You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NIVESHAK 25<br />
Article Cover FinLife of the Story Month<br />
price of the equity.<br />
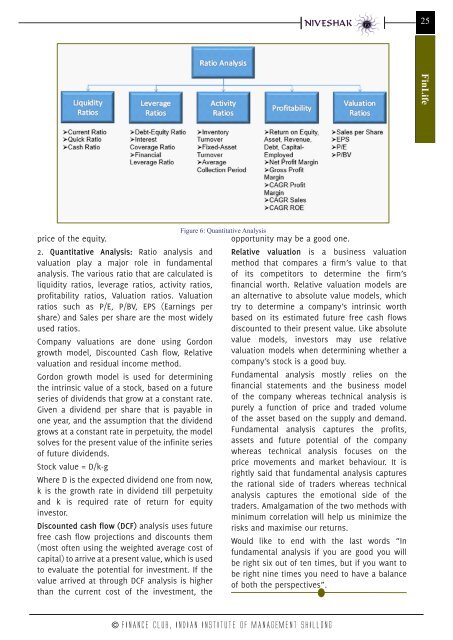
2. Quantitative Analysis: Ratio analysis and<br />
valuation play a major role in fundamental<br />
analysis. The various ratio that are calculated is<br />
liquidity ratios, leverage ratios, activity ratios,<br />
profitability ratios, Valuation ratios. Valuation<br />
ratios such as P/E, P/BV, EPS (Earnings per<br />
share) and Sales per share are the most widely<br />
used ratios.<br />
Company valuations are done using Gordon<br />
growth model, Discounted Cash flow, Relative<br />
valuation and residual income method.<br />
Gordon growth model is used for determining<br />
the intrinsic value of a stock, based on a future<br />
series of dividends that grow at a constant rate.<br />
Given a dividend per share that is payable in<br />
one year, and the assumption that the dividend<br />
grows at a constant rate in perpetuity, the model<br />
solves for the present value of the infinite series<br />
of future dividends.<br />
Stock value = D/k-g<br />
Where D is the expected dividend one from now,<br />
k is the growth rate in dividend till perpetuity<br />
and k is required rate of return for equity<br />
investor.<br />
Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis uses future<br />
free cash flow projections and discounts them<br />
(most often using the weighted average cost of<br />
capital) to arrive at a present value, which is used<br />
to evaluate the potential for investment. If the<br />
value arrived at through DCF analysis is higher<br />
than the current cost of the investment, the<br />
Figure 6: Quantitative Analysis<br />
opportunity may be a good one.<br />
Relative valuation is a business valuation<br />
method that compares a firm’s value to that<br />
of its competitors to determine the firm’s<br />
financial worth. Relative valuation models are<br />
an alternative to absolute value models, which<br />
try to determine a company’s intrinsic worth<br />
based on its estimated future free cash flows<br />
discounted to their present value. Like absolute<br />
value models, investors may use relative<br />
valuation models when determining whether a<br />
company’s stock is a good buy.<br />
Fundamental analysis mostly relies on the<br />
financial statements and the business model<br />
of the company whereas technical analysis is<br />
purely a function of price and traded volume<br />
of the asset based on the supply and demand.<br />
Fundamental analysis captures the profits,<br />
assets and future potential of the company<br />
whereas technical analysis focuses on the<br />
price movements and market behaviour. It is<br />
rightly said that fundamental analysis captures<br />
the rational side of traders whereas technical<br />
analysis captures the emotional side of the<br />
traders. Amalgamation of the two methods with<br />
minimum correlation will help us minimize the<br />
risks and maximise our returns.<br />
Would like to end with the last words “In<br />
fundamental analysis if you are good you will<br />
be right six out of ten times, but if you want to<br />
be right nine times you need to have a balance<br />
of both the perspectives”.<br />
© FINANCE CLUB, INDIAN INSTITUTE Of MANAGEMENT SHILLONG