Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Acid-Base Balance<br />
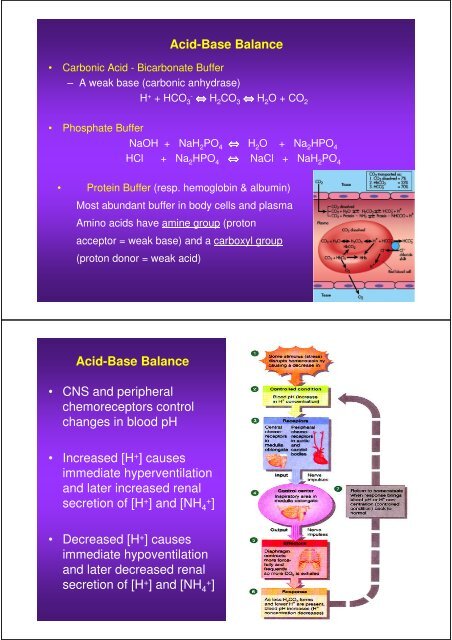
• Carbonic Acid - Bicarbonate Buffer<br />
– A weak base (carbonic anhydrase)<br />
H + + HCO 3- ⇔ H 2 CO 3 ⇔ H 2 O + CO 2<br />
• Phosphate Buffer<br />
NaOH + NaH 2 PO 4 ⇔ H 2 O + Na 2 HPO 4<br />
HCl + Na 2 HPO 4 ⇔ NaCl + NaH 2 PO 4<br />
• Prote<strong>in</strong> Buffer (resp. hemoglob<strong>in</strong> & album<strong>in</strong>)<br />
Most abundant buffer <strong>in</strong> <strong>body</strong> cells <strong>and</strong> plasma<br />
Am<strong>in</strong>o acids have am<strong>in</strong>e group (proton<br />
acceptor = weak base) <strong>and</strong> a carboxyl group<br />
(proton donor = weak acid)<br />
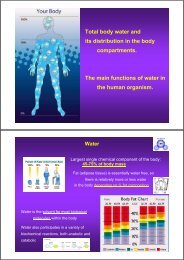
Acid-Base Balance<br />
• CNS <strong>and</strong> peripheral<br />
chemoreceptors control<br />
changes <strong>in</strong> blood pH<br />
• Increased [H + ] causes<br />
immediate hyperventilation<br />
<strong>and</strong> later <strong>in</strong>creased renal<br />
secretion of [H + ] <strong>and</strong> [NH 4+ ]<br />
• Decreased [H + ] causes<br />
immediate hypoventilation<br />
<strong>and</strong> later decreased renal<br />
secretion of [H + ] <strong>and</strong> [NH 4+ ]