geostationary telecommunications satellites electronic telephone set ...
geostationary telecommunications satellites electronic telephone set ...
geostationary telecommunications satellites electronic telephone set ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
137<br />
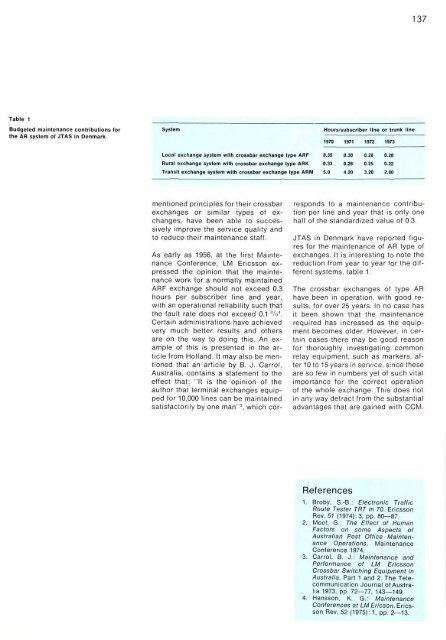
Table 1<br />
Budgeted maintenance contributions for<br />
the AR system of JTAS in Denmark<br />
System<br />
Hours/subscriber line or trunk line<br />
1970 1971 1972 1973<br />
Local exchange system with crossbar exchange type ARF<br />
Rural exchange system with crossbar exchange type ARK<br />
Transit exchange system with crossbar exchange type ARM<br />
0.35<br />
0.33<br />
5.0<br />
0.30 0.26 0.28<br />
0.28 0.25 0.22<br />
4.20 3.20 2.80<br />
mentioned principles for their crossbar<br />
exchanges or similar types of exchanges,<br />
have been able to successively<br />
improve the service quality and<br />
to reduce their maintenance staff.<br />
As early as 1956, at the first Maintenance<br />
Conference, LM Ericsson expressed<br />
the opinion that the maintenance<br />
work for a normally maintained<br />
ARF exchange should not exceed 0.3<br />
hours per subscriber line and year,<br />
with an operational reliability such that<br />
the fault rate does not exceed 0.1 % 4 .<br />
Certain administrations have achieved<br />
very much better results and others<br />
are on the way to doing this. An example<br />
of this is presented in the article<br />
from Holland. It may also be mentioned<br />
that an article by B. J. Carrol,<br />
Australia, contains a statement to the<br />
effect that: "It is the opinion of the<br />
author that terminal exchanges equipped<br />
for 10,000 lines can be maintained<br />
satisfactorily by one man" 3 , which corresponds<br />
to a maintenance contribution<br />
per line and year that is only one<br />
half of the standardized value of 0.3.<br />
JTAS in Denmark have reported figures<br />
for the maintenance of AR type of<br />
exchanges. It is interesting to note the<br />
reduction from year to year for the different<br />
systems, table 1.<br />
The crossbar exchanges of type AR<br />
have been in operation, with good results,<br />
for over 25 years. In no case has<br />
it been shown that the maintenance<br />
required has increased as the equipment<br />
becomes older. However, in certain<br />
cases there may be good reason<br />
for thoroughly investigating common<br />
relay equipment, such as markers, after<br />
10 to 15 years in service, since these<br />
are so few in numbers yet of such vital<br />
importance for the correct operation<br />
of the whole exchange. This does not<br />
in any way detract from the substantial<br />
advantages that are gained with CCM.<br />
References<br />
1. Broby, S.-B.: Electronic Traffic<br />
Route Tester TRT m 70. Ericsson<br />
Rev. 51 (1974): 3, pp. 80—87.<br />
2. Moot, G.: The Effect of Human<br />
Factors on some Aspects of<br />
Australian Post Office Maintenance<br />
Operations. Maintenance<br />
Conference 1974.<br />
3. Carrol, B. J.: Maintenance and<br />
Performance of LM Ericsson<br />
Crossbar Switching Equipment in<br />
Australia. Part 1 and 2. The Telecommunication<br />
Journal of Australia<br />
1973, pp. 72—77, 143—149.<br />
4. Hansson, K. G.: Maintenance<br />
Conferences at LM Ericson. Ericsson<br />
Rev. 52 (1975): 1, pp. 2—13.