Vibration suppression of a 90-m-tall steel
Vibration suppression of a 90-m-tall steel
Vibration suppression of a 90-m-tall steel
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
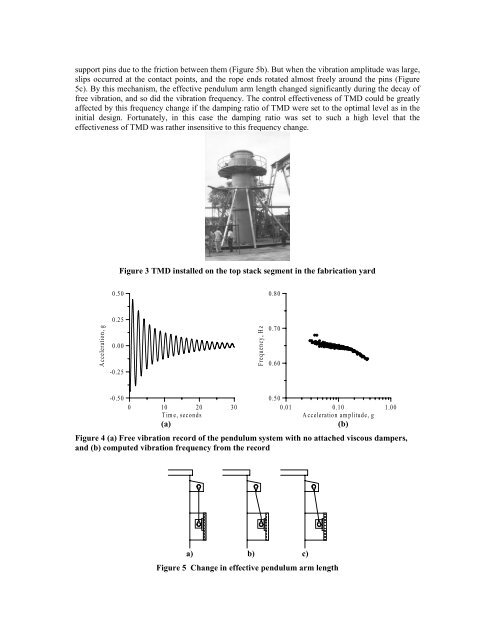
support pins due to the friction between them (Figure 5b). But when the vibration amplitude was large,<br />
slips occurred at the contact points, and the rope ends rotated almost freely around the pins (Figure<br />
5c). By this mechanism, the effective pendulum arm length changed significantly during the decay <strong>of</strong><br />
free vibration, and so did the vibration frequency. The control effectiveness <strong>of</strong> TMD could be greatly<br />
affected by this frequency change if the damping ratio <strong>of</strong> TMD were set to the optimal level as in the<br />
initial design. Fortunately, in this case the damping ratio was set to such a high level that the<br />
effectiveness <strong>of</strong> TMD was rather insensitive to this frequency change.<br />
Acceleration, g<br />
0.50<br />
0.25<br />
0.00<br />
-0.25<br />
Figure 3 TMD ins<strong>tall</strong>ed on the top stack segment in the fabrication yard<br />
-0.50<br />
0.50<br />
0 10 20 30<br />
0.01 0.10 1.00<br />
Time, seconds<br />
Acceleration amp litude, g<br />
(a) (b)<br />
Figure 4 (a) Free vibration record <strong>of</strong> the pendulum system with no attached viscous dampers,<br />
and (b) computed vibration frequency from the record<br />
Frequency, Hz<br />
0.80<br />
0.70<br />
0.60<br />
a) b) c)<br />
Figure 5 Change in effective pendulum arm length