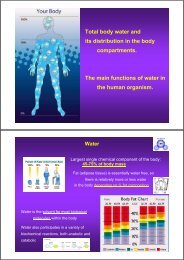
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Acid-Base Balance<br />
• Normal metabolism produces H + (acidity)<br />
• Three Homeostatic mechanisms:<br />
– Buffer systems - <strong>in</strong>stantaneous; temporary<br />
– Exhalation of CO 2 - operates with<strong>in</strong> m<strong>in</strong>utes; cannot<br />
completely correct serious im<strong>balance</strong>s<br />
– Kidney excretion - can completely correct any im<strong>balance</strong><br />
(eventually)<br />
• Buffer Systems<br />
– Consists of a weak acid <strong>and</strong> the salt of that acid which<br />
functions as a weak base<br />
Acid-Base Balance<br />
• Carbonic Acid - Bicarbonate Buffer<br />
– A weak base (carbonic anhydrase)<br />
H + + HCO 3- ⇔ H 2 CO 3 ⇔ H 2 O + CO 2<br />
• Phosphate Buffer<br />
NaOH + NaH 2 PO 4 ⇔ H 2 O + Na 2 HPO 4<br />
HCl + Na 2 HPO 4 ⇔ NaCl + NaH 2 PO 4<br />
- ma<strong>in</strong>ly <strong>in</strong>tracellularly, dur<strong>in</strong>g acidemia proton is bound, dur<strong>in</strong>g alkalemia proton is<br />
released via cell membrane K + /H + antiporter<br />
• Prote<strong>in</strong> Buffer (resp. album<strong>in</strong> & hemoglob<strong>in</strong> )<br />
Am<strong>in</strong>o acids have am<strong>in</strong>e group (proton<br />
acceptor = weak base) <strong>and</strong> a carboxyl group<br />
(proton donor = weak acid)<br />
hemoglob<strong>in</strong>- oxyhemoglob<strong>in</strong> systém, where<br />
oxyhemoglob<strong>in</strong> is stronger acid than<br />
hemoglob<strong>in</strong> (proton is more simply released)