permalloy (FE-Ni) material, the electrical<br />
resistance changes when an external magnetic field is applied in<br />
the plane of the film. The change is due to the rotation of the film<br />
magnetization. The variation of the resistance due an external<br />
field is called the anisotropic magnetoresistive (AMR) effect.<br />
Quelle : Prof. Dr. -Ing. J. M. Pacas, Universität Siegen<br />
Current Measurement<br />
The operating principle of by MRSensors<br />
current sensors is based on a differential<br />
field measurement with compensation.<br />
The primary current is fed through a<br />
conductor, creating a field gradient Hprim<br />
between the two sides of the conductor.<br />
The thin film magnetoresistive resistors<br />
are placed on a silicon chip and are<br />
connected in a Wheatstone bridge. The<br />
chip is mounted together with the<br />
analogue interface electronics on a single<br />
in-line hybrid circuit. In order to obtain a<br />
high linearity (0.1%) and a low<br />
temperature sensitivity, a current I S is fed<br />
back to the sensor chip through a<br />
compensation conductor located above<br />
the magnetoresistive resistors. The<br />
resulting field Hcomp exactly<br />
compensates Hprim, so that the sensor<br />
always works aro<strong>und</strong> a single point. At<br />
the output of the sensors, the<br />
compensation current flows.