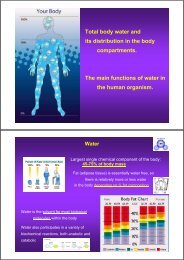
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
• Hypokalemia<br />
- Potassium level 5.5 mmol/L<br />
- Caused by <strong>in</strong>creased <strong>in</strong>take, shift of K+ from ICF, decreased renal excretion,<br />
<strong>in</strong>sul<strong>in</strong> deficiency, or cell trauma<br />
- Mild attacks<br />
- Hypopolarized membrane, caus<strong>in</strong>g neuromuscular irritability, T<strong>in</strong>gl<strong>in</strong>g of lips<br />
<strong>and</strong> f<strong>in</strong>gers, restlessness, <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>al cramp<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>and</strong> diarrhea<br />
- Severe attacks<br />
- The cell is not able to repolarize, result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> muscle weakness, loss or<br />
muscle tone<br />
Electrolytes<br />
• Calcium (Ca 2+ )<br />
– Most abundant ion <strong>in</strong> <strong>body</strong><br />
• plasma 2.3-2.6 mmol/L<br />
• most stored <strong>in</strong> bone (98%) as hydroxyapatite<br />
- Necessary for structure of bones <strong>and</strong> teeth, blood clott<strong>in</strong>g, hormone<br />
secretion, <strong>and</strong> cell receptor function<br />
- Regulation:<br />
• Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) - ↑ blood Ca 2+<br />
• Calciton<strong>in</strong> (CT) - ↓ blood Ca 2+<br />
– Homeostatic im<strong>balance</strong>s:<br />
• Hypocalcemia - muscle cramps, convulsions<br />
• Hypercalcemia - vomit<strong>in</strong>g, cardiovascular symptoms, coma;<br />
prolonged abnormal calcium deposition, e.g., stone<br />
formation