Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Fluid balance and electrolyte distribution in human body.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
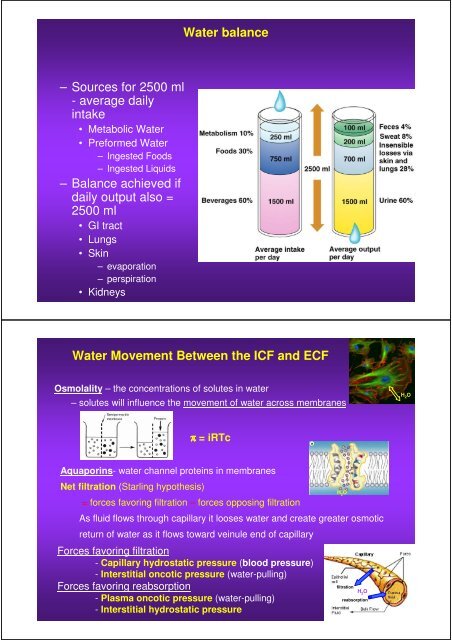
Water <strong>balance</strong><br />
– Sources for 2500 ml<br />
- average daily<br />
<strong>in</strong>take<br />
• Metabolic Water<br />
• Preformed Water<br />
– Ingested Foods<br />
– Ingested Liquids<br />
– Balance achieved if<br />
daily output also =<br />
2500 ml<br />
• GI tract<br />
• Lungs<br />
• Sk<strong>in</strong><br />
– evaporation<br />
– perspiration<br />
• Kidneys<br />
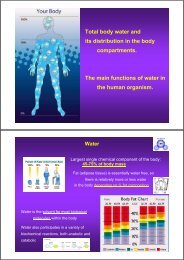
Water Movement Between the ICF <strong>and</strong> ECF<br />
Osmolality – the concentrations of solutes <strong>in</strong> water<br />
– solutes will <strong>in</strong>fluence the movement of water across membranes<br />
H 2<br />
O<br />
π = iRTc<br />
Aquapor<strong>in</strong>s- water channel prote<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> membranes<br />
Net filtration (Starl<strong>in</strong>g hypothesis)<br />
= forces favor<strong>in</strong>g filtration – forces oppos<strong>in</strong>g filtration<br />
As fluid flows through capillary it looses water <strong>and</strong> create greater osmotic<br />
return of water as it flows toward ve<strong>in</strong>ule end of capillary<br />
Forces favor<strong>in</strong>g filtration<br />
- Capillary hydrostatic pressure (blood pressure)<br />
- Interstitial oncotic pressure (water-pull<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
Forces favor<strong>in</strong>g reabsorption<br />
- Plasma oncotic pressure (water-pull<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
- Interstitial hydrostatic pressure<br />
H 2<br />
O<br />
filtration<br />
H 2<br />
O<br />
reabsorption